미듐이 두개...
1110. Delete Nodes And Return Forest
Given the root of a binary tree, each node in the tree has a distinct value.
After deleting all nodes with a value in to_delete, we are left with a forest (a disjoint union of trees).
Return the roots of the trees in the remaining forest. You may return the result in any order.
My Answer 1: Accepted (Runtime: 120 ms - 5.10% / Memory Usage: 14.7 MB - 92.59%)
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def delNodes(self, root: TreeNode, to_delete: List[int]) -> List[TreeNode]:
def func(root, prev):
if root is None:
return
if root.val in to_delete:
root.val = None
if root.left:
func(root.left, root.left)
if root.left.val != None:
self.ans.add(root.left)
if root.right:
func(root.right, root.right)
if root.right.val != None:
self.ans.add(root.right)
else:
if root.left:
if root.left.val in to_delete:
tmp = root.left
root.left = None
self.ans.add(prev)
func(tmp, tmp)
else:
func(root.left, prev)
if root.right:
if root.right.val in to_delete:
tmp = root.right
root.right = None
self.ans.add(prev)
func(tmp, tmp)
else:
func(root.right, prev)
self.ans = set()
func(root, root)
return list(self.ans)삭제해야 하는 값을 발견하면 잘라서 지금 보고 있는 트리의 루트 값인 prev 를 self.ans 에 추가
삭제해야 하는 값의 자식 노드들도 봐서 각각 재귀 돌림 => 각각 self.ans 에 저장
Solution 1: Accepted (Runtime: 100 ms - 8.16% / Memory Usage: 14.8 MB - 79.24%)
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def delNodes(self, root: TreeNode, to_delete: List[int]) -> List[TreeNode]:
to_delete_set = set(to_delete)
res = []
def helper(root, is_root):
if not root: return None
root_deleted = root.val in to_delete_set
if is_root and not root_deleted:
res.append(root)
root.left = helper(root.left, root_deleted)
root.right = helper(root.right, root_deleted)
return None if root_deleted else root
helper(root, True)
return resroot_deleted = root.val in to_delete_set
=> 삭제해야할 값이면 True 아니면 False
if is_root and not root_deleted: res.append(root)
=> res 에는 루트 + 삭제해야할 값이 아닌 root 를 넣음
left, right 확인
return None if root_deleted else root
=> 삭제되는 값은 None 이 return 돼서 알아서 잘려서 이전 root 의 left / right 에 들어감
688. Knight Probability in Chessboard
On an n x n chessboard, a knight starts at the cell (row, column) and attempts to make exactly k moves. The rows and columns are 0-indexed, so the top-left cell is (0, 0), and the bottom-right cell is (n - 1, n - 1).
A chess knight has eight possible moves it can make, as illustrated below. Each move is two cells in a cardinal direction, then one cell in an orthogonal direction.
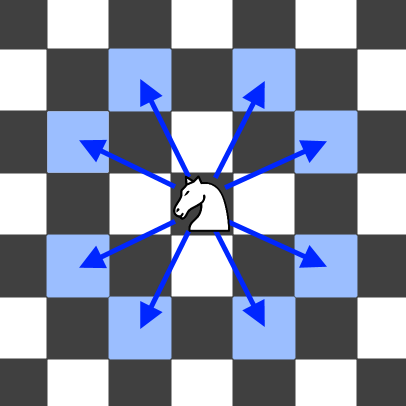
Each time the knight is to move, it chooses one of eight possible moves uniformly at random (even if the piece would go off the chessboard) and moves there.
The knight continues moving until it has made exactly k moves or has moved off the chessboard.
Return the probability that the knight remains on the board after it has stopped moving.
My Answer 1: Wrong Answer (7 / 22 test cases passed.)
class Solution:
def knightProbability(self, n: int, k: int, row: int, column: int) -> float:
def func(k, r, c):
if r < 0 or r >= n or c < 0 or c >= n:
return
if [r,c] in self.index:
return
self.index.append([r, c])
if k == 0:
return
if r+2 < n and c+1 < n:
func(k-1, r+2, c+1)
if r+1 < n and c+2 < n:
func(k-1, r+1, c+2)
if r-2 >= 0 and c+1 < n:
func(k-1, r-2, c+1)
if r-1 >= 0 and c+2 < n:
func(k-1, r-1, c+2)
if r+2 < n and c+1 < n:
func(k-1, r+2, c-1)
if r+1 < n and c-2 >= 0:
func(k-1, r+1, c-2)
if r-1 >= 0 and c-2 >= 0:
func(k-1, r-1, c-2)
if r-2 >= 0 and c-1 >= 0:
func(k-1, r-2, c-1)
self.index = []
self.ans = 1.0
func(k, row, column)
if len(self.index) > 1:
self.ans = ((len(self.index)-1)/8) ** k
else:
if k > 0:
self.ans = 0.0
return self.ans좌표로 이동할 때마다 self.index 리스트에 [r,c] 저장
확률 계산을 재귀 함수 내에서 해야하는데 외부에서 처리한게 잘못된 듯
문제 이해도 제대로 못한 느낌...ㅎ
Solution 1: Accepted (Runtime: 400 ms - 20.06% / Memory Usage: 23.9 MB - 12.62%)
class Solution:
def knightProbability(self, n: int, k: int, row: int, column: int) -> float:
memo = {}
def dfs(i, j, p, k):
if 0 <= i < n and 0 <= j < n and k < self.K:
sm = 0
for x, y in ((-1, -2), (-2, -1), (-2, 1), (-1, 2), (1, 2), (2, 1), (2, -1), (1, -2)):
if (i + x, j + y, k) not in memo:
memo[(i + x, j + y, k)] = dfs(i + x, j + y, p / 8, k + 1)
sm += memo[(i + x, j + y, k)]
return sm
else:
return 0 <= i < n and 0 <= j < n and p or 0
self.K = k
return dfs(row, column, 1, 0)dp 처럼 구한 값을 memo 에 저장
return 0 <= i < N and 0 <= j < N and p or 0
=> k == 0 일 경우 1.0 return / 인덱스 범위 초과할 경우 0 return
냅다 외워!!!
