What is Test Double?
Test Double is the Object which will be make test more easier. Test doubles are largely divided into Dummy, Fake, Stub, Spy, Mock. And We will talk about each one step by step.
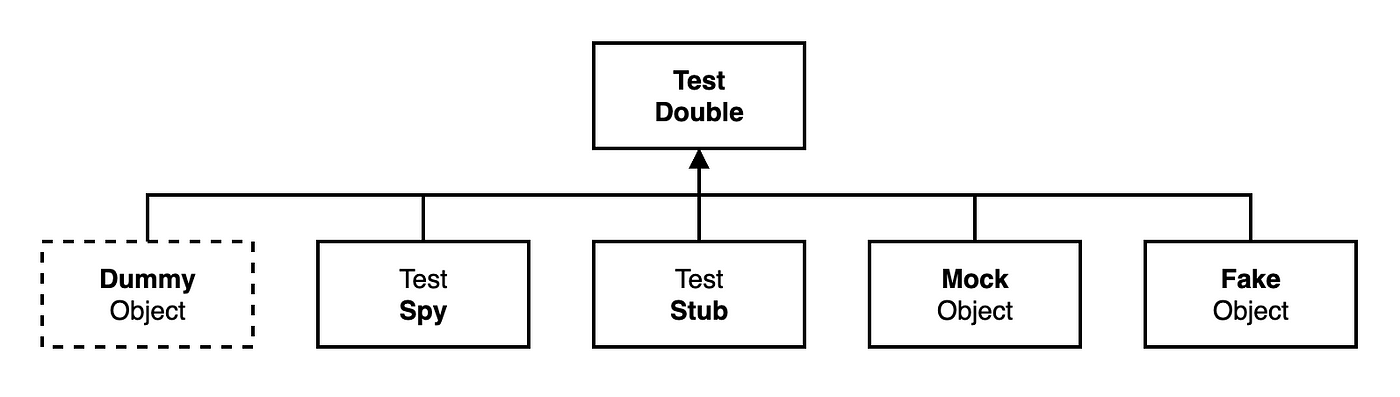
Why Test Double needed?
For instance, We implemented a logic which look up the data from Database. Test with Dependency like this can be complicate. This test can be affected by Database which is not target of this test.
1. Dummy
- Most basic
- Use When Instanced Object without function required
- Normal operation is not guaranteed
- Object is passed but not used
Let's see how it works
pub trait PrintHelloWrold{
fn print_hello_world();
}
pub struct DummyStruct;
impl PrintHelloWrold for DummyStruct{
fn print_hello_world() {
// nothing
}
}DummyStruct implements the PrintHelloWorld trait, But actually Dummy struct doesn't do anything.
2. Fake
- Object which simplify complicated logic or another external object's function
- Involve function, but inappropriate to production
Let's see how it works
pub trait Database{
fn get_user_id(&self) -> String;
}
pub struct RealDatabaseStruct;
impl Database for RealDatabaseStruct{
fn get_user_id(&self) -> String {
// something that return real value
"real value".to_string()
}
}
pub struct FakeDatabaseStruct{
pub(crate) users: Vec<String>
}
impl Database for FakeDatabaseStruct{
fn get_user_id(&self) -> String {
self.users.first().unwrap().clone()
}
}Suppose we need object which is related to database. If connection database isn't the part of target of test, we can use fake object like this.
3. Stub
- Dummy object that looks like operate like production
- Minimal implementation of interface or class
- Offer prepared response within test
In other word,Stuboffer prepared response for test.
use std::marker::PhantomData;
pub struct Real;
pub struct Stub;
pub trait Database{
fn get_user_id() -> &'static str;
}
pub struct DatabaseStruct<T>{
_phantom_data: PhantomData<T>,
}
impl Database for DatabaseStruct<Real>{
fn get_user_id() -> &'static str {
// something that return real value
"real value"
}
}
impl Database for DatabaseStruct<Stub>{
fn get_user_id() -> &'static str {
"Expected value"
}
}4. Spy
- Involves
Stub's roll and record information - When called by object implemented as a
Test Double, record the parts that need to be verified - It can be made to act like a real object, and for the necessary parts, it can be made into a Stub to specify the behavior.
pub struct PaymentManager{
count: u32,
}
impl PaymentManager{
pub fn payment(&mut self){
self.count += 1;
// Make payment
}
}5. Mock
- Objects programmed to behave as expected when called.
pub struct MockDatabase{
databse: Vec<(i64, String)>,
}
impl MockDatabase{
pub fn push_user(&mut self, id: i64, user_name: String){
self.databse.push((id, user_name));
}
pub fn get_user(&mut self, id: i64) -> (i64, String){
self.databse.iter().filter(|user| user.0 == id ).collect::<Vec<&(i64, String)>>()[0].clone()
}
}Conclusion
Testing is a crucial skill for developers. The five outlined methods help ensure test conditions are more independent and decoupled
