홈 화면과 레이아웃
@Controller
@Slf4j
public class HomeController {
@RequestMapping("/")
public String home() {
log.info("home controller");
return "home";
}
}스프링부트 타임리프 기본 설정
spring:
thymeleaf:
prefix: classpath:/templates/
suffix: .html- 스프링 부트 타임리프 viewName 매핑
- resources:templates/ +{ViewName}+ .html
- resources:templates/home.html
- 반환한 문자( home )과 스프링부트 설정 prefix , suffix 정보를 사용해서 렌더링할 뷰( html )를 찾는다.
회원 등록
- 폼 객체를 사용해서 화면 계층과 서비스 계층을 명확하게 분리한다.
package jpabook.jpashop.domain.controller;
import jakarta.validation.Valid;
import jpabook.jpashop.domain.Address;
import jpabook.jpashop.domain.Member;
import jpabook.jpashop.service.MemberService;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
@Controller
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class MemberController {
private final MemberService memberService;
@GetMapping("/members/new")
public String createFrom(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("memberForm", new MemberForm());
return "members/createMemberForm";
}
@PostMapping("/members/new")
public String create(@Valid MemberForm form, BindingResult result) {
if (result.hasErrors()) {
return "members/createMemberForm";
}
Address address = new Address(form.getCity(), form.getStreet(), form.getZipcode());
Member member = new Member();
member.setName(form.getName());
member.setAddress(address);
memberService.join(member);
return "redirect:/";
}
}
-
model.addAttribute를 사용하면, controller에서 view로 넘어갈 때 데이터를 실어서 넘긴다.
-
BindingResult를 사용하면 오류가 담겨서 코드가 실행된다!
-
Member 엔티티를 그대로 넣지 않고, MemberForm 을 사용하는 이유?
- 컨트롤러에서 화면으로 넘어올 때의 validation과 실제 도메인이 원하는 validation이 다를 수 있다. 엔티티를 화면에서 왔다갔다하는 폼 데이토로 쓰기 시작하면 안 맞는 경우가 발생한다. 따라서 화면에 깔끔하게 핏한 form을 만들고 그걸로 데이터를 받는 것이 낫다. (실무에서는 엔티티를 그대로 파라미터로 받아서 처리할 정도로 간단한 폼화면이 거의 없기 때문에!)
회원 등록 폼 화면 (templates/members/createMemberForm.html)
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head th:replace="fragments/header :: header" />
<style>
.fieldError {
border-color: #bd2130;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div th:replace="fragments/bodyHeader :: bodyHeader"/>
<form role="form" action="/members/new" th:object="${memberForm}"
method="post">
<div class="form-group">
<label th:for="name">이름</label>
<input type="text" th:field="*{name}" class="form-control"
placeholder="이름을 입력하세요"
th:class="${#fields.hasErrors('name')}? 'form-control
fieldError' : 'form-control'">
<p th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('name')}"
th:errors="*{name}">Incorrect date</p>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label th:for="city">도시</label>
<input type="text" th:field="*{city}" class="form-control"
placeholder="도시를 입력하세요">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label th:for="street">거리</label>
<input type="text" th:field="*{street}" class="form-control"
placeholder="거리를 입력하세요">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label th:for="zipcode">우편번호</label>
<input type="text" th:field="*{zipcode}" class="form-control"
placeholder="우편번호를 입력하세요">
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</form>
<br/>
<div th:replace="fragments/footer :: footer" />
</div> <!-- /container -->
</body>
</html>회원 목록 조회
@GetMapping("/members")
public String list(Model model) {
List<Member> members = memberService.findMembers();
model.addAttribute("members", members);
return "members/memberList";
}<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head th:replace="fragments/header :: header" />
<body>
<div class="container">
<div th:replace="fragments/bodyHeader :: bodyHeader" />
<div>
<table class="table table-striped">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>#</th>
<th>이름</th>
<th>도시</th>
<th>주소</th>
<th>우편번호</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="member : ${members}">
<td th:text="${member.id}"></td>
<td th:text="${member.name}"></td>
<td th:text="${member.address?.city}"></td>
<td th:text="${member.address?.street}"></td>
<td th:text="${member.address?.zipcode}"></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
<div th:replace="fragments/footer :: footer" />
</div> <!-- /container -->
</body>
</html>- 엔티티를 폼으로 사용할 때의 문제:
- 엔티티에 화면을 처리하기 위한 기능이 증가되고, 결과적으로 엔티티가 화면 종속적이게 되고, 지저분해진다. -> 유지보수가 어려워짐!
