Cloud Computing: Formal Definition
최소한의 관리 노력이나 서비스 공급자와의 상호작용없이 신속하게 provisioned(제공), released(해제)할수있는 구성가능한 컴퓨팅 리소스, 컴퓨터를 utility로 사용하는 것
– 제 3자 또는 내부 조직에 outsource
Essential characteristics:
– On-demand self service : 주문형 셀프 서비스
– Broad network access : 광범위한 네트워크 접속
– Resource pooling : 리소스 풀링
– Rapid elasticity : 빠른 탄력성
– Measured service : 측정서비스
Problems of on-premise
-
load가 다양해서 dimension이 어려움
해결방안
→ Provisioning for the peak load (최대 부하 기준)
: over provisioning → waste of money. inefficient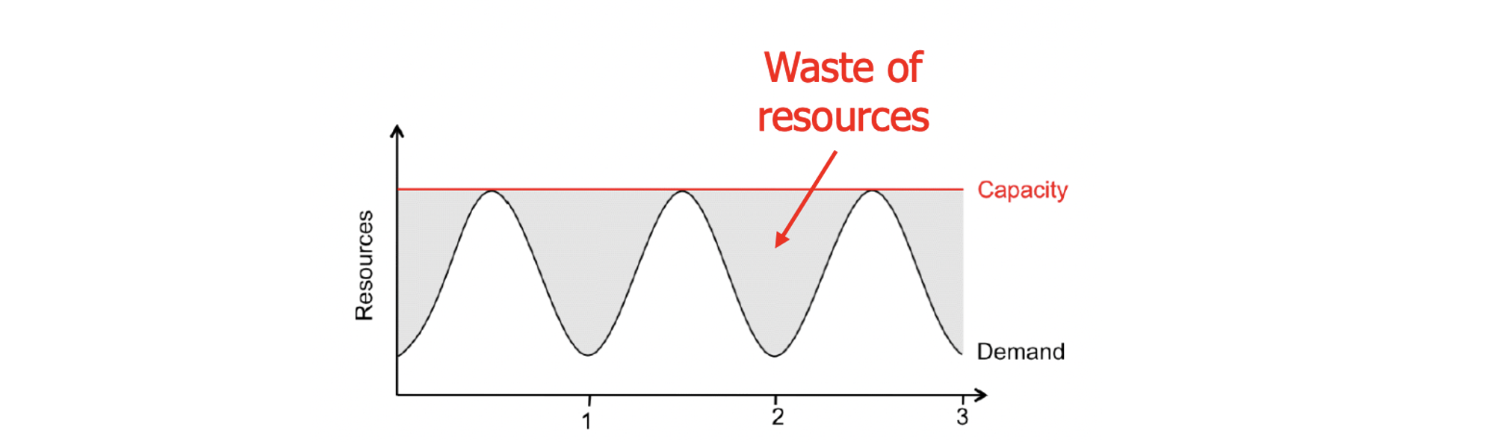
→ Provisioning below the peak (최대 load 미만)
: under provisioning → 사용자 떠남 / over provisioning
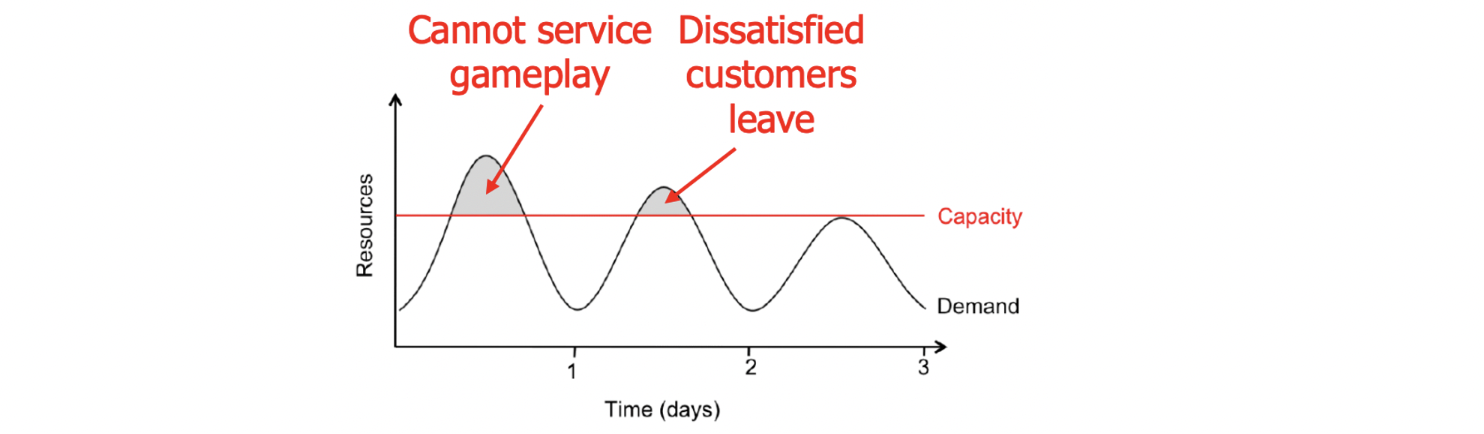 correctly capture expected load가 어려움
correctly capture expected load가 어려움 -
Building, maintaining에 많은 비용이 든다
하드웨어에 많은 돈 투자
ex small server cluster가 $100,000이상, Microsoft는 single datacenter에 $499 million 투자전문 지식(expertise)이 필요
cluster of servers 계획, 설계 번거로움, special software 필요하기도유지보수(maintenance)가 필요
결함있는 hw 교체, sw업그레이드, 사용자계정 유지관리 등 -
Scaling up,Scaling down 이 어려움
Scaling up: CPU나 메모리 upgrade : 한 server의 capacity를 UP
새 server주문해서 설치하고 기존 클러스터와 통합해야 함, 시간이 많이 필요함 (몇 주 소요)
major redesign이 필요하기도
ex 100servers i7(100W/server)→i9(120W/server)으로 업그레이드. i9이 consume more power
100,000W → 120,000W : power limitation이 100000W⇒ i9설치 불가 or Room을 바꿔야함
