시간복잡도
time complexity: how can we analyze the runtime of an algorithm as the size of the inputs increases =>입력의 크기가 증가할 때 알고리즘의 실행 시간을 어떻게 분석할 수 있는지
- 상수는 중요하지 않다! 작은연산도 중요하지 않다!
- Arithmetic operations are constant : 산수는 상수다. 덧셈, 뺄셈, 곱셈, 나눗셈 포함
- Variable assignment is constant : 변수 배정도 상수. 변수에 값을 배정하는데 걸리는 시간은 비슷하다.
- Accessing elements in an array(by index) or object(by key) is constant
- In a loop, the complexity is the length of the loop times the complexity of whatever happens inside of the loop
function logAtLeast5(n) {
for (var i =1; i <= Math.max(5,n); i++) {
console.log(i);
}
}
=> O(N)
function logAtMost5(n) {
for (var i =1; i<= Math.min(5,n); i++) {
console.log(i);
}
}
=> O(1) 공간 복잡도:
space complexity: how much additional memory do we need to allocate in order to run the code in our algorithm
=> 알고리즘을 실행하기 위해 추가적으로 할당해야 하는 메모리의 양을 나타내는 개념
- Anxiliary space complexity: space required by the algorithm, not including space taken up by the inputs.
- 공간복잡도 사실상 보조 공간 복잡도를 의미한다.
Space Complexity in JS
- Most primitives (booleans, numbers, undefined, null) are constant space
- Strings require O(n) space (where n is the string length) => 문자열은 O(n)
- Reference types are generally O(n), where n is the length (for arrays) or the number of keys (for objects) - 배열 길이, 객체 키 갯수
function sum(arr) { let total =0; for (let i=0; i<arr.length; i++) { total += arr[i]; } return total; } => O(1) space! -------------------------- function double(arr) { let newArr =[]; for (let i=0; i<arr.length; i++) { newArr.push(2 * arr[i]); } return newArr; } => O(N) space!
Logarithms
log(value) = exponent <=> 10^exponenet =value
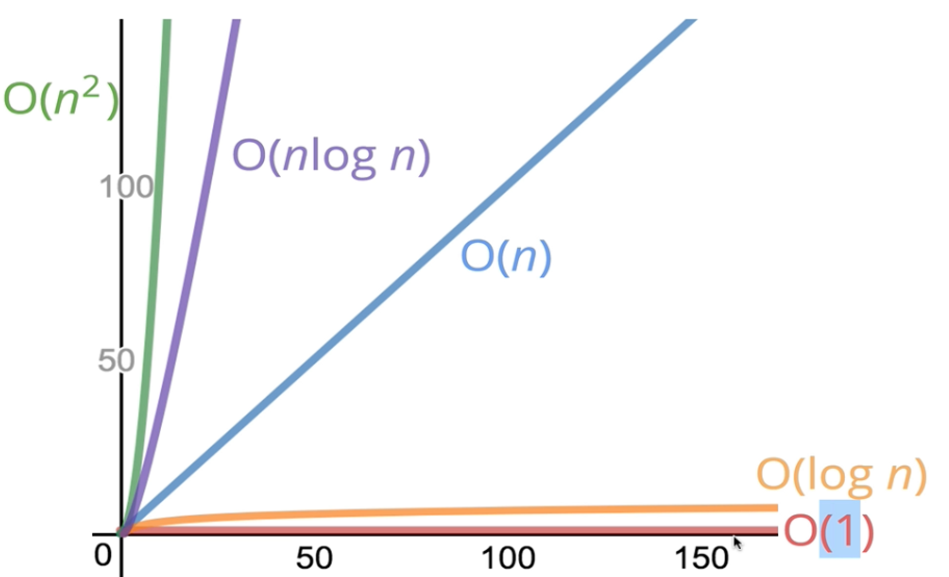
Logarithm time complexity is great
: O(log n) is much better than O(n)
- certain searching algorithms have logarithm time complexity
- efficient sorting algoritms involve logarithms
- recursion(재귀) sometimes involves logarithmic space time complexity
정리
- To analyze the performace of an algorithm, we use Big O notation
- Big O notation can give us a high level of understanding of the time or space complexity of an algorithm
- Big O notation doesn’t care about precision, only about general trends (linear? quadratic? constant?)
