Destructuring
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s5QZIhooG0U
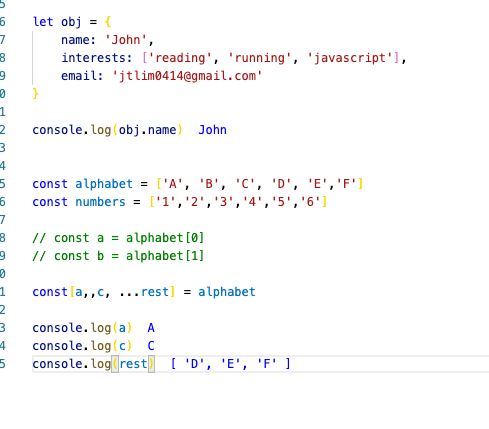
let obj = {
name: 'John',
interests: ['reading', 'running', 'javascript'],
email: 'jtlim0414@gmail.com'
}
console.log(obj.name)https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NIq3qLaHCIs
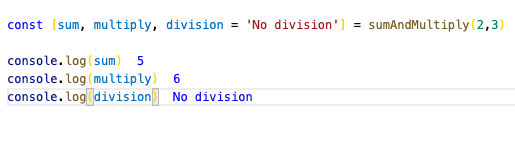
const personOne= {
name: 'Kyle',
age: 24,
address: {
city: 'Somewhere',
states: 'One of them'
}
}
const personTwo = {
name: 'Sally',
age: 32,
address: {
ciry: 'Somewhere else',
states: 'Another one of them'
}
}

QUEUE
https://st-lab.tistory.com/183
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=A3ZUpyrnCbM
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bK7I79hcm08
function Queue {
collection = [];
this.print = function () {
console.log(collection);
}
this.enqueue = function(element) {
collection.push(element)
};
this.dequeue = function() {
return collection.shift();
}
this.front = function() {
return collection[0]
}
this.size = function() {
return collection.length
}
this.isEmpty = function() {
return (colletion.length ===0);
};
}var Queue = function () {
this.head = 0;
this.tail = 0;
this._storage = {};
};
Queue.prototype.add = function (val) {
this._storage[this.head] = val;
this.head++;
};
Queue.prototype.remove = function () {
if (this.head === this.tail) {
return undefined;
}
let removedElement = this._storage[this.tail];
delete this._storage[this.tail];
this.tail++;
return removedElement;
};
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lccLGGaOMi4
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=okr-XE8yTO8
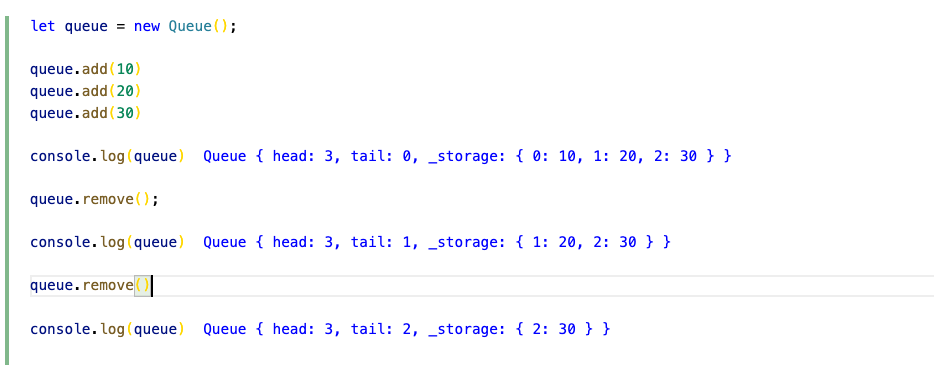
아 this.head 랑 this.tail이 index 역할을 하는거다.
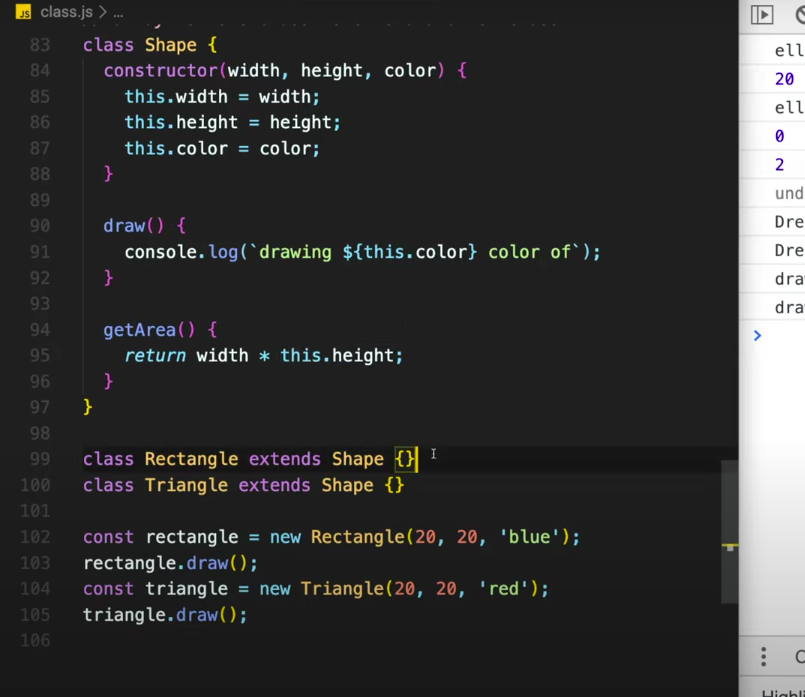
Inheritance Class
class Person {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
get profile() {
return `Name: ${this.name}, Age: ${this.age}`;
}
introduce() {
return `Hello, my name is ${this.name}`;
}
}
var person = new Person("James", 90);
console.log(person.profile);
console.log(person.introduce());
class Developer extends Person {
constructor(name, age) {
super(name, age);
}
work() {
return 'doing javascript';
}
}
var developer = new Developer("John", 80);
console.log(developer.introduce());
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_DLhUBWsRtw
https://medium.com/@chinup.peter/prototypal-inheritance-in-javascript-the-big-picture-1fb20b63b210
Recurssion Array
https://medium.com/@daniel.oliver.king/getting-started-with-recursion-f89f57c5b60e
Most of the time, I have heard people teaching recursion focus far too much on the base case, and not enough on the recursive case. People usually don’t have much trouble realizing what the base case should be — the harder part is deciding how the recursive call should be structured in order to accomplish the computation you want. Unfortunately, it is difficult to find useful advice about how we should go about doing this. This is what I would like to talk about here — how we should think when writing a recursive algorithm.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0wf14oAZPo8
function flatten (array) {
///create a brand new array
let arr=[];
// write a for loop
for(let i =0; i<array.length;i++) {
let element = array[i];
// if the element is an array, recurse
if (Array.isArray(element)) {
flatten(element);
} else {
// else, push the single value into the new array
arr.push(element);
}
}
return arr;
}
flatten([1,2,[3,4,[5]]]);
function flatten (array) {
/// create a blank array
let arr =[];
/// create a helper function with array argument
function helper (array) {
/// wirte a for loop
for(let i=0; i< array.length; i++) {
let element = array[i];
/// if the element is an array, recurse with helper function
if(Array.isArray(element)) {
helper(element);
} else {
arr.push(element)
}
/// else, push the element into the balnk array
}
}
/// call helper function
helper(array);
/// return the array
return arr;
}
flatten([1,2,[3,4,[5]]]);const printArray = function (arr) {
if (arr.length === 0) {
return;
}
arr.forEach(el => {
if (Array.isArray(el) === true) {
printArray(el);
} else {
console.log(el);
}
});
};