Service?
안드로이드의 Service는 UI 없이 백그라운드에서 실행되는 컴포넌트로, 장시간 실행되는 작업(음악 재생, 네트워크 통신, 데이터 동기화 등)을 수행할 수 있는 애플리케이션 구성 요소이다.
컴포넌트이기 때문에 사용을 위해선 아래와 같이 Manifest에 등록 후 사용해야한다.
<service
android:name=".MyService"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="false">
</service>- android:name : 서비스 클래스 이름
- android:enabled : 서비스 활성화 여부 (기본값: true)
- android:exported : 다른 앱에서 이 서비스를 사용할 수 있는지 여부 (true = 허용, false = 비허용, 기본값: false)
다른 앱에서 서비스를 사용해야 한다면 android:exported="true"와 intent-filter를 설정해야 함.
Service 특징
- UI 없이 실행
- 백그라운드에서 동작
- 시스템이 관리하는 컴포넌트
onCreate(),onStartCommand(),onDestroy() - 다른 앱과 상호작용 가능
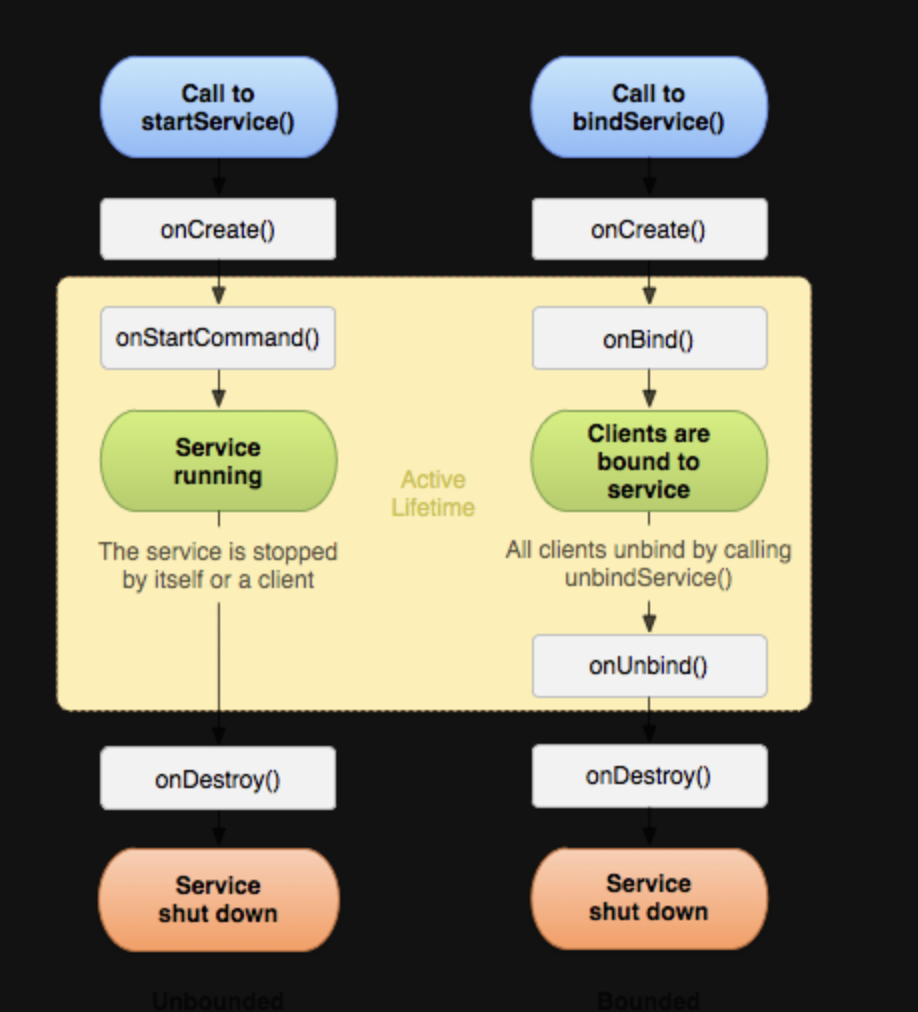
Service 생명주기
- onCreate() : 서비스가 처음 실행될 때 호출 (한번만 실행)
- onStartCommand() :
startService()로 서비스가 시작될 때 호출 - onBind() :
bindService()를 호출할 때 실행되며,Binder객체를 반환 - onUnbind() : 모든 클라이언트가
unbindService()를 호출하면 실행됨 - onDestroy() : 서비스가 종료될 떄 호출됨
Service 시작 방식 별 생명주기 동작은 아래와 같다.
Service 종류
Foreground Service
실행되는동안 사용자에게 Notification으로 지속적인 알림을 제공한다. 사용자에게 보여지며 실행되기 때문에 메모리가 부족해도 강제 해제되지 않는다.
startForeground()로 실행한다.
사용 예시
class MyForegroundService : Service() {
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
startForeground(1, createNotification())
}
private fun createNotification(): Notification {
val channelId = "ForegroundServiceChannel"
val notification = NotificationCompat.Builder(this, channelId)
.setContentTitle("Foreground Service")
.setContentText("실행 중...")