- JPA를 쓸 때, 엔티티는 최대한 순수하게 유지해야 한다. 오직 핵심 비즈니스 로직에만 dependency가 있도록 설계해야 한다. -> 그래야 애플리케이션이 점점 커져서 엔티티를 여려 곳에서 유연하게 사용하더라도 유지보수성이 높아지기 때문이다.
결론 : 실무에서는 엔티티는 핵심 비즈니스 로직만 가지고있고, 화면을 위한 로직은 없어야 한다. -> 화면에 오가는 데이터를 담기 위해서는 form 객체나 DTO를 사용해야 한다. 엔티티는 최대한 순수하게 유지하자!
- API를 만들 때는 이유를 불문하고 절대 외부로 엔티티를 넘기면 안된다 !!!
- API라는 건 스펙이다. 엔티티를 넘기게 되면, 엔티티의 로직을 추가하면 그것으로 인해 API 스펙이 변하게 되는 것이다 ! 그렇게 되면 굉장히 불완전한 API 스펙이 되고, 그걸 갖다 쓰는 개발팀들은 엄청 괴로울 것..
상품 등록
package jpabook.jpashop.domain.controller;
import jpabook.jpashop.domain.item.Book;
import jpabook.jpashop.service.ItemService;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
@Controller
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class ItemController {
private final ItemService itemService;
@GetMapping("/items/new")
public String createForm(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("form", new BookForm());
return "items/createItemForm";
}
@PostMapping("/items/new")
public String create(BookForm form) {
Book book = new Book();
book.setStockQuantity(form.getStockQuantity());
book.setPrice(form.getPrice());
book.setName(form.getName());
book.setAuthor(form.getAuthor());
book.setIsbn(form.getIsbn());
itemService.saveItem(book);
return "redirect:/";
}
}
items/createItemForm.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head th:replace="fragments/header :: header" />
<body>
<div class="container">
<div th:replace="fragments/bodyHeader :: bodyHeader"/>