- The time or space complexity (as measured by Big O) depends only on the algorithm, not the hardware used to run the algorithm
- Big O notaiton is everywhere!!!
Objects(객체) : Unordered, key value pairs
let instructor = { firstName: "kelly", isInstructor: true, favoriteNumber: [1,2,3,4] }
- when you don’t need order
- when you need fast access / insertion and removal
Insertion - O(1)
Removal - O(1)
Searching - O(N)
Access - O(1)
- 기본적인 연산은 빠르게 처리, 객체에 시작과 끝이 있지는 않다.
- 탐색은 선형 시간 → 속성이 많을수록 O(n)
Object.keys - O(N)
Object.values - O(N)
Object.entries - O(N)
hasOwnProperty - O(1) : 상수, 키가 존재하는지 true, false
Arrays: ordered lists
let name = ["michale", "melissa", "andrea"] let values = [true, {}, [], 2, "awesome"]
- when you need order
- when you need fast access / insertion and removal
Insertion, Removal - it depends
- 배열 앞에 push(), remove() ⇒ O(n) 선형 시간 - 인덱스가 엘리먼트 마다 새로 정렬되어야 하기 때문에. 끝에 추가하고 제거하는 것보다 비효율적
Searching - O(N)
Access - O(1)
: 하는 것은 숫자, 인덱스만 있다면 상수 시간이다. 배열 [100000]이라도 상관없음.
⇒ push(), pop()하는 작업(배열 맨 끝)이 shift(), unshift() 작업(reindex every element)보다 빠르다!(비어있는 배열 제외)
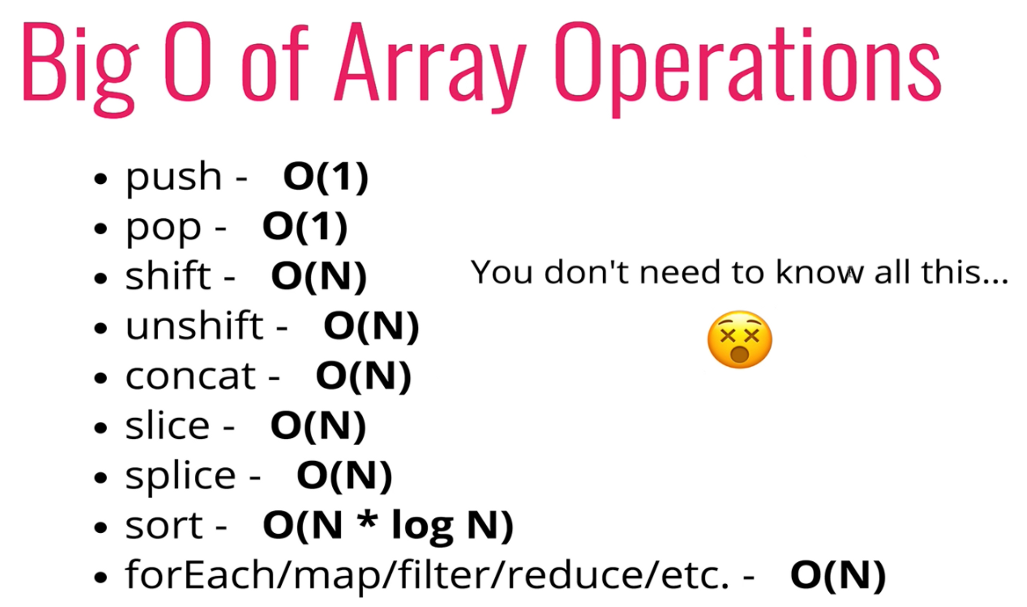
- concat(): 배열을 합쳐줌. 결합할 배열이 커질수록, 끝에 붙일 배열의 크기만큼 시간도 늘어남
- slice(): 배열 일부나 전부를 가져옴. 걸리는 시간은 복사하는 엘리먼트 갯수만큼 늘어남
- splice(): 엘리먼트 제거하고 추가, 배열 시작에도 추가할 수 있고 끝에도 할 수 있다. 하지만 배열 추가하면 단순하게 in general, O(N)
months.splice(1,0,'Feb') : insert at 1st index
months.splice(4,1,"May") : replaces 1 element at 4th index- sort() : 더 복잡. 여기서 가장 느림.