Wrapper 클래스
기존 기본 자료형은 자료의 크기만 나타냈다.
즉, 클래스가 아니었기에 기능을 추가할 수 없었다.
기본 타입의 데이터를 인스턴스화하기 위해 Wrapper 클래스를 만들었다.
- 장점
- 기능, 속성을 가질 수 있다.
- 클래스는 최상위 부모가 Object 여서 여러 메소드를 사용할 수 있다.
- 다형성도 적용할 수 있다.
Wrapper 클래스 종류
| 기본 타입 | 래퍼 클래스 |
|---|---|
| byte | Byte |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| long | Long |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
| char | Character |
| boolean | Boolean |
Boxing, UnBoxing
Boxing: 기본 타입을 래퍼클래스의 인스턴스로 인스턴스화 하는 것UnBoxing: 래퍼클래스 타입의 인스턴스를 기본 타입으로 변경하는 것

public static void main(String[] args) {
int intValue = 20;
// 박싱
Integer boxingInt = (Integer)20;
Integer boxingInt2 = Integer.valueOf(intValue);
// 언박싱
int unboxingValue = boxingInt.intValue();JDK 1.5부터는 Boxing, UnBoxing을 필요한 상황에서 컴파일러가 자동으로 해준다.
// 오토박싱, 오토언박싱
Integer autoBoxingInt = intValue;
int autoUnboxingInt = autoBoxingInt;
}
}Application 클래스에 아래 메소드를 추가해보자.
public static void anythingMethod(Object obj) {
System.out.println("obj : " + obj.toString());
}매개변수로 Object를 받는데
Application 에서
anythingMethod(10);를 하면 뭐가 나올까?
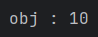
int형을 받는데 Integer로 오토박싱이 된 후, Object로 다형성이 실행된다.
출력 ->
Object의toString()에서(정적 바인딩)Integer의toString()이(동적바인딩) 실행됨
Wrapper 클래스 주소 값 비교
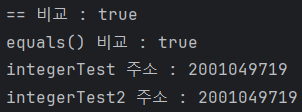
Integer integerTest = 30;
Integer integerTest2 = 30;
System.out.println("== 비교 : " + (integerTest == integerTest2));
System.out.println("equals() 비교 : " + integerTest.equals(integerTest2));
System.out.println("integerTest 주소 : " + System.identityHashCode(integerTest));
System.out.println("integerTest2 주소 : " + System.identityHashCode(integerTest2));