29. binaryHeap
- 문제:
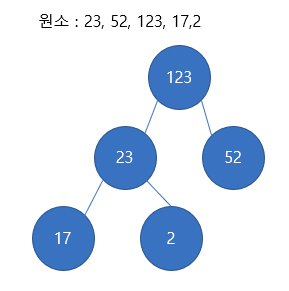
정수를 요소로 갖는 배열을 입력받아 이진 힙(binary heap)*을 리턴해야 합니다.
- 참고:
- 이진 힙(binary heap)은 노드의 값이 특정한 순서를 가지고 있는 완전 이진 트리(Complete Binary Tree)입니다.
- 완전 이진 트리는 이진 트리의 (마지막 레벨 또는 마지막 깊이를 제외하고) 모든 레벨이 노드로 가득 채워져 있어야 합니다. 마지막 레벨은 왼쪽부터 차례대로 채워져 있습니다.
- 이진 힙에서 부모 노드의 값이 (이진 트리이므로 2개의) 자식 노드의 값보다 큰 경우를 최대 힙(max heap), 반대의 경우를 최소 힙(min heap)이라고 합니다.
- 입출력 예시:
let output = binaryHeap([5, 4, 3, 2, 1]);
console.log(output); // --> [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
output = binaryHeap([3, 1, 21]);
console.log(output); // --> [21, 1, 3]
output = binaryHeap([4, 10, 3, 5, 1]);
console.log(output); // --> [10, 5, 3, 4, 1]- 힌트:
- 이진 힙은 트리 객체를 이용해 구현할 수도 있고, 배열로도 구현할 수 있습니다. 사실 거의 모든 트리를 배열로 구현할 수 있습니다. 트리를 배열로 구현했을 때의 장점은 (데이터가 선형적으로 저장되기 때문에) 저장공간을 절약할 수 있고 노드 접근 시 오버헤드(재귀호출, 반복문 등)가 약간 줄어듭니다. 다만 이를 위해서 매우 복잡한 인덱스 관리가 필요합니다. 반면, 트리 객체를 이용한 구현은 직관적(이해하기 쉬움)입니다. 그 대신 저장 공간과 약간의 오버헤드를 희생해야 합니다. 거의 모든 기술(구현)은 다수의 선택 사이의 트레이드 오프(trade-off)입니다. 무엇을 선택할 지는 요구사항(requirements), 즉 주어진 문제의 제약과 조건을 고려하여 결정해야 합니다. 이 점을 반드시 기억하시기 바랍니다.
- 완전 이진 트리는 노드가 낮은 레벨부터 채워지고, 같은 레벨에서는 왼쪽부터 채워지기 때문에 배열로 구현하는 것이 쉽습니다.
- 최대 힙과 이진 검색 트리(binary search tree)는 둘다 완전 이진 트리입니다. 하지만 이진 검색 트리에서는 모든 노드가 정렬되는 것과 달리 최대 힙에서는 오직 부모 노드와 직계 자식들 간의 관계만 유지됩니다. 이는 아래의 사실로부터 바로 알 수 있습니다.
- 이진 검색 트리에서 오른쪽 자식 노드의 값은 부모 노드의 값보다 크지만, 최대 힙에서는 부모 노드의 값이 두 자식 노드의 값보다 크다.
- 풀이1:
- 부모 노드에 2개의 자식 노드 (또는 잎)이 들어갈 수 있다.
- 트리를 배열로 구현한다면, 인덱스 번호로 부모-자식 로직을 구현할 수 있다. 예를 들어 0 인덱스는 root이자 부모일테고 1, 2 인덱스는 자식일 것이다. 1 인덱스의 자식은 3, 4 인덱스 그리고 2 인덱스의 자식은 5, 6 인덱스이다. 이와 같은 로직으로 쉽게 부모 idx는 (자식 idx - 1) / 2의 값의 정수라는 것을 알 수 있다.
- 자식이 부모보다 큰 수일 경우, 서로의 위치를 swap 함수로 바꿔준다. 위치를 바꾸고 난 후, 부모의 자식의 관계를 재설정해 준다.
