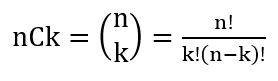11050. 이항 계수 1
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/11050
내 풀이 - 성공
from sys import stdin
N, K = map(int, stdin.readline().split())
ans = 1
for i in range(N-K+1, N+1):
ans *= i
for i in range(1, K+1):
ans //= i
print(ans)이항 계수 수식 이용
n! 을 구한 후, k! 과 (n-k)! 으로 나누는 것보다는
n (n-1) ... * (n-k+1) 을 구하고 k! 으로 나누는 게
반복문도 3 개에서 2 개로 줄고 더 빠르게 구현됐다

다른 사람의 풀이
from sys import stdin
N, K = map(int, stdin.readline().split())
def func(N):
if N <= 1:
return 1
return N * func(N-1)
print(func(N) // (func(K) * func(N-K)))팩토리얼 함수 func 을 직접 구현해서
nCk 공식 그대로 출력하는 방식

다른 사람의 풀이 2
from sys import stdin
from math import factorial
N, K = map(int, stdin.readline().split())
print(factorial(N) // (factorial(K) * factorial(N-K)))math.factorial 을 이용

11279. 최대 힙
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/11279
내 풀이 - 성공
from sys import stdin
import heapq
N = int(stdin.readline())
maxheap = []
for _ in range(N):
x = int(stdin.readline())
if x == 0:
if maxheap:
h = heapq.heappop(maxheap)
print(h[1])
else:
print(0)
else:
heapq.heappush(maxheap, (-x, x))heapq 가 기본적으로 최소 힙으로 되어있으므로
최대 힙을 이용하기 위해서는 두개의 인자를 사용해서 저장해야한다.
(-x, x) 로 저장하면 -x 를 기준으로 오름차순으로 정렬하기 때문에
x 는 결과적으로 내림차순으로 저장되는 효과를 갖게 됨
pop 할 때는 h[1] 을 출력하도록 함