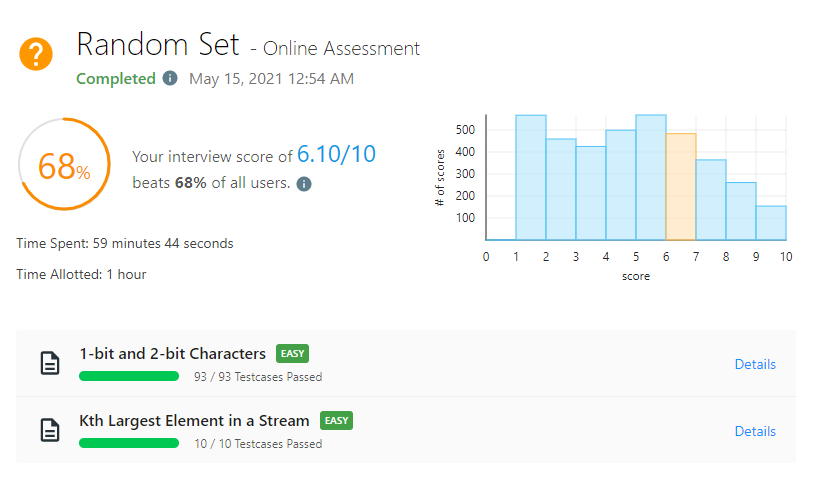
놀다가 한 17분 남았을 때부터 풀었다...^^
717. 1-bit and 2-bit Characters
We have two special characters. The first character can be represented by one bit 0. The second character can be represented by two bits (10 or 11).
Now given a string represented by several bits. Return whether the last character must be a one-bit character or not. The given string will always end with a zero.
My Answer 1: Accepted (Runtime: 56 ms - 15.23% / Memory Usage: 14.3 MB - 39.69%)
class Solution:
def isOneBitCharacter(self, bits: List[int]) -> bool:
tmp = []
t = ""
carry = 1
for i in range(len(bits)):
if t == "10" or t == "11" or t == "0":
tmp.append(t)
t = ""
t += str(bits[i])
tmp.append(t)
if tmp[-1] != "0":
return False
return Truet 에 값을 넣어가면서 10, 11, 0 으로 구분해서 넣어주고
맨 마지막 값이 1 bit 인지 확인해줬음
int 형 그대로 써서 해도 될 듯 -> carry 이용
703. Kth Largest Element in a Stream
Design a class to find the kth largest element in a stream. Note that it is the kth largest element in the sorted order, not the kth distinct element.
Implement KthLargest class:
KthLargest(int k, int[] nums) Initializes the object with the integer k and the stream of integers nums.
int add(int val) Returns the element representing the kth largest element in the stream.
My Answer 1: Accepted (Runtime: 960 ms - 11.26% / Memory Usage: 18.7 MB - 8.77%)
class KthLargest:
def __init__(self, k: int, nums: List[int]):
self.arr = sorted(nums)
self.kth = k
def add(self, val: int) -> int:
self.arr.append(val)
self.arr.sort()
ans = self.arr[len(self.arr) - self.kth]
return ans
# Your KthLargest object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = KthLargest(k, nums)
# param_1 = obj.add(val)시간 없어서 초비효율 코드 등장^^
일단 넣고 sort 로 정렬한 후 k 번째로 큰 값 return
그 와중에 k 번째로 작은 값인줄 알고 삽질도 함...ㅠ
My Answer 2: Accepted (Runtime: 180 ms - 19.68% / Memory Usage: 18.7 MB - 14.81%)
class KthLargest:
def __init__(self, k: int, nums: List[int]):
self.arr = sorted(nums)
self.kth = k
def add(self, val: int) -> int:
l = 0
r = len(self.arr)-1
while l <= r:
m = (l+r) // 2
if self.arr[m] > val:
r = m - 1
else:
l = m + 1
self.arr.insert(l, val)
ans = self.arr[len(self.arr) - self.kth]
return ans
# Your KthLargest object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = KthLargest(k, nums)
# param_1 = obj.add(val)막판 한 1분만에 Binary Search 로 찾아주고 insert 하는 걸로 변경
쬐끔 더 빠르다^^
시간이 더 있었다면 min-heap 사용했을 듯
Solution 1: Accepted (Runtime: 96 ms - 71.63% / Memory Usage: 18.4 MB - 51.87%)
class KthLargest:
def __init__(self, k: int, nums: List[int]):
self.heap = nums
heapq.heapify(self.heap)
self.k = k
def add(self, val: int) -> int:
heapq.heappush(self.heap,val)
# if heap grows bigger then k remove elements
while len(self.heap) > self.k:
heapq.heappop(self.heap)
return self.heap[0]
# Your KthLargest object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = KthLargest(k, nums)
# param_1 = obj.add(val)Min-Heap 사용
add 할 때마다 pop 을 이용해서 self.heap[0] 값을 계속 k 번째 큰 값으로 유지해줌