- 풀이2:
// 아래 코드는 수정하지 마세요.
function swap(idx1, idx2, arr) {
// 두 변수를 바꾸는 방법
// 1) 임시 변수를 활용한 방법
// let temp = arr[idx1];
// arr[idx1] = arr[idx2];
// arr[idx2] = temp;
// 2) Destructuring assignment를 활용한 방법
// arr이 reference type이라 가능
[arr[idx1], arr[idx2]] = [arr[idx2], arr[idx1]];
// 3) XOR 연산을 활용한 방법
// arr이 reference type이라 가능
// arr[idx1] ^= arr[idx2];
// arr[idx2] ^= arr[idx1];
// arr[idx1] ^= arr[idx2];
}
function getParentIdx(idx) {
// 부모의 인덱스 번호 확인하기
// 최대 힙의 경우 왼쪽부터 채워진다.
// 0의 자식은 1, 2 / 1의 자식은 3, 4 / 2의 자식은 5, 6...
return Number.parseInt((idx - 1) / 2)
}
function insert(heap, item) {
heap.push(item);
childIdx = heap.length - 1;
parentIdx = getParentIdx(childIdx);
while (parentIdx >= 0 && heap[parentIdx] < heap[childIdx]) {
swap(parentIdx, childIdx, heap);
childIdx = parentIdx;
parentIdx = getParentIdx(childIdx);
}
return heap
}
// downHeapify 방식으로??
// 아래 코드는 수정하지 마세요.
const binaryHeap = function (arr) {
return arr.reduce((heap, item) => {
return insert(heap, item);
}, []);
};
30. heapSort
- 문제:
정수를 요소로 갖는 배열을 입력받아 오름차순으로 정렬하여 리턴해야 합니다.
- 참고:
- binaryHeap과 유사하지만, 오름차순 정렬을 위해서 root를 제거하는 알고리즘 하나가 더 필요하다.
- 최소힙으로 정렬 후, root를 제거한 트리를 다시 최소힙으로 만들어야 한다. 빈 배열에 계속 최소힙을 넣어주면 heapSort가 구현된다.
- 풀이:
// 아래 코드는 수정하지 마세요.
function swap(idx1, idx2, arr) {
[arr[idx1], arr[idx2]] = [arr[idx2], arr[idx1]];
}
function getParentIdx(idx) {
return Number.parseInt((idx - 1) / 2)
}
function insert(heap, item) {
heap.push(item);
let childIdx = heap.length - 1;
let parentIdx = getParentIdx(childIdx);
// binaryHeap에서 부등호만 바꿔줬다.
while (parentIdx >= 0 && heap[parentIdx] > heap[childIdx]) {
swap(parentIdx, childIdx, heap);
childIdx = parentIdx;
parentIdx = getParentIdx(childIdx);
}
return heap
}
function removeRoot(heap) {
// 가장 마지막 노드와 root를 교환한 후, 배열 길이를 줄여준 다음 최소 힙 구현을 해준다.
swap(0, heap.length - 1, heap); // 가장 마지막 노드와 root 교환
heap.pop(); // 배열 길이 1만큼 축소
if (heap.length === 0) return [];
let curIdx; // root부터 아래로 내려가면서 확인할 예정
let parentIdx = 0; // root idx
while (curIdx !== parentIdx) {
curIdx = parentIdx; // root부터 시작!
let leftChild = curIdx * 2 + 1;
let rightChild = curIdx * 2 + 2;
if (leftChild < heap.length && heap[leftChild] < heap[parentIdx]) {
parentIdx = leftChild; // 자식보다 부모가 크면 최소 힙 구현을 위해 자식, 부모 인덱스에 자녀 인덱스 할당 후 swap 진행
}
if (rightChild < heap.length && heap[rightChild] < heap[parentIdx]) {
parentIdx = rightChild;
}
swap(curIdx, parentIdx, heap);
}
return heap
}
// 아래 코드는 수정하지 마세요.
const binaryHeap = function (arr) {
return arr.reduce((heap, item) => {
return insert(heap, item);
}, []);
};
const heapSort = function (arr) {
let minHeap = binaryHeap(arr);
const result = [];
// 큐처럼 활용하는구나
while (minHeap.length > 0) {
result.push(minHeap[0]); // 최소힙의 root 값을 넣어주고 다시 최소힙 구현
minHeap = removeRoot(minHeap);
}
return result;
};