Problem
Solution
1) Sliding window
문자열에 있는 문자를 key로 하고, 문자의 index를 value로 집어넣는 dict()를 정의한다. 이 때 문자열에서 해당 문자의 반복이 나타날 경우 dict()의 index는 마지막 index로 업데이트한다.
seen[charactor] = index
중요한 점은 현재 window 영역 안에 문자의 반복이 나타날 경우 pointer를 옮겨야한다.
window는 두 개의 포인터 간 영역을 말한다.
아래 그림을 보면 고려해야 할 케이스에 대해 잘 설명이 되어있다.
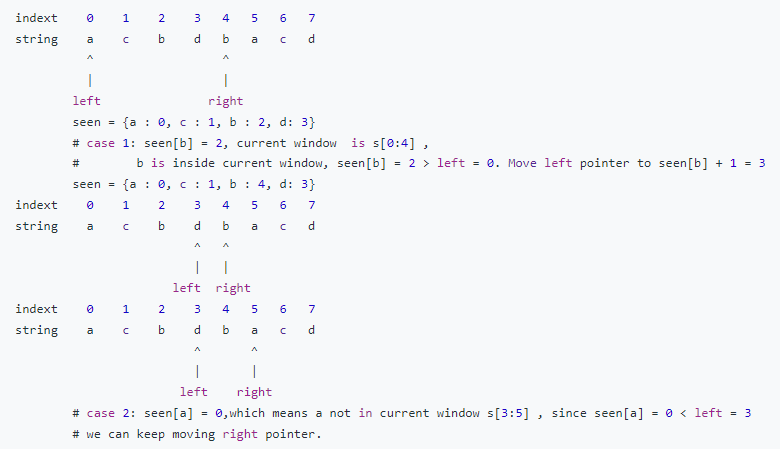
case 1) 문자가 현재 window 안에 있을 때
현재 window가 s[0:4]일 때 즉 b가 반복해서 나오기 전까지를 window로 볼 때 각 문자들을 key로, index를 value로 나타내면 seen = {a:0, c:1, b:2, d:3}이 된다. b은 현재 window 안에 있고, b의 index 2는 left 0보다 크다. seen[b] + 1 = 3 즉, left pointer를 반복 문자인 b의 다음 index 3으로 이동시킨다. 그러면 dict seen은 seen = {a:0, c:1, b:4, d:3}이 된다.
case 2) 문자가 현재 window 밖에 있을 때
현재 window가 s[3:5]일 때 seen[a]의 index 0은 left pointer 3보다 작다. 따라서 right pointer를 계속 옮겨 window 크기를 늘린다.
class Solution:
def lengthOfLongestSubstring(self, s: str) -> int:
seen = {}
l = 0
output = 0
for r in range(len(s)): # 문자열의 문자 반복
"""
If s[r] not in seen, we can keep increasing the window size by moving right pointer
"""
if s[r] not in seen: # dict에 현재 문자가 없을 경우
output = max(output, r-l+1) # window size를 늘린다
"""
There are two cases if s[r] in seen:
case1: s[r] is inside the current window, we need to change the window by moving left pointer to seen[s[r]] + 1.
case2: s[r] is not inside the current window, we can keep increase the window
"""
else: # 반복 문자가 나타났을 경우
if seen[s[r]] < l: # 문자가 현재 윈도우의 left pointer보다 왼쪽에 있을 경우
output = max(output, r-l+1)
else: # left pointer의 위치를 업데이트 해준다.
l = seen[s[r]] + 1
seen[s[r]] = r
return output2) enumerate()를 이용하여 1) 간소화
class Solution:
def lengthOfLongestSubstring(self, s: str) -> int:
left = 0
seen = {}
output = 0
for right, curr in enumerate(s): # right pointer와 문자를 iterate
if curr in seen:
left = max(left, seen[curr] + 1) # 문자가 seen 안에 있으면 left pointer 업데이트
output = max(output, right - left + 1) # 현재 window 크기와 이전 window 크기 비교
seen[curr] = right # dict에 현재 문자 추가
return output