Object
Object : Java에서 최상위 부모 클래스로, 다양한 메소드로 구성돼 있다.
모든 클래스는 Object 클래스를 상속하고 있고, Object 안에 있는 메소드를 사용할 수 있다.
(오버라이딩도 가능)
주요 메소드
| 메소드 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| boolean equals(Object obj) | 전달 받은 객체와 같은지 여부를 반환한다.(동일하면 true, 다르면 false) |
| int hashCode() | 객체의 해시 코드를 반환한다. |
| String toString() | 객체의 정보를 문자열로 반환한다. |
활용
toString()
BookDTO
public class BookDTO {
private int number;
private String title;
private String author;
private int price;
public BookDTO() {
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BookDTO{" +
"number=" + number +
", title='" + title + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
public int getNumber() {
return number;
}
public void setNumber(int number) {
this.number = number;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public BookDTO(int number, String title, String author, int price) {
this.number = number;
this.title = title;
this.author = author;
this.price = price;
}
}인텔리제이에서는 Alt+Insert 를 누르면 몇 가지를 자동으로 만들어줄 수 있게끔 하는데 거기에서 toString()을 누르면
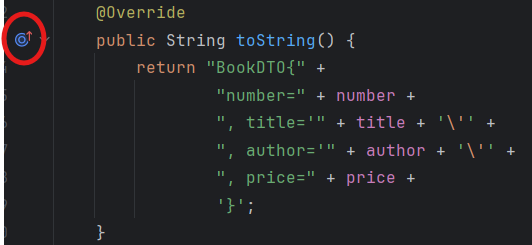
이 부분이 생긴다. 눌러보면 Object 메소드를 다시 정의한 것과 같다.
Application
public class Application1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BookDTO book1 = new BookDTO(1, "홍길동전", "허균", 50000);
BookDTO book2 = new BookDTO(2, "목민심서", "정약용", 30000);
BookDTO book3 = new BookDTO(3, "칭찬은 고래도 춤추게 한다.", "고래", 10000);
System.out.println(book1.toString());
System.out.println(book2.toString());
System.out.println(book3.toString()); // 동적 바인딩에 의한 자식 클래스의 toString() 실행
}
}
Object 클래스에 있는 toString 메소드이다.
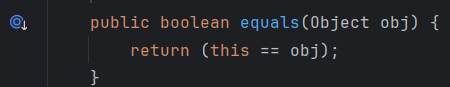
equals
equals 메소드는 매개변수로 전달받은 인스턴스와 == 연산해서 true, false 로 반환한다.
동일한 인스턴스인지 비교하는 기능
동일 객체와 동등 객체
- 동일 객체 : 주소가 동일한 인스턴스를 동일 객체라고 한다
- 동등 객체 : 주소는 다르더라도 필드값이 동일한 객체를 동등 객체라고 한다.
위와 같은 BookDTO를 이용해서 해보자.
Application2
public class Application2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BookDTO book1 = new BookDTO(1, "홍길동전", "허균", 50000);
BookDTO book2 = new BookDTO(2, "홍길동전", "허균", 50000);
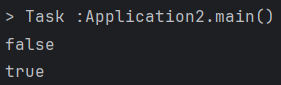
System.out.println(book1 == book2); // 동일하지 않다. (주소값을 비교)
System.out.println(book1.equals(book2)); // 동일하지 않다.
}
}그렇다고 둘이 같을까? -> 다르다.
equals()는 다형성이 적용됐다.
경우에 따라서는 동등객체를 동일 객체로 취급해서 비교하고 싶은 경우가 발생한다.
즉, 동일한 필드값을 가지는 객체를 같은 객체로 판단할 수 있도록 하는 경우이다.
-> equals() 메소드를 오버라이딩해, 각각의 필드가 같은 값인지 확인하고 같으면 true, 아니면 false를 반환한다.
그럼
BookDTO에서title,author,price가 같은지 비교해서 하는String에서의equals()처럼 만들어보자.
BookDTO
package com.ohgiraffers.section01.object.dto;
public class BookDTO {
private int number;
private String title;
private String author;
private int price;
... (중략)
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
return this.title.equals(((BookDTO) o).getTitle()) && this.author.equals(((BookDTO) o).getAuthor()) && this.price == ((BookDTO) o).getPrice();
}
}
위에서 toString()을 자동으로 만든 것처럼 equals(), hashCode()도 자동으로 만들 수 있다.
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
BookDTO bookDTO = (BookDTO) o;
return price == bookDTO.price && Objects.equals(title, bookDTO.title) && Objects.equals(author, bookDTO.author);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(title, author, price);
}hashCode()에 대해서는 다음 주제로 다뤄보자.
hashCode()
hashCode : 해시코드는 객체를 식별하는 값
hashCode()메소드는 객체의 메모리 주소값을 이용해 해시코드를 만들어서 반환
(자바의 hashCode는 C++로 작성된 메소드여서 인텔리제이로 더 타고 들어갈 수 없다.)
컬렉션(Collection) 에서의 두 객체가 같은지 판단할 때
1. hashCode 비교 (같은 분류인지 확인)
2. equals 비교 (같은 분류 속에서 동등한지)
위 2가지와 같이 작동한다.
Object 클래스의 명세에 작성된 일반 규약에서 -> equals() 메소드를 재정의 하면 반드시 hashCode() 메소드도 재정의해야 함
만약 hashCode()를 재정의 하지 않으면 같은 값을 가지는 동등 객체는 같은 해시코드 값을 가져야 한다는 규약에 위반되게 된다. (강제성은 없지만 규약대로 작성하는 것이 좋다)
Application
package com.ohgiraffers.section01.object.run;
import com.ohgiraffers.section01.object.dto.BookDTO;
public class Application2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BookDTO book1 = new BookDTO(1, "홍길동전", "허균", 50000);
BookDTO book2 = new BookDTO(2, "홍길동전", "허균", 50000);
System.out.println(book1 == book2); // 동일하지 않다. (주소값을 비교)
System.out.println(book1.equals(book2)); // 동일하지 않다.
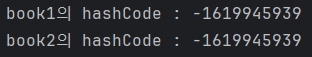
System.out.println("book1의 hashCode : " + book1.hashCode());
System.out.println("book2의 hashCode : " + book2.hashCode());
}
}