Supplemental Page Table - Revisit
supplemental_page_table_copy
bool supplemental_page_table_copy (struct supplemental_page_table *dst,
struct supplemental_page_table *src);supplemental page table 복사하는 함수로 → fork()할 때 사용된다.
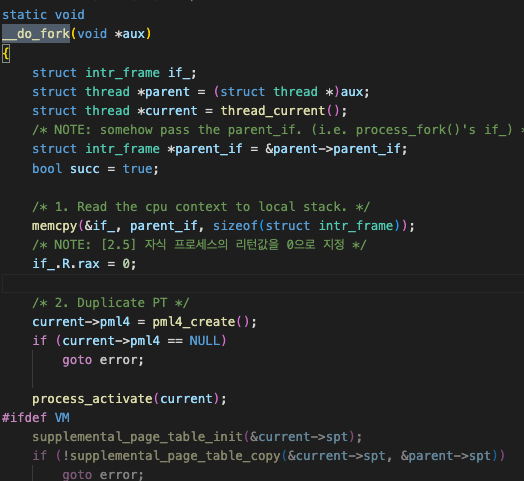
부모 프로세스의 spt도 자식에게 복사해주어야 한다.
부모 프로세스의 spt에 있는 모든 페이지를 각 페이지 타입에 맞게 할당하고, 필요한 경우 페이지 내용을 그대로 복사해서 자식 프로세스의 spt에 추가한다.
/* Copy supplemental page table from src to dst
src에서 dst까지의 spt 복사 */
bool
supplemental_page_table_copy (struct supplemental_page_table *dst UNUSED,
struct supplemental_page_table *src UNUSED) {
//해쉬 테이블을 순회하기 위한 hash_iterator i
struct hash_iterator i;
//해쉬 테이블의 첫 번쨰 요소 가리키도록 i 초기화
hash_first(&i, &src->spt_hash);
//spt 테이블의 모든 요소 순회
while(hash_next(&i)) {
//src_page => 현재 i가 가리키고 있는 hash_elem의 struct page
struct page *src_page = hash_entry(hash_cur(&i), struct page, hash_elem);
enum vm_type type = src_page->operations->type;
void *upage = src_page->va;
bool writable = src_page->writable;
//UNINIT type인 경우(초기화되지 않은 VM_UNINT 페이지)
// - init, aux는 lazy loading에 필요
if (type == VM_UNINIT) {
vm_initializer *init = src_page->uninit.init;
void *aux = src_page->uninit.aux;
vm_alloc_page_with_initializer(VM_ANON, upage, writable, init, aux);
continue;
}
...
// - init, aux는 lazy loading에 필요한 것이므로 필요하지 않다.
// 이미 type이 UNINIT이 아님
// 지금 생성하는 페이지는 lazy loading이 아니라 바로 load할 것임
if (!vm_alloc_page(type, upage, writable)){
return false;
}
if (!vm_claim_page(upage))
return false;
struct page *dst_page = spt_find_page(dst, upage);
memcpy(dst_page->frame->kva, src_page->frame->kva, PGSIZE);
}
return true ;
}hash_iterator를 사용해서 부모 프로세스의 spt 해시 테이블의 모든 엔트리를 순회한다.
1.
VM_UNINIT타입인 경우
초기화되지 않은 페이지의 경우에는 init 함수와 aux를 가져온 다음,vm_alloc_page_with_initializer를 활용해서 자식 프로세스의 spt에 해당 페이지를 할당한다.
- 함수 내부에spt_isnert_page가 있음
2. UNINIT 페이지 타입이 아닌 경우 - lazy loading이 필요하지 않다.
그냥vm_alloc_page를 사용해서 바로 할당한다.
vm_claim_page 를 통해 가상 주소 upage와 물리 메모리 매핑.
spt_find_page 를 통해 자식 프로세스의 spt에서 해당 페이지를 찾고,
memcpy를 통해서 부모 프로세스의 내용을 자식 프로세스의 페이지에 복사한다.
supplemental_page_table_kill
/* Free the resource hold by the supplemental page table */\
/* 프로세스가 종료될 때(process_exit)와 실행될 떄(process_exec)
process_cleanup()에서 실행됨 */
void
supplemental_page_table_kill (struct supplemental_page_table *spt UNUSED) {
/* TODO: Destroy all the supplemental_page_table hold by thread and
* TODO: writeback all the modified contents to the storage. */
hash_clear(&spt->spt_hash, hash_page_destroy);
}
void hash_page_destroy(struct hash_elem *e, void *aux){
struct page *page = hash_entry(e, struct page, hash_elem);
destroy(page); //페이지 제거
free(page); //메모리 해제
}프로세스가 종료될 때 (process_exit())와 실행될 때(process_exec()) process_cleanup에서 실행된다.
⇒ supplemental page table에 의해 유지되던 모든 자원 해제된다.
destroy 호출을 통해서 페이지 타입에 맞는 uninit_destroy or anon_destroy가 호출된다.
hash_destory가 아닌 hash_clear를 쓰는 이유?
프로세스가 실행될 때도 호출되기 때문에 - 빈 해시 테이블이 필요함
hash_destroy함수는 해쉬 테이블과 그 안의 모든 요소를 제거 → 해쉬 테이블이 사용하던 메모리도 모두 release. 해쉬 테이블 자체를 완전히 제거하고 싶을 때 사용hash_clear함수는 테이블 내의 모든 요소는 제거하지만 해쉬 테이블 구조체 자체는 유지 → 해쉬 테이블의 메모리 구조(bucket 등)은 남겨두고 내용만 비움 → 해쉬 테이블 나중에 재사용하고 싶을 때
이렇게 까지 하면 test 결과 38 of 141