<form th:action="@{/items/new}" th:object="${form}" method="post">
<div class="form-group">
<label th:for="name">상품명</label>
<input type="text" th:field="*{name}" class="form-control"
placeholder="이름을 입력하세요">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label th:for="price">가격</label>
<input type="number" th:field="*{price}" class="form-control"
placeholder="가격을 입력하세요">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label th:for="stockQuantity">수량</label>
<input type="number" th:field="*{stockQuantity}" class="formcontrol" placeholder="수량을 입력하세요">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label th:for="author">저자</label>
<input type="text" th:field="*{author}" class="form-control"
placeholder="저자를 입력하세요">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label th:for="isbn">ISBN</label>
<input type="text" th:field="*{isbn}" class="form-control"
placeholder="ISBN을 입력하세요">
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</form>
<br/>
<div th:replace="fragments/footer :: footer" />
</div> <!-- /container -->
</body>
</html>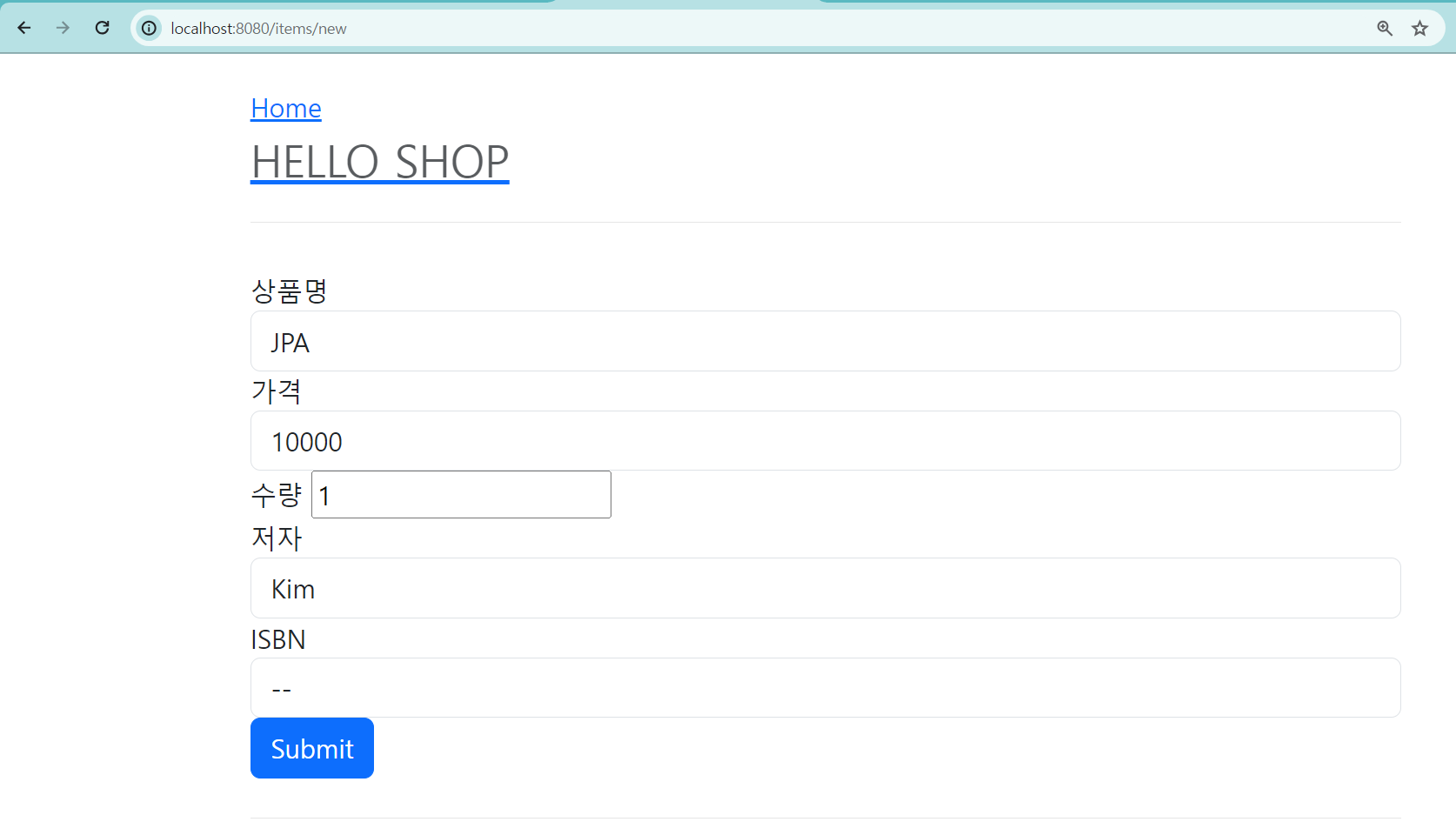
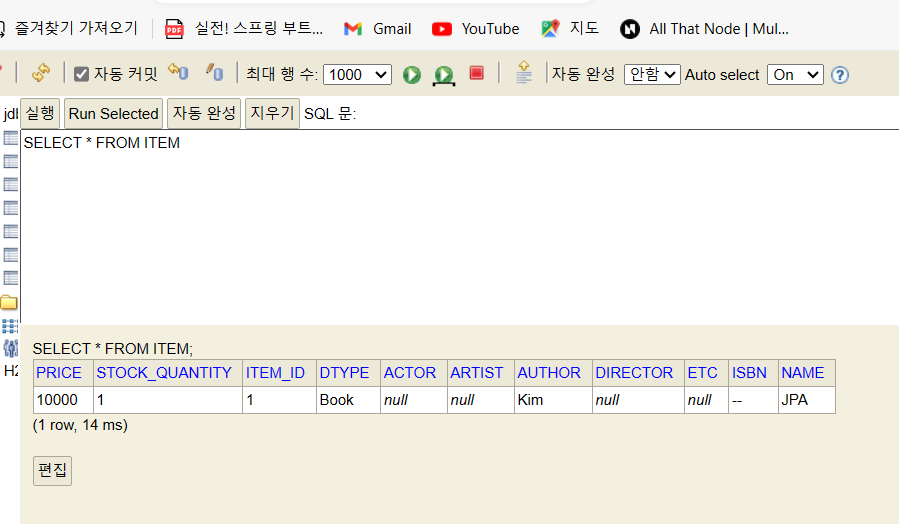
상품 목록
@GetMapping("/items")
public String list(Model model) {
List<Item> items = itemService.findItems();
model.addAttribute("items", items);
return "items/itemList";
}<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head th:replace="fragments/header :: header" />
<body>
<div class="container">
<div th:replace="fragments/bodyHeader :: bodyHeader"/>