: 업그레이드를 위해 전력, 빌딩까지 바꿔야 할수도 있다. 큰 변화. 어려움Scaling down: CPU나 메모리 downgrade
unnecessary hardware으로 할수있는게 없음
idle state에서도 최대 전력의 약 60%를 소비
Many fixed costsScaling out : server개수를 늘려 확장.
(각각 server의 amount는 줄임. 전체 capacity는 같음.) computing resource증가.
Benefits of Cloud
investments, proportional(비례적인) cost 절감
– hw, sw 구입 소유 비용과 같은 IT 초기 투자(up-front) 감소
Pay-as-you-go (usage-based) pricing
– 종량제(사용기준) 가격 책정
– 분당, 바이트당 요금 부과
– 최소요금(minimum) 또는 선불 요금(up-front fee) 없음
– app의 활용도가 가변적일때 유용
확장성(scalability) 향상
– 요구가 있을 때 IT 리소스를 즉각적이고 동적으로 할당
– user늘어나면 capability of IT resources 즉시 향상
Economies of scale
– 시스템을 규모에 맞게 구입, 전원공급 및 관리해서 per-unit costs 절감
– Cheaper usage fee for cloud customers
가용성(availability) 및 신뢰성(reliability) 향상
– 가용성 향상된 IT resource를 장기간 접속 가능 (accessible for longer periods of time)
– 신뢰성 향상된 IT resource는 예외 조건(exception conditions)을 효과적으로 방지, 복구
– Cloud providers는 높은 수준의 가용성 보장하는 탄력적인(resilient) IT 리소스 제공
– 클라우드 환경의 modular architecture는 안정성 높이는 extensive failover(장애 극복 기능) support 제공

Casestudy 사례 연구
-
Animoto: 자신의 사진/음악으로 비디오 생성 가능
사진을 자동 편집하여 음악에 맞춰 정렬
Built using Amazon EC2+S3+SQS
Released a Facebook app in mid-April 2008
More than 750,000 people signed up within 3 days
EC2 usage: 50 machines → 3,500 machines (x70 scalability!)
