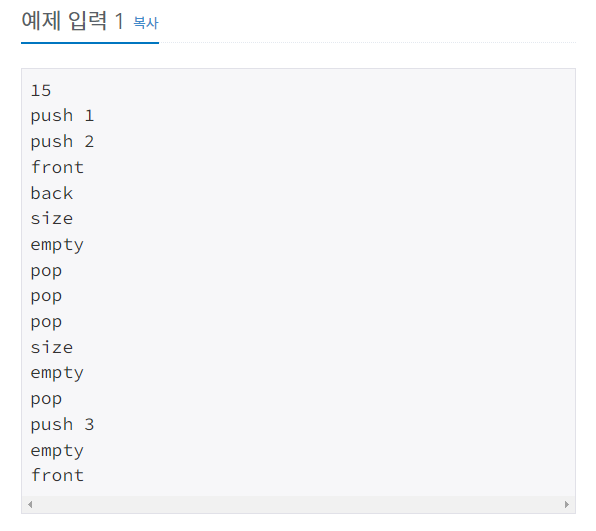
문제
정수를 저장하는 큐를 구현한 다음, 입력으로 주어지는 명령을 처리하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
명령은 총 여섯 가지이다.
push X: 정수 X를 큐에 넣는 연산이다.
pop: 큐에서 가장 앞에 있는 정수를 빼고, 그 수를 출력한다. 만약 큐에 들어있는 정수가 없는 경우에는 -1을 출력한다.
size: 큐에 들어있는 정수의 개수를 출력한다.
empty: 큐가 비어있으면 1, 아니면 0을 출력한다.
front: 큐의 가장 앞에 있는 정수를 출력한다. 만약 큐에 들어있는 정수가 없는 경우에는 -1을 출력한다.
back: 큐의 가장 뒤에 있는 정수를 출력한다. 만약 큐에 들어있는 정수가 없는 경우에는 -1을 출력한다.
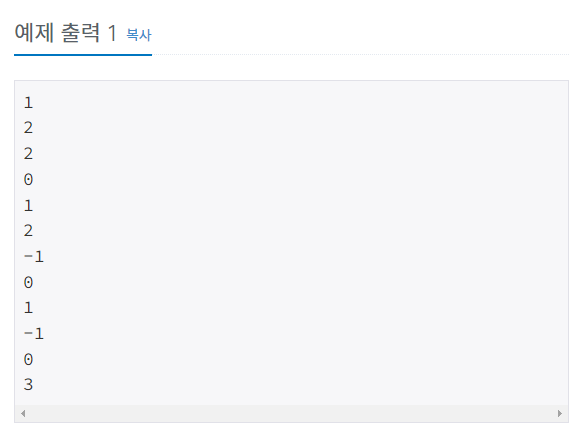
입력
첫째 줄에 주어지는 명령의 수 N (1 ≤ N ≤ 10,000)이 주어진다. 둘째 줄부터 N개의 줄에는 명령이 하나씩 주어진다. 주어지는 정수는 1보다 크거나 같고, 100,000보다 작거나 같다. 문제에 나와있지 않은 명령이 주어지는 경우는 없다.
출력
출력해야하는 명령이 주어질 때마다, 한 줄에 하나씩 출력한다.
코드
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int num = sc.nextInt();
Queue q = new Queue(num);
for(int i = 0; i<num; i++) {
String input = sc.next();
switch(input) {
case "push":
q.push(sc.nextInt());
break;
case "pop":
sb.append(q.pop());
sb.append('\n');
break;
case "empty":
sb.append(q.empty());
sb.append('\n');
break;
case "front":
sb.append(q.front());
sb.append('\n');
break;
case "back":
sb.append(q.back());
sb.append('\n');
break;
case "size":
sb.append(q.size());
sb.append('\n');
break;
default:
System.exit(0);
}
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
static class Queue {
int[] array;
int size = 0;
int front = 0;
int back = 0;
int popVal;
public Queue(int a) {
array = new int[a];
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public int empty() {
if(size==0) {
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
public int front() {
if(size==0) {
return -1;
}
return array[front];
}
public int back() {
if(size==0) {
return -1;
}else {
return array[back-1];
}
}
public void push(int b) {
array[back++] = b;
size++;
}
public int pop() {
if(size==0) {
return -1;
}
popVal = array[front++];
size--;
return popVal;
}
}
}