<div>
<table class="table table-striped">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>#</th>
<th>상품명</th>
<th>가격</th>
<th>재고수량</th>
<th></th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="item : ${items}">
<td th:text="${item.id}"></td>
<td th:text="${item.name}"></td>
<td th:text="${item.price}"></td>
<td th:text="${item.stockQuantity}"></td>
<td>
<a href="#" th:href="@{/items/{id}/edit (id=${item.id})}"
class="btn btn-primary" role="button">수정</a>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
<div th:replace="fragments/footer :: footer"/>
</div> <!-- /container -->
</body>
</html>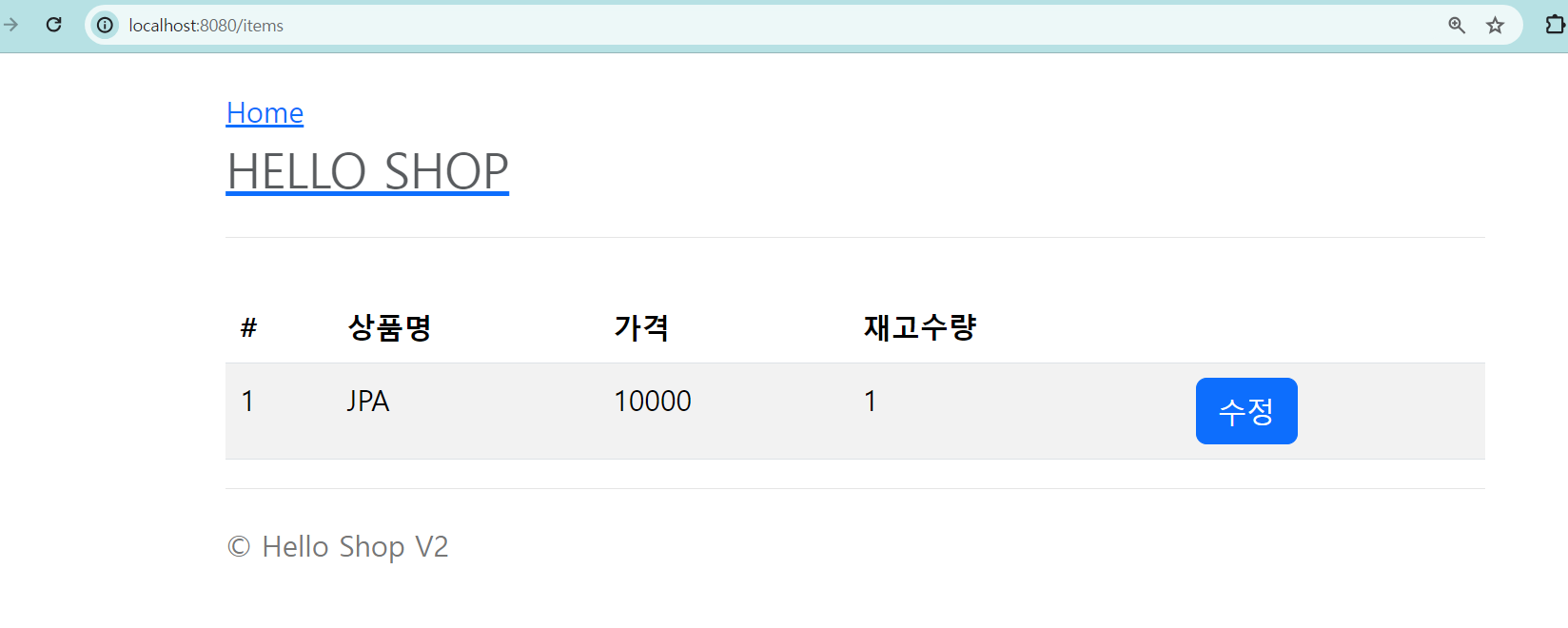
상품 수정
@GetMapping("/items/{itemId}/edit")
public String updateItemForm(@PathVariable("itemId") Long itemId, Model model) {
Book item = (Book) itemService.findOne(itemId);
BookForm form = new BookForm();
form.setId(item.getId());
form.setAuthor(item.getAuthor());
form.setIsbn(item.getIsbn());
form.setName(item.getName());
form.setPrice(item.getPrice());
form.setStockQuantity(item.getStockQuantity());
model.addAttribute("form", form);
return "items/updateItemForm";
}
@PostMapping("/items/{itemId}/edit")
public String updateItem(@ModelAttribute("form")BookForm form, @PathVariable("itemId") Long itemId) {
Book book = new Book();
book.setId(form.getId());
book.setAuthor(form.getAuthor());
book.setName(form.getName());
book.setPrice(form.getPrice());
book.setIsbn(form.getIsbn());
