Here is a comprehensive summary of the uploaded paper based on your requirements:
1. Title, Authors, and Academic Society
- Title: Recommender Systems with Generative Retrieval
- Authors: Shashank Rajput, Nikhil Mehta, Anima Singh, Raghunandan Keshavan, Trung Vu, Lukasz Heldt, Lichan Hong, Yi Tay, Vinh Q. Tran, Jonah Samost, Maciej Kula, Ed H. Chi, Maheswaran Sathiamoorthy.
- Submission: 37th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2023).
2. Paper Summary (Using the Index)
Abstract
The paper introduces a novel framework for recommender systems called TIGER (Transformer Index for Generative Recommenders), which redefines item retrieval as a generative task. Instead of traditional embedding-based retrieval models, TIGER uses Semantic IDs, hierarchical sequences of tokens derived from item content, for generative autoregressive decoding. It significantly improves recommendation performance, particularly in cold-start scenarios, and provides a scalable alternative for handling large item corpora.
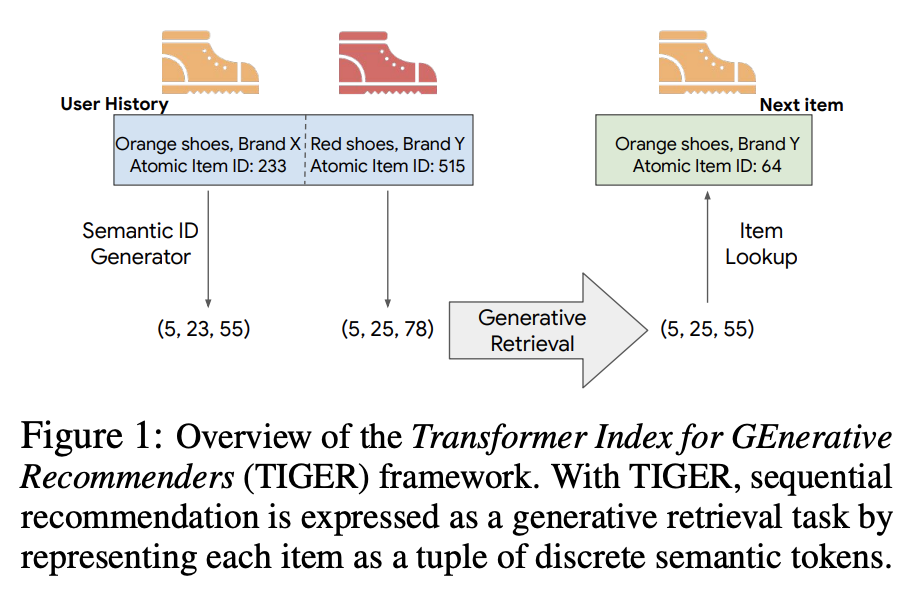
Proposal
- Problem Statement: Current recommender systems rely on embedding-based retrieval methods that struggle with:
- Scalability, due to large embedding tables.
- Generalization, especially for cold-start items (items with no prior interactions).
- Diversity, due to feedback loops in recommendations.
- Proposed Solution: Replace embedding-based retrieval with generative retrieval that:
- Represents items using Semantic IDs (generated from content embeddings).
- Trains a sequence-to-sequence Transformer model to autoregressively predict the Semantic IDs of target items.
- Incorporates hierarchical quantization to capture both coarse and fine-grained semantics.
Methodology
Semantic ID Generation
-
Embedding: Items' textual metadata (titles, descriptions, etc.) are processed using pre-trained models like Sentence-T5 to generate semantic embeddings.
-
Quantization: The embeddings are quantized using Residual Quantized Variational Autoencoder (RQ-VAE) to produce tuples of discrete tokens:
- At each level, residual errors are quantized using a specific codebook.
- Each token captures finer details at successive levels of quantization.