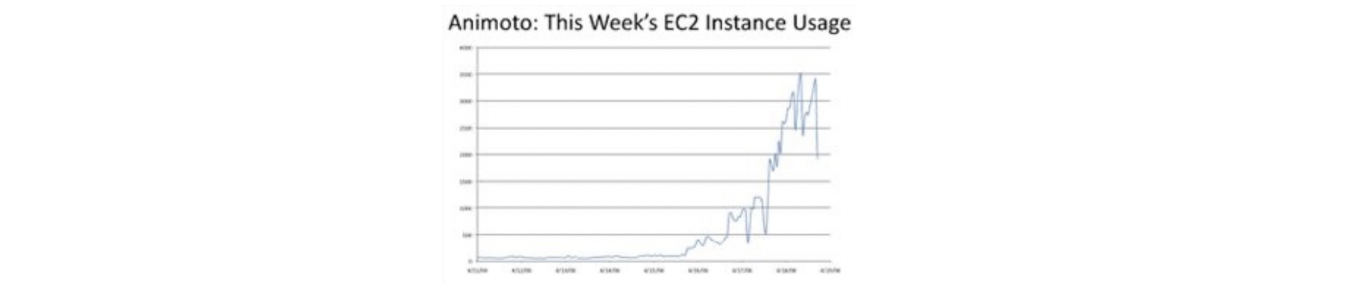
⇒ on-premise server을 쓰는 것은 불가능한 일
-
March 19, 2008: 힐러리 클린턴 백악관 공식 일정 공개
17,481페이지 분량의 검색 불가, 저품질 PDF
journalists에게는 매우 흥미롭지만 evaluate에 수백 시간의 인력이 필요
Peter Harkins, Senior Engineer at The Washington Post: 동일한 뉴스 주기 내에서 이상적으로 데이터를 보다 신속하게 이용할 수 있도록 할 수 있습니까?
다양한 OCR(Optical Character Recognition) 프로그램 테스트, 소요 속도 예상
200개의 EC2 인스턴스 시작, 1,407시간의 VM 시간(144.62달러)을 사용하여 9시간 내에 프로젝트 완료
결과: 출시 후 26시간 만에 웹에서 확인 가능
Risks and Challenges of Cloud
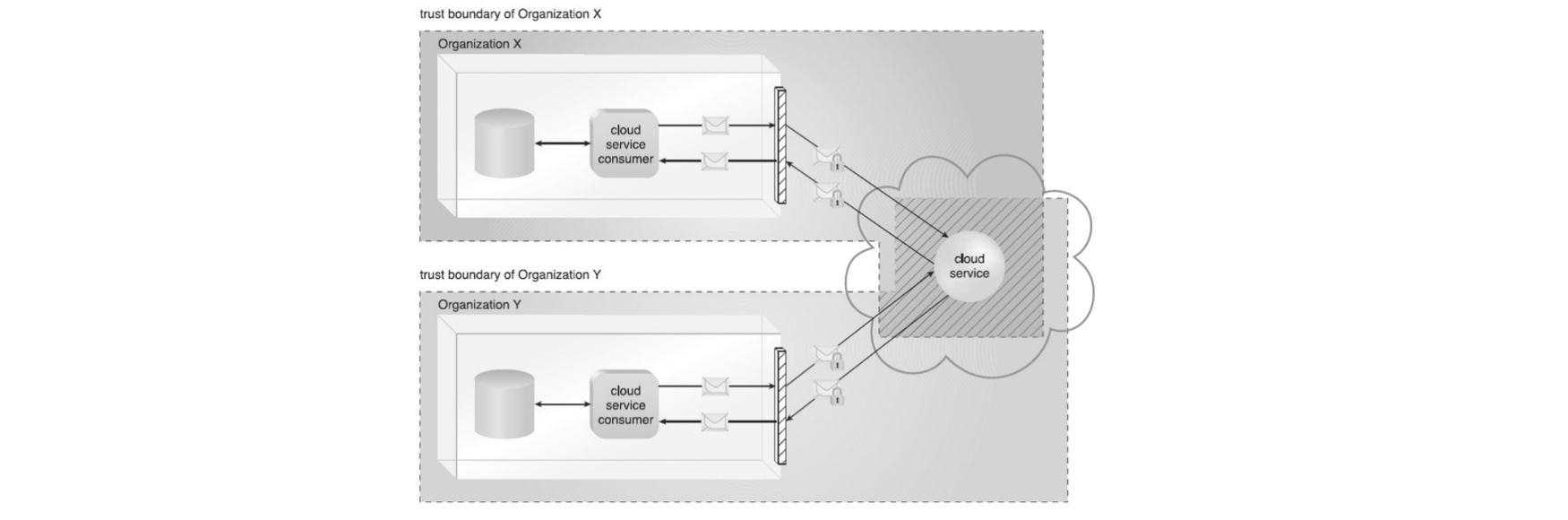
- security vulnerabilities(보안 취약점) 증가
- 클라우드 소비자들의 privileged(권한있는) access: 본인의 data를 클라우드로 보냄
- Malicious cloud consumers에게 IT 리소스를 공격하고 비즈니스 데이터를 훔치거나 손상할 수 있는 기회가 많음