book.setIsbn(form.getIsbn());
itemService.saveItem(book);
return "redirect:/items";
}<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head th:replace="fragments/header :: header" />
<body>
<div class="container">
<div th:replace="fragments/bodyHeader :: bodyHeader"/>
<form th:object="${form}" method="post">
<!-- id -->
<input type="hidden" th:field="*{id}" />
<div class="form-group">
<label th:for="name">상품명</label>
<input type="text" th:field="*{name}" class="form-control"
placeholder="이름을 입력하세요" />
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label th:for="price">가격</label>
<input type="number" th:field="*{price}" class="form-control"
placeholder="가격을 입력하세요" />
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label th:for="stockQuantity">수량</label>
<input type="number" th:field="*{stockQuantity}" class="formcontrol" placeholder="수량을 입력하세요" />
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label th:for="author">저자</label>
<input type="text" th:field="*{author}" class="form-control"
placeholder="저자를 입력하세요" />
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label th:for="isbn">ISBN</label>
<input type="text" th:field="*{isbn}" class="form-control"
placeholder="ISBN을 입력하세요" />
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</form>
<div th:replace="fragments/footer :: footer" />
</div> <!-- /container -->
</body>
</html>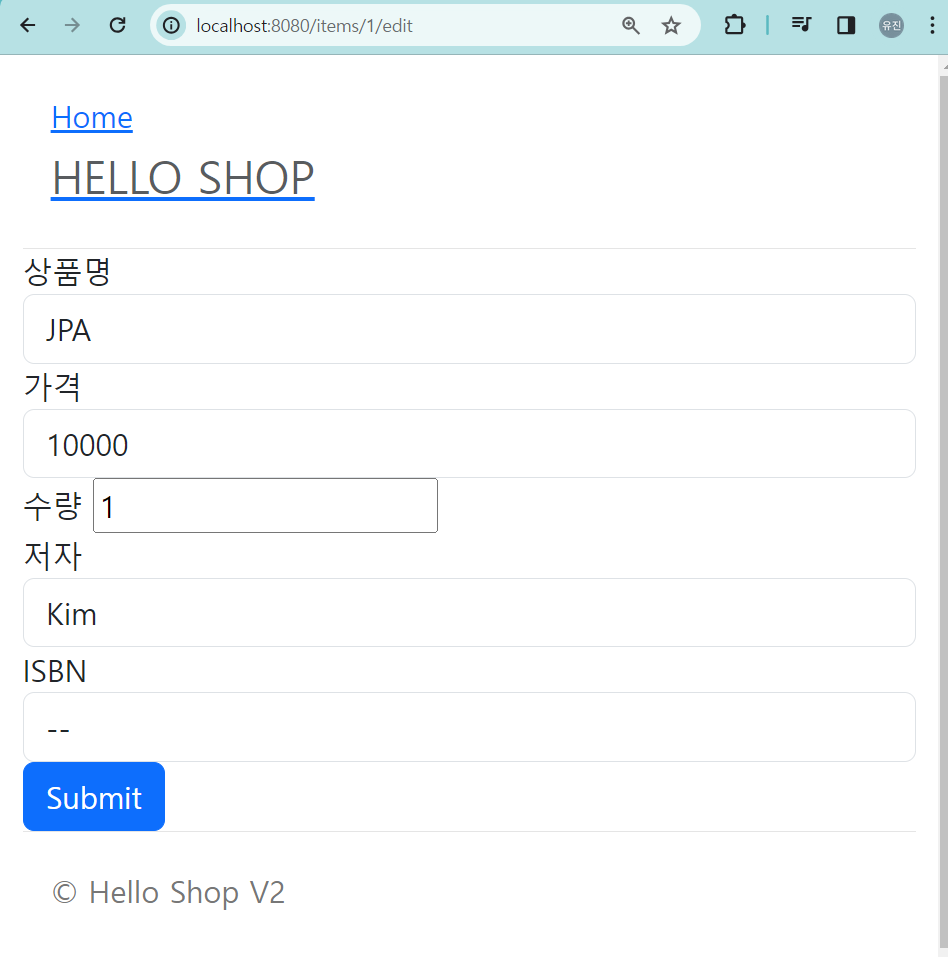
⭐ 변경 감지와 병합(merge)
정말 중요한 내용이니 꼭! 완벽하게 이해해야 한다.