RQ-VAE Formula:
At level ( d ):
[
rd = r{d-1} - e{c{d-1}}, \quad cd = \text{argmin}_i |r_d - e{ci}|
]
where ( rd ) is the residual, ( c_d ) is the codeword, and ( e{ci} ) is the closest vector in the codebook. -
Collision Handling: Semantic collisions are resolved by appending additional tokens to the ID to ensure uniqueness.
Generative Retrieval
- Items are represented as sequences of Semantic IDs.
- A sequence-to-sequence Transformer predicts the Semantic ID of the next item in a user’s interaction sequence.
- Generative models allow for direct prediction of items based on content, enabling cold-start capabilities.
Experimental Process
Dataset Details
- Datasets Used: Amazon Product Reviews (categories: "Beauty," "Sports and Outdoors," "Toys and Games").
- Statistics:
- Beauty: 22,363 users, 12,101 items.
- Sports: 35,598 users, 18,357 items.
- Toys: 19,412 users, 11,924 items.
- Preprocessing:
- Chronological sequences of user-item interactions are prepared.
- Leave-one-out validation is used, with the last interaction for testing, the second-to-last for validation, and the rest for training.
Experimental Method
- Implementation:
- RQ-VAE:
- Embeddings: 768-dimensional content embeddings from Sentence-T5.
- Encoder: Three intermediate layers (512, 256, 128 units).
- Codebooks: 256 entries per level, 3 levels.
- Training: 20,000 epochs using Adagrad optimizer.
- Transformer Model:
- 4 encoder and decoder layers with 6 attention heads.
- Embedding dimension: 128, with a 0.1 dropout rate.
- Vocabulary: 1,024 tokens for Semantic IDs, 2,000 tokens for user IDs.
- RQ-VAE:
- Evaluation Metrics:
- Top-k Recall (Recall@K) and Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain (NDCG@K) for ( K = 5, 10 ).
Results
- Performance:
- TIGER outperforms baselines like SASRec, BERT4Rec, and S3-Rec.
- Achieved 29% improvement in NDCG@5 and 17.3% improvement in Recall@5 on the Beauty dataset compared to S3-Rec.
- Cold-Start:
- Introduced unseen items by removing 5% of items during training.
- TIGER outperformed Semantic KNN in recommending cold-start items.
- Diversity:
- Used temperature sampling during decoding to improve diversity.
- Higher temperatures increased entropy, reflecting more varied recommendations.
Novelty
- Semantic Representation: The use of hierarchical Semantic IDs captures both broad and specific item properties, enabling better generalization.
- Generative Framework: The transition from matching-based to generative retrieval is novel for recommender systems.
- Scalability: Semantic IDs reduce memory usage compared to traditional embedding-based methods.
- Enhanced Diversity: Temperature-based sampling controls diversity, mitigating feedback loops.
Conclusion
TIGER demonstrates a paradigm shift in recommender systems by introducing generative retrieval with Semantic IDs. The model achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple datasets, offers robust solutions for cold-start and diversity challenges, and reduces memory requirements, paving the way for scalable, content-based recommendation systems.
3. Summary Table
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Title | Recommender Systems with Generative Retrieval |
| Authors | Shashank Rajput, Nikhil Mehta, Anima Singh, et al. |
| Submission | NeurIPS 2023 |
| Proposal | Replace embedding-based retrieval with generative retrieval using Semantic IDs. |
| Semantic ID Method | Generated via RQ-VAE, using hierarchical quantization of content embeddings. |
| Transformer Details | Sequence-to-sequence model with 4 encoder/decoder layers and 1,024-token vocabulary. |
| Datasets | Amazon Reviews (Beauty, Sports, Toys categories). |
| Results | Up to 29% improvement in NDCG@5 over SOTA baselines. |
| Cold-Start Capability | Successfully recommends new items using content-based Semantic IDs. |
| Diversity | Temperature sampling increases recommendation variety. |
| Applications | Scalable, cold-start capable, and diverse recommendation systems. |