- operational governance control(사용가능한 관리 규제) 감소
- on-premise IT resources보다 낮은 level의 governance control
- choice가 적음
ex 클라우드가 SKT쓰면 나도 SKT써야함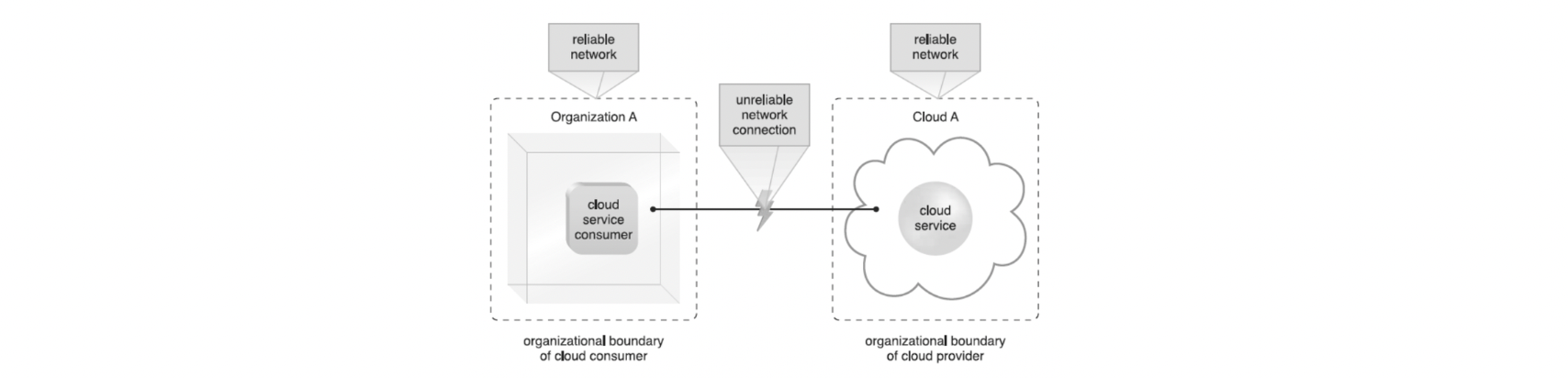
- cloud providers사이의 제한된 이동성(portability)
- Public clouds는 various extents에서 proprietary(독점적)
- 한 클라우드 공급자에서 다른 클라우드 공급자로 이동하는 것이 어려움
- Multi-regional compliance and legal issues
- ex 게임이 미국과 한국 연령대 모두 따라야 하는경우
- data and privacy: 지역마다 데이터 및 개인정보 보호 규정이 다름
Cloud infrastructure
Cloud infrastructure는 고객에게 cloud services를 제공하는데 필요한 모든 hardware and software components로 구성됨
주요 물리적 구성 요소: servers, networking equipment, storages
