CS50 Sandbox
https://sandbox.cs50.io
1. 실습 파일 작성 (filename.c)
2. 코드 작성
3. terminal 에clang 파일이름.c-> out 결과 파일 생성
4. terminal에.\결과파일이름-> 출력
++ how to clear the terminal : ctrl + L
1) C 기초
C
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
printf("hello, world\n");
}-
#include <stdio.h>: “stdio.h”라는 이름의 파일을 찾아서 “printf” 함수에 접근 -
int main(void){}: to start -
printf(“text”);:
compiler
source code(code that we coded) is changing by COMPILER to machine code(computer can understand)
terminal $ (prompt shell)
clang filename.c: compile "filename" with "clang"compiler
"a.out" is made.
./a out: file "a.out" runs at current dir(.)
2) string
사용자로부터 문자열을 입력받고 이를 다른 문자열과 합쳐서 출력하는 프로그램을 C로 작성
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cs50.h>
int main(void)
{
printf("hello, world\n");
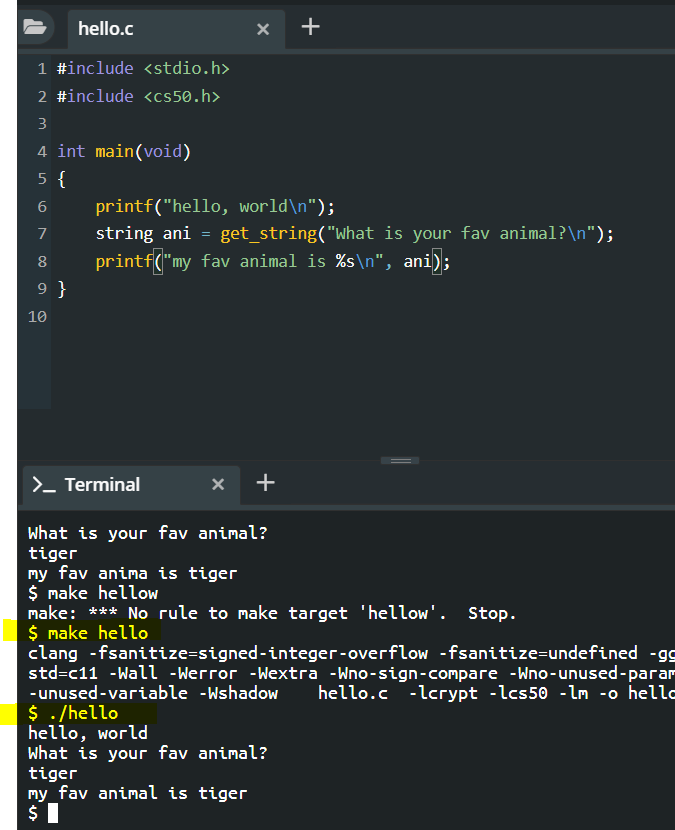
string answer = get_string("What is your name?\n");
printf("hello, %s\n", answer);
}
$ make NAME#include <cs50.h>: string 쓰려면 이거 추가해줘야함 (CS50 라이브러리. 수업 위해서 만든거 ). 원래는 C 표준 라이브러리 써야함.get_string(""\n): function to get string$ make Programname: 컴파일 바로해서 program 만들어줌
원래는..
clang -o hello hello.c -lcs50
./hello-lc로 link 해 줘야함.
ex
3) condition, loop
if()
{}
else if ( )
{}
else
{}while (true)
{ }ex
int i = 0;
while (i <10)
{
printf("hello, world\n");
i ++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i += 1)
{
printf("hello, world\n"
}4) data type, 형식 지정자, 연산자
data type
bool: 불리언 표현, (예) True, False, 1, 0, yes, no
char: 문자 하나 (예) 'a', 'Z', '?'
string: 문자열
int: 특정 크기 또는 특정 비트까지의 정수 (예) 5, 28, -3, 0
long: 더 큰 크기의 정수
float: 부동소수점을 갖는 실수 (예) 3.14, 0.0, -28.56
double: 부동소수점을 포함한 더 큰 실수CS50 라이브러리 내 함수
get_char
get_double
get_float
get_int
get_long
get_string
Type Specifiers
%c : char
%f : float, double
%i : int
%li : long
%s : stringoperators, comment
+: 더하기
-: 빼기
*: 곱하기
/: 나누기
%: 나머지
&&: 그리고
||: 또는
//: 주석5) 사용자 정의 함수, 중첩 루프
custom funtion
#include <stdio.h>
void function_name(void)
{
printf("blabla");
}
int main(void)
{
function_name();
}ex)
#include <stdio.h>
void cough(void);
int main(void)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
cough();
}
}
void cough(void)
{
printf("cough\n");
}-
main 파트가 위에 있는게 좋음. -> 함수 첫줄 위에다 넣어주고 밑으로 보내면 됌.
-
void : 값을 반환하지 않는다.
#include <stdio.h>
void cough(int n);
int main(void)
{
cough(3);
}
void cough(int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
{
printf("cough!\n");
}
}nested loop
ex. 2
#include <cs50.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int n;
do
{
n = get_int("Size: ");
}
while (n < 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
printf("#");
}
printf("\n");
}
}6) 하드웨어의 한계
RAM(랜덤 액세스 메모리) : 물리적 저장장치. 한계가 있으니 부정확한 결과 가져오기도 함.
부동 소수점 부정확성
정확한 결과는 0.1이 되어야 하지만, float 에서 저장 가능한 비트 수가 유한하기 때문에 다소 부정확한 결과를 냄
integer overflow
계속 2를 곱하면...
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(void)
{
for (int i = 1; ; i *= 2)
{
printf("%i\n", i);
sleep(1);
}
}overflow 가 옴. -> 에러 출력
bit가 제한되어있어서 자리수가 넘으면 뒷자리에 0만 보임