미로탐색 << 문제 클릭!
✅문제 설명
: NXM 크기의 배열로 표현되는 미로가 있을 때 1은 이동할 수 있는 칸, 0은 이동할 수 없는 칸이다.
: (1,1)에서 출발해서 (N,M)의 위치로 이동할 때 지나야 할 최소의 칸 수를 구한다.
: 서로 인접한 칸으로만 이동 가능하다.
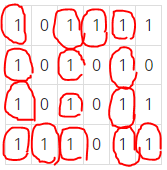
- 입력
: 첫째 줄은 두 정수 N,M(2<=N,M<=100)
: N개의 줄에는 M개의 정수로 미로가 주어짐
: 이때 각 수들은 붙어서 입력으로 주어짐!
: 항상 도착위치로 이동할 수 있는 경우로만 주어짐.
- 출력
: 첫째 줄에는 지나야 하는 최소 칸 수
❗핵심원리
- BFS(Breadth First Search)
: BFS를 이용하여 인접한 블록에 대하여 블록값이 1인 모든 블록을 순회하여 각 거리값을 계산한다.
그래프가 아니라 좌표에서 BFS의 적용 순서를 보면 위 그림처럼 시작 좌표에서 인접한 주변 좌표에 대해 하나씩 접근하게 된다.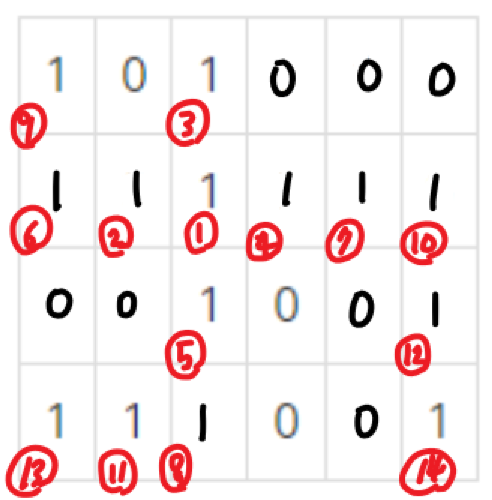
💻코드
1차
- 먼저 미로를 저장하기 위해 포인터를 이용하여 2차원 동적 배열을 할당하고 만들었다!
- 큐를 이용하여 시작 위치의 값을 넣고 BFS 구현
- 2차원 동적 배열을 이용해서 인접한 좌표에 대해 값이 1인 좌표에 접근하여 거리를 업데이트 및 큐에 push 한다.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int N, M; // 정수
cin >> N >> M;
int** arr = new int*[N]; // 행 받기 - 이때 크기가 n인 INT* 배열을 가리키는 포인터 변수 정의
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
arr[i] = new int[M]; //열받기
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
string temp; // 임시저장
cin >> temp;
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
arr[i][j] = temp[j] - '0'; // 값 넣기, 그냥 int(temp[j])로 두면 49가 나온다.
}
}
queue<pair<int, int>> q; // 큐를 만들어줌
q.push({0,0}); // 초기 위치 값 넣기
int dx[4] = {1,0,-1,0 }; // 시계방향으로
int dy[4] = {0,1,0,-1};
while (!q.empty()) {
pair<int, int> temp = q.front(); //앞의 값 꺼내기
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int x = temp.first + dx[i];
int y = temp.second + dy[i];
if (x < 0 || x > N || y < 0 || y > M) continue; // 미로 범위 밖일 경우
if (arr[x][y] != 1) continue; // 이미 접근했거나 0인 경우
// 접근 가능
arr[x][y] = arr[temp.first][temp.second] + 1; // 인접한 블록이므로!
q.push({ x,y });
}
}
cout << arr[N - 1][M - 1];
// 해제
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
delete[] arr[i];
}
delete[] arr;
return 0;
}
✅문제 원인
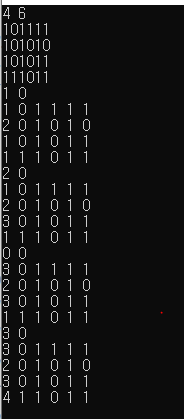
한번 과정을 확인해보니 <2,0> 위치까지는 잘 이동하였으나 갑자기 <0,0>로 이동하고 멈춘다.
