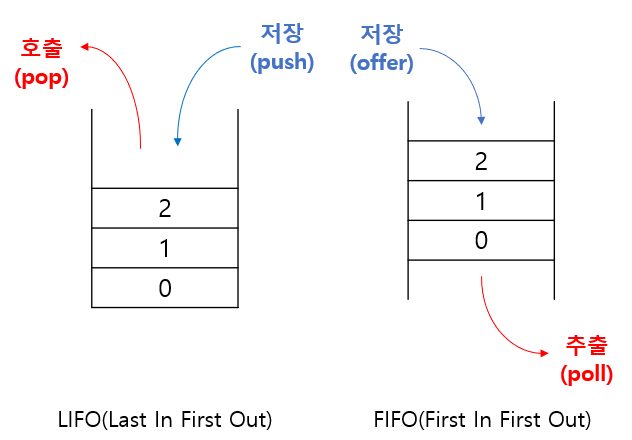
Stack과 Queue
- 스택(Stack): LIFO구조. 마지막에 저장된 것을 제일 먼저 꺼내게 된다.
- 큐(Queue): FIFO구조. 제일 먼저 저장한 것을 제일 먼저 꺼내게 된다.
| 메서드 | 설명 |
|---|
| boolean empty() | Stack이 비어있는지 알려준다. |
| Object peek() | Stack의 맨 위(가장 마지막에 들어온 값) 객체를 반환한다. pop()과 달리 Stack에서 객체를 삭제하지는 않고 단순히 조회만 한다. (비어있는 경우 EmptyStackException이 발생한다.) |
| Object pop() | Stack의 맨 위에 저장된 객체를 꺼낸다. (비었을 때는 EmptyStackException이 발생한다.) |
| Object push(Object item) | Stack에 객체를 저장한다. |
| int search(Object o) | Stack에서 주어진 객체를 찾아서 그 위치를 받환한다. 못찾으면 -1을 반환한다. (배열과 달리 위치는 0이 아닌 1부터 시작한다. 즉 가장 맨 위(가장 마지막에)에 있는 요소가 1이다.) |
| 메서드 | 설명 |
|---|
| boolean isEmpty() | Queue가 비어있는지 알려준다. |
| boolean add(Object o) | 객체를 Queue에 추가한다. 성공하면 true를 반환하며, 저장공간이 부족하다면 illegalStateException이 발생한다. |
| boolean offer(Object o) | 객체를 Queue에 추가한다. 성공하면 true, 실패하면 false를 반환한다. |
| Object remove() | Queue에서 객체를 꺼내 반환한다. 비어있으면 NoSuchElementException이 발생한다. |
| Object poll() | Queue의 객체를 꺼내서 반환한다. 비어있으면 null을 반환한다. |
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackQueueEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack st = new Stack();
Queue q = new LinkedList();
st.push("0");
st.push("1");
st.push("2");
q.offer("0");
q.offer("1");
q.offer("2");
System.out.println("= Stack =");
while(!st.empty()) {
System.out.println(st.pop());
}
System.out.println("= Queue =");
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(q.poll());
}
}
}
import java.util.*;
public class PriorityQueueEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue pq = new PriorityQueue();
pq.offer(3);
pq.offer(1);
pq.offer(5);
pq.offer(2);
pq.offer(4);
System.out.println(pq);
Object obj = null;
while((obj= pq.poll())!=null) {
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
}