-
준영속 엔티티?
- JPA의 영속성 컨텍스트가 더는 관리하지 않는 엔티티를 말한다.
@PostMapping("/items/{itemId}/edit") public String updateItem(@ModelAttribute("form")BookForm form, @PathVariable("itemId") Long itemId) { Book book = new Book(); book.setId(form.getId()); book.setAuthor(form.getAuthor()); book.setName(form.getName()); book.setPrice(form.getPrice()); book.setIsbn(form.getIsbn()); book.setIsbn(form.getIsbn()); itemService.saveItem(book); return "redirect:/items"; }-
(여기서는 itemService.saveItem(book) 에서 수정을 시도하는 Book 객체다. Book 객체는 이미 DB에 한번 저장되어서 식별자가 존재한다. 이렇게 임의로 만들어낸 엔티티도 기존 식별자를 가지고 있으면, 준영속 엔티티로 볼 수 있다.)
-
JPA가 관리하는 영속 상태 엔티티는 변경 감지 (dirty checking)가 일어난다. 뭐가 변경되는지 JPA가 다 감지한다. 그래서 트랜잭션 커밋 시점에 변경될 것은 바꿔치기를 해준다.(UPDATE 쿼리 DB에 날림)
-
하지만 위의 Book 객체는 내가 new 로 만든 객체이기 때문에, 기본적으로 JPA가 관리하지 않는다. 트랜잭션이 있다고 하더라도 JPA가 관리하지 않기 때문에, 해당 객체를 변경하더라도 JPA가 해당 객체를 업데이트할 근거 자체가 없다.
❓ 그럼 이런 준영속 상태의 엔티티는 도대체 어떻게 데이터를 변경할 수 있을까?
-
준영속 엔티티를 수정하는 2가지 방법
-
✅ 변경 감지 기능 사용 (dirty checking) - 더 나은 방법이다 !
-
✅ 병합 (merge) 사용
-
변경 감지 기능 사용
ItemService 클래스
@Transactional void update(Item itemParam) { //itemParam: 파리미터로 넘어온 준영속 상태의 엔티티 Item findItem = em.find(Item.class, itemParam.getId()); //같은 엔티티를 조회한다. findItem.setPrice(itemParam.getPrice()); //데이터를 수정한다. }- 영속성 컨텍스트에서 엔티티를 다시 조회한 후에 데이터를 수정하는 방법이다.
- 트랜잭션 안에서 엔티티를 다시 조회, 변경할 값 선택 ➡ 트랜잭션 커밋 시점에 변경 감지(Dirty Checking)이 동작해서 데이터베이스에 UPDATE SQL 실행
-
-
병합 사용
병합은 준영속 상태의 엔티티를 영속 상태로 변경할 때 사용하는 기능이다.
단순하게 설명하면, 변경 감지 기능을 사용하는 코드와 똑같은 코드가 실행되는 것이다.