cloud infrastructures는 servers, networking equipment, storages가 많은 datacenter 형태로 구축됨
Server
클라이언트에게 서비스를 제공하는 컴퓨터
신뢰성(reliability)을 확보하고 많은 요청(requests)을 처리할 수 있도록 설계됨
Multi-core CPU: 1개 또는 2개의 소켓(=CPU)과 안정성 기능(reliability features)
Main memory with ECC(ErrorCorrectionCode)
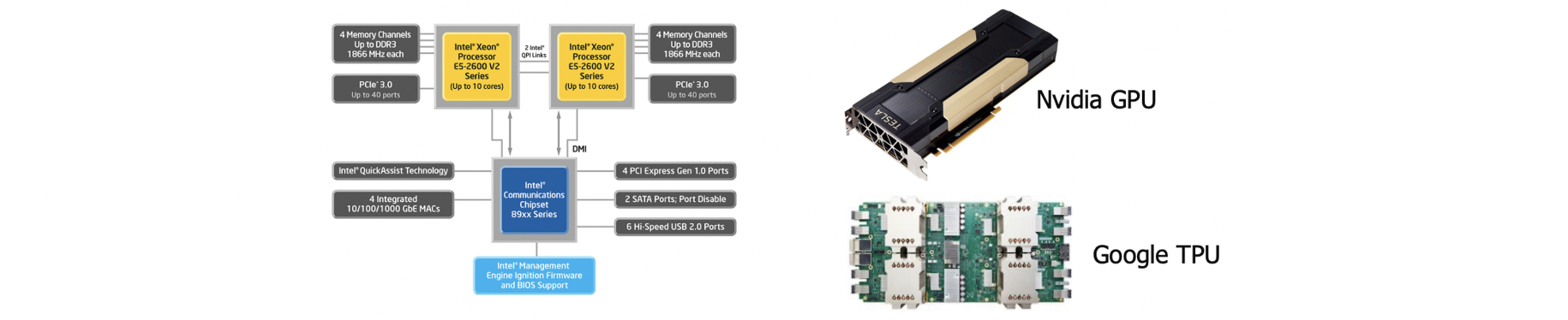
What's new recently?
GPUs(그래픽application, Ai training), FPGAs(programming으로 build socket할수있는 custom device), custom accelerators for AI
Google TPU: 구글이 만든 ai computer
Blade Server
Organizations는 computer infrastructure를 위한 floor space를 절약하려 함
large-scale installations (use compact servers)는 "blades"라 부름
이점: Floor space, Manageability, Scalability,Power and cooling

