def solution(lines):
def formatline(x):
x = x.split()
end = x[1].split(':')
end = int(end[0])*3600 + int(end[1])*60 + float(end[2])
return round(end-float(x[2][:-1]) + 0.001,3),end
answer = 0
lines = list(map(lambda x: formatline(x), lines))
for i in range(len(lines)):
start, end = lines[i]
k = 0
for s,e in lines:
if (end <= e <= round(end + 0.999,3)) or (end <= s <= round(end + 0.999,3)) or (s <= end and round(end+0.999,3) <= e):
k+=1
answer = max(answer, k)
return answer아 어렵다.
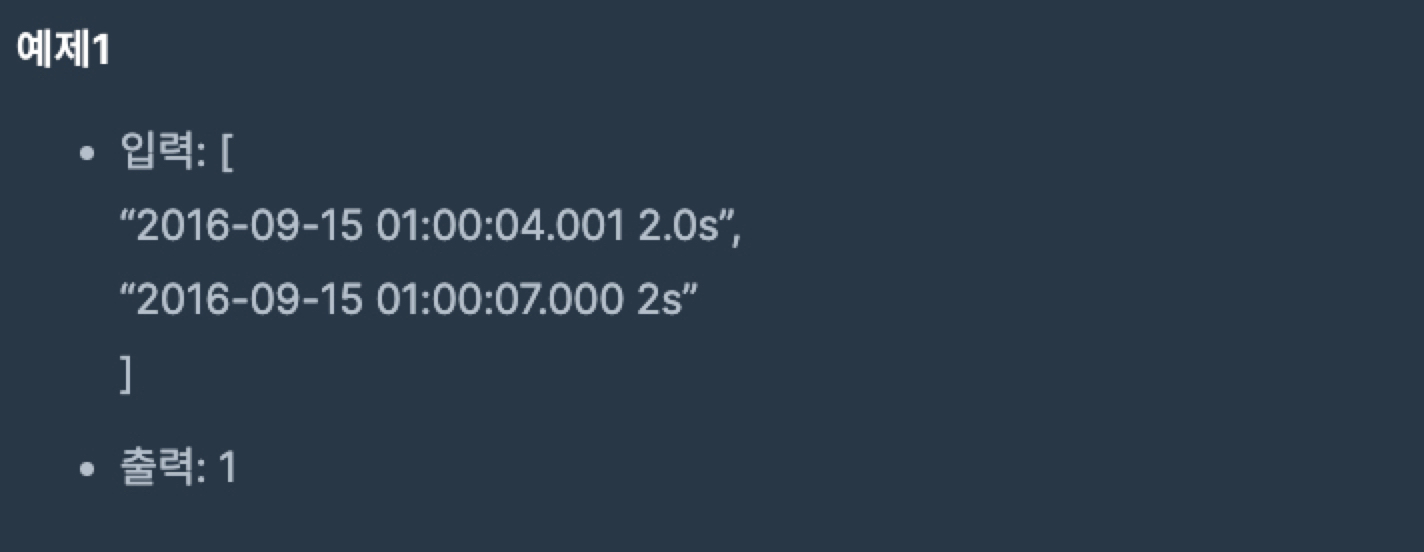
formatline : input을 초로 환산하고 처리시간을 이용하여 초로 환산된 시작시간과 끝시간으로 새로운 lines 배열을 만든다.
for i in range(len(lines)):
start, end = lines[i]
k = 0
for s,e in lines:
if (end <= e <= round(end + 0.999,3)) or (end <= s <= round(end + 0.999,3)) or (s <= end and round(end+0.999,3) <= e):
k+=1
answer = max(answer, k)전체 lines 들 중 조건을 만족하는 것들의 개수를 계산한다.
Others
def solution(lines):
#get input
S , E= [], []
totalLines = 0
for line in lines:
totalLines += 1
(d,s,t) = line.split(" ")
##time to float
t = float(t[0:-1])
(hh, mm, ss) = s.split(":")
seconds = float(hh) * 3600 + float(mm) * 60 + float(ss)
E.append(seconds + 1)
S.append(seconds - t + 0.001)
#count the maxTraffic
S.sort()
curTraffic = 0
maxTraffic = 0
countE = 0
countS = 0
while((countE < totalLines) & (countS < totalLines)):
if(S[countS] < E[countE]):
curTraffic += 1
maxTraffic = max(maxTraffic, curTraffic)
countS += 1
else: ## it means that a line is over.
curTraffic -= 1
countE += 1
return maxTrafficStart 와 End 점들을 각각 S, E 에 추가하고 정렬
굳이 점들을 비교할 필요 없이 현재 존재하는 traffic 양만 확인하면 된다
바로 다음에 오는 점이 S 이면 (S[countS] < E[countE]) 이면 현재 traffic 에 1을 더하고, E이면 하나가 끝난 것이므로 1을 빼준다. 어떤 것이 빠졌는 지는 확인할 필요가 없다...
1초간이라는 것은 끝난 traffic 도 1초동안에는 traffic 계산에 영향을 준다는 것이므로 모든 End 점에 + 1s 를 하여 해결했다.