영속성 컨텍스트에서 itemId로 DB에서 찾아서 해당 item을 찾는다. em.merge(item)에서 인자로 넘긴 item 의 데이터로 DB에서 찾아온 item의 모든 데이터를 다 바꿔치기 한다. 따라서 트랜잭션 커밋 시점에 변경 내용이 다 반영이 된다. 한마디로 내가 변경 감지 기능을 사용한 코드의 내용을 JPA가 em.merge(item) 이 한 줄로 실행해주는 것이다.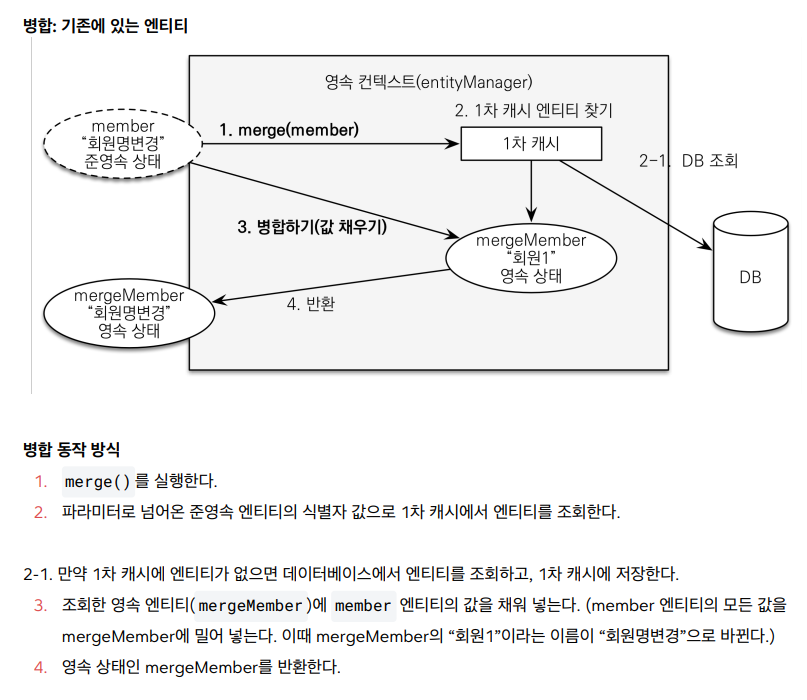
병합시 동작 방식을 간단히 정리
1. 준영속 엔티티의 식별자 값으로 영속 엔티티를 조회한다.
2. 영속 엔티티의 값을 준영속 엔티티의 값으로 모두 교체한다.(병합한다.)
3. 트랜잭션 커밋 시점에 변경 감지 기능이 동작해서 데이터베이스에 UPDATE SQL이 실행
❗ 주의: 변경 감지 기능을 사용하면 원하는 속성만 선택해서 변경할 수 있지만, 병합을 사용하면 모든 속성이 변경된
다. 병합시 값이 없으면 null 로 업데이트 할 위험도 있다. (병합은 모든 필드를 교체한다.) -> 따라서 가급적 merger를 사용하지 말아야 한다!!
참고: 실무에서는 보통 업데이트 기능이 매우 제한적이다. 그런데 병합은 모든 필드를 변경해버리고, 데이터가 없으면 null 로 업데이트 해버린다. 병합을 사용하면서 이 문제를 해결하려면, 변경 폼 화면에서 모든 데이터를 항상 유지해야 한다. 실무에서는 보통 변경가능한 데이터만 노출하기 때문에, 병합을 사용하는 것이 오히려 번거롭다.
-
💖 가장 좋은 해결 방법
엔티티를 변경할 때는 항상 변경 감지를 사용하세요-
컨트롤러에서 어설프게 엔티티를 생성하지 마세요.
-
트랜잭션이 있는 서비스 계층에 식별자( id )와 변경할 데이터를 명확하게 전달하세요.(파라미터 or dto)
-
트랜잭션이 있는 서비스 계층에서 영속 상태의 엔티티를 조회하고, 엔티티의 데이터를 직접 변경하세요.
-
트랜잭션 커밋 시점에 변경 감지가 실행됩니다.