.setSmallIcon(R.drawable.ic_notification)
.build()
return notification
}
override fun onStartCommand(intent: Intent?, flags: Int, startId: Int): Int {
return START_STICKY
}
override fun onDestroy() {
stopForeground(true)
super.onDestroy()
}
override fun onBind(intent: Intent?): IBinder? {
return null
}
}Android 8 이상에서는 포그라운드 서비스 실행 시 Notification Channel을 설정해야한다.
여러 제약사항
Android 14(API 34)부터 포그라운드 서비스를 선언할 때 android:foregroundServiceType 속성을 통해 아래같이 서비스 유형을 반드시 명시해야 한다.
<service
android:name=".MyService"
android:foregroundServiceType="mediaPlayback" />BOOT_COMPLETED 브로드캐스트 리시버에서 특정 포그라운드 서비스는 시작할 수 없다.
- microphone (14)
- dataSync (15)
- camera (15)
- mediaPlayback (15)
- phoneCall (15)
- mediaProjection (15 신규)
SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW 권한을 가진 앱의 포그라운드 서비스 시작이 제한된다. (15)
해당 권한을 보유하고, 실제로 오버레이 창을 표시하고 있는 경우에만 백그라운드에서 포그라운드 서비스를 시작할 수 있다.
Started Service
onStartCommand()에서 실행되고, 명시적으로 종료해야한다.
startService()로 실행하고, stopSelf(), stopService()로 종료 가능하다.
최초의 서비스 인텐트 발생 시 onCreate() 가 호출 되면서 서비스 객체가 생성된다. 그리고 stopService() 호출 시 onDestroy() 가 호출되면서 서비스는 멈춘다. 그런데 만약 서비스 구동 중에 두 번째 인텐트가 발생하면 onCreate() 호출 없이 onStartCommand() 만 다시 호출된다.
서비스는 싱글톤이기 때문에 onCreate() 함수는 서비스 객체 생성 시 최초의 단 한번만 호출된다. 그래서 서비스 요청을 구분해서 처리하고 싶다면 onStartCommand() 에서 멀티 스레드 환경을 구현하는 식으로 분기처리가 필요하다.
서비스 자신을 실행시킨 인텐트 정보는 onStartCommand() 의 매개변수로 전달되기 때문에 구분이 가능하다.
사용 예시
class MyService : Service() {
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
Log.d("Service", "서비스 생성됨")
}
override fun onStartCommand(intent: Intent?, flags: Int, startId: Int): Int {
Log.d("Service", "서비스 실행 중")
return START_STICKY
}
override fun onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy()
Log.d("Service", "서비스 종료됨")
}
override fun onBind(intent: Intent?): IBinder? {
return null // Started Service는 바인딩을 제공하지 않음
}
}Activity에서 실행 및 중지
val intent = Intent(this, MyService::class.java)
startService(intent) // 서비스 시작
stopService(intent) // 서비스 종료onStartCommand() 반환값
-
START_STICKY: 시스템이
onStartCommand()반환 후에 서비스를 중단하면 서비스를 자동으로 다시 생성하고 인텐트는null로 전달한다. -
START_NOT_STICKY: 시스템이 서비스를
onStartCommand()를 반환 후에 중단시키면 서비스를 재생성 하지 않는다. -
START_REDELIVER_INTENT: 시스템이
onStartCommand()를 반환 후에 서비스를 중단하는 경우, 서비스를 다시 생성하고 이 서비스에 전달된 마지막 인텐트로onStartCommand()를 호출하면 모든 보류 인텐트가 차례로 전달된다.
Bound Service
클라이언트와 바인딩되어 양방향 통신이 가능하다.
bindService()로 실행하며 unbindService()로 종료 가능하다.
startService 와의 차이점은 onCreate() 호출 이후 onBind() 와 onUnbind() 가 호출 된다는 것이다. 싱글톤이기 때문에 동일하게 인텐트가 발생하면 onBind() 만 다시 호출된 후, 종료될 때 다시 onUnbind() 함수가 호출 된다.
사용 예시
class MyBoundService : Service() {
private val binder = LocalBinder()
inner class LocalBinder : Binder() {
fun getService(): MyBoundService = this@MyBoundService
}
override fun onBind(intent: Intent?): IBinder {
return binder
}
}Activity에서 서비스 바인딩
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private var myService: MyBoundService? = null
private var isBound = false
private val connection = object : ServiceConnection {
override fun onServiceConnected(name: ComponentName?, service: IBinder?) {
val binder = service as MyBoundService.LocalBinder
myService = binder.getService()
isBound = true
}
override fun onServiceDisconnected(name: ComponentName?) {
isBound = false
}
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
val intent = Intent(this, MyBoundService::class.java)
bindService(intent, connection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE)
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
if (isBound) {
unbindService(connection)
isBound = false
}
}
}Activity가 종료되면 서비스가 자동 종료되기 때문에 센서 데이터 제공이나 Activity- Service간 직접 통신이 필요한 경우 사용하기 적합하다.