즉, <1,0>에서 큐에 <2,0> 과 <0,0>이 push 된 것임을 알 수 있다.
이는 if(arr[x][y] != 1) 조건에 의해 <0,0>까지 포함 된 것이다...
따라서 거리 테이블을 만들어준다...
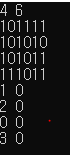
호우... 만들어줘도 문제가 발생한다.. 왜이래...

아니.. x > N 을 x >= N으로, y > M을 y >= M으로 바꾸니까 된다... 아 x=N일때 값을 찾고 있어서 에러가 난 듯 하다...
2차
- 미로를 저장하기 위한 2차원 배열과 거리를 저장하기 위한 2차원 배열을 만듬
- 이때 거리를 저장하기 위한 배열은 0으로 모두 초기화
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int N, M; // 정수
cin >> N >> M;
int** arr = new int*[N]; // 행 받기 - 이때 크기가 n인 INT* 배열을 가리키는 포인터 변수 정의
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
arr[i] = new int[M]; //열받기
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
string temp; // 임시저장
cin >> temp;
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
arr[i][j] = temp[j] - '0'; // 값 넣기, 그냥 int(temp[j])로 두면 49가 나온다.
}
}
queue<pair<int, int>> q; // 큐를 만들어줌
q.push({0,0}); // 초기 위치 값 넣기
int dx[4] = {1,0,-1,0 }; // 시계방향으로
int dy[4] = {0,1,0,-1};
while (!q.empty()) {
pair<int, int> temp = q.front(); //앞의 값 꺼내기
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int x = temp.first + dx[i];
int y = temp.second + dy[i];
if (x < 0 || x > N || y < 0 || y > M) continue; // 미로 범위 밖일 경우
if (arr[x][y] != 1) continue; // 이미 접근했거나 0인 경우
// 접근 가능
arr[x][y] = arr[temp.first][temp.second] + 1; // 인접한 블록이므로!
q.push({ x,y });
}
}
cout << arr[N - 1][M - 1];
// 해제
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
delete[] arr[i];
}
delete[] arr;
return 0;
}

맞았다!
다른 분들의 풀이 출처
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define X first
#define Y second // pair에서 first, second를 줄여서 쓰기 위해서 사용
string board[102]; // '1'이 파란 칸, '0'이 빨간 칸에 대응
int dist[102][102]; // 해당 칸을 방문했는지 여부를 저장
int n,m;
int dx[4] = {1,0,-1,0};
int dy[4] = {0,1,0,-1}; // 상하좌우 네 방향을 의미
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> board[i];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) fill(dist[i],dist[i]+m,-1);
queue<pair<int,int> > Q;
Q.push({0,0});
dist[0][0] = 0;
while(!Q.empty()){
auto cur = Q.front(); Q.pop();
for(int dir = 0; dir < 4; dir++){ // 상하좌우 칸을 살펴볼 것이다.
int nx = cur.X + dx[dir];
int ny = cur.Y + dy[dir]; // nx, ny에 dir에서 정한 방향의 인접한 칸의 좌표가 들어감
if(nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= m) continue; // 범위 밖일 경우 넘어감
if(dist[nx][ny] >= 0 || board[nx][ny] != '1') continue; // 이미 방문한 칸이거나 이동할 수 없는 칸일 경우
dist[nx][ny] = dist[cur.X][cur.Y]+1; // (nx, ny)의 거리는 현재 보고 있는 위치의 거리 + 1
Q.push({nx,ny});
}
}
cout << dist[n-1][m-1]+1; // 문제의 특성상 거리+1이 정답
}- 이 분은 그냥 미로를 저장할 때 string 배열로 바로 저장했음.. 크으으..