@Controller @RequiredArgsConstructor public class ItemController { private final ItemService itemService; /** * 상품 수정, 권장 코드 */ @PostMapping(value = "/items/{itemId}/edit") public String updateItem(@PathVariable Long itemId, @ModelAttribute("form") BookForm form) { itemService.updateItem(itemId, form.getName(), form.getPrice(), form.getStockQuantity()); return "redirect:/items"; }package jpabook.jpashop.service; @Service @RequiredArgsConstructor public class ItemService { private final ItemRepository itemRepository; /** * 영속성 컨텍스트가 자동 변경 */ @Transactional public void updateItem(Long id, String name, int price, int stockQuantity) { Item item = itemRepository.findOne(id); item.setName(name); item.setPrice(price); item.setStockQuantity(stockQuantity); } }
-
상품 주문
package jpabook.jpashop.domain.controller;
import jpabook.jpashop.domain.Member;
import jpabook.jpashop.domain.item.Item;
import jpabook.jpashop.service.ItemService;
import jpabook.jpashop.service.MemberService;
import jpabook.jpashop.service.OrderService;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import java.util.List;
@Controller
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class OrderController {
private final OrderService orderService;
private final MemberService memberService;
private final ItemService itemService;
@GetMapping("/order")
public String createForm(Model model) {
List<Member> members = memberService.findMembers();
List<Item> items = itemService.findItems();
model.addAttribute("members", members);
model.addAttribute("items", items);
return "order/orderForm";
}
@PostMapping("/order")
public String order(@RequestParam("memberId") Long memberId,
@RequestParam("itemId") Long itemId,
@RequestParam("count") int count) {
orderService.order(memberId, itemId, count);
return "redirect:/orders";
}
}
- controller에서는 식별자만 넘기고, service 계층에서 넘겨받은 식별자를 통해 엔티티를 조회하고 사용하는 것이 훨씬 깔끔하다. service 계층에서는 transaction안에서 진행되기 때문에 엔티티들이 영속 상태로 흘러감. 따라서 엔티티의 상태를 변경할 수 있음.
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head th:replace="fragments/header :: header" />
<body>
<div class="container">
<div th:replace="fragments/bodyHeader :: bodyHeader"/>
<form role="form" action="/order" method="post">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="member">주문회원</label>
<select name="memberId" id="member" class="form-control">
<option value="">회원선택</option>
<option th:each="member : ${members}"
th:value="${member.id}"
th:text="${member.name}" />
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="item">상품명</label>
<select name="itemId" id="item" class="form-control">
<option value="">상품선택</option>
<option th:each="item : ${items}"
th:value="${item.id}"
th:text="${item.name}" />
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="count">주문수량</label>
<input type="number" name="count" class="form-control" id="count"
placeholder="주문 수량을 입력하세요">
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</form>
<br/>
<div th:replace="fragments/footer :: footer" />
</div> <!-- /container -->
</body>
</html>주문 목록 검색, 취소
@GetMapping("/orders")
public String orderList(@ModelAttribute("orderSearch")OrderSearch orderSearch, Model model) {
List<Order> orders = orderService.findOrders(orderSearch);
model.addAttribute("orders", orders);
return "order/orderList";
}
@PostMapping("/orders/{orderId}/cancel")
public String cancelOrder(@PathVariable("orderId") Long orderId) {
orderService.cancelOrder(orderId);
return "redirect:/orders";
}<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head th:replace="fragments/header :: header"/>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div th:replace="fragments/bodyHeader :: bodyHeader"/>
<div>
<div>
<form th:object="${orderSearch}" class="form-inline">
<div class="form-group mb-2">
<input type="text" th:field="*{memberName}" class="formcontrol" placeholder="회원명"/>
</div>
<div class="form-group mx-sm-1 mb-2">
<select th:field="*{orderStatus}" class="form-control">
<option value="">주문상태</option>
<option th:each=
"status : ${T(jpabook.jpashop.domain.OrderStatus).values()}"
th:value="${status}"
th:text="${status}">option
</option>
</select>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary mb-2">검색</button>
</form>
</div>
<table class="table table-striped">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>#</th>
<th>회원명</th>
<th>대표상품 이름</th>
<th>대표상품 주문가격</th>
<th>대표상품 주문수량</th>
<th>상태</th>
<th>일시</th>
<th></th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="item : ${orders}">
<td th:text="${item.id}"></td>
<td th:text="${item.member.name}"></td>
<td th:text="${item.orderItems[0].item.name}"></td>
<td th:text="${item.orderItems[0].orderPrice}"></td>
<td th:text="${item.orderItems[0].count}"></td>
<td th:text="${item.status}"></td>
<td th:text="${item.orderDate}"></td>
<td>
<a th:if="${item.status.name() == 'ORDER'}" href="#"
th:href="'javascript:cancel('+${item.id}+')'"
class="btn btn-danger">CANCEL</a>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
<div th:replace="fragments/footer :: footer"/>
</div> <!-- /container -->
</body>
<script>
function cancel(id) {
var form = document.createElement("form");
form.setAttribute("method", "post");
form.setAttribute("action", "/orders/" + id + "/cancel");
document.body.appendChild(form);
form.submit();
}
</script>
</html>