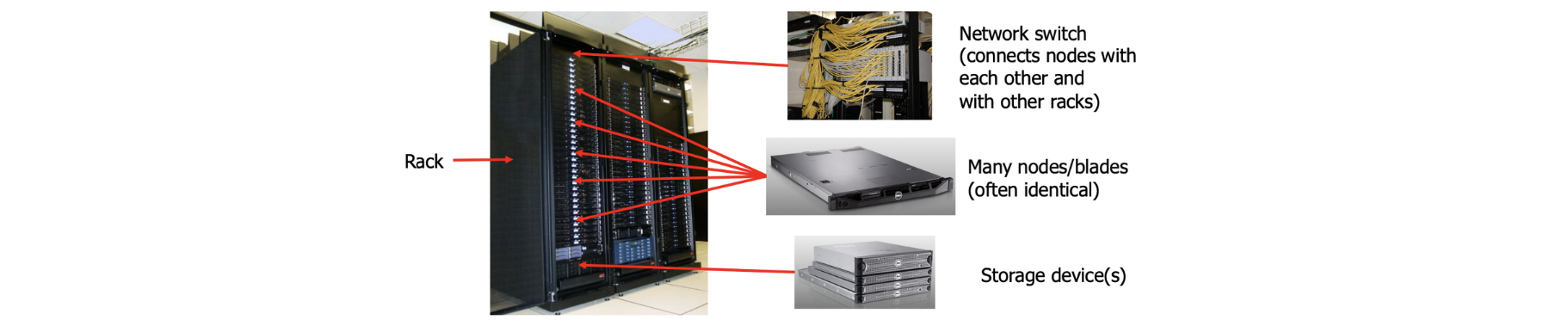
Racks
Blade servers를 racks에 배치
Blade servers는 rack units에 맞게 modular fashion으로 설계됨
랙 하나에 최대 42대의 1U 블레이드 서버 수용 가능 (4U라면 최대 10개)

Heterogeneous Servers
모든 서버가 동일하지 않음(not homogeneous)
– 서버가 다양한 internal hardware configurations을 가질 수 있다
major app classes에 최적화된 구성(configurations)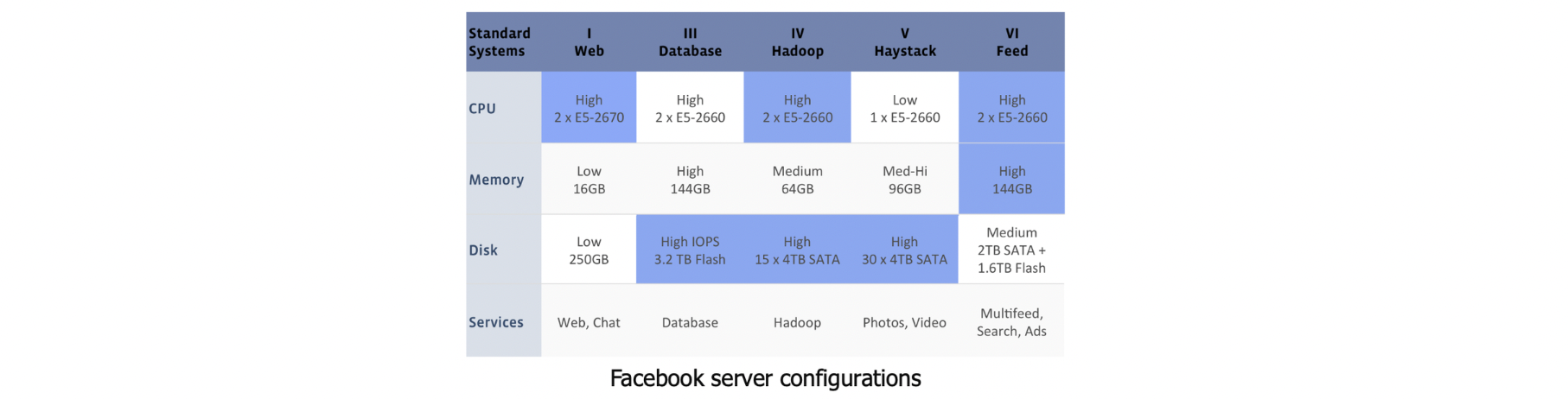
Networking
cloud resources는 인터넷을 통해 사용자에게 제공
third-party service(타사 서비스) providers를 위해 networking infrastructure를 구축,유지할 필요가 있음
essential networking equipment: physical cables, switches, routers, wireless access points

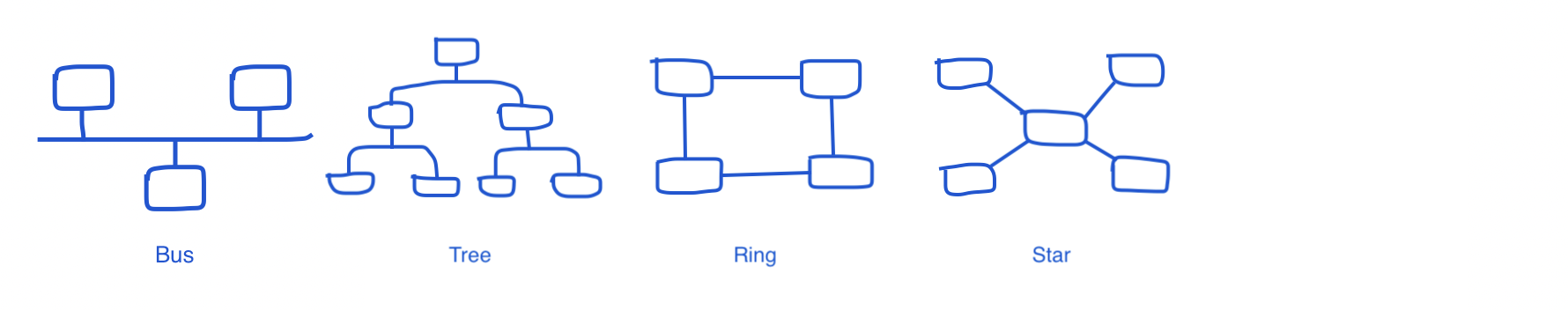
Networking Topologies(위상)
장치(nodes,servers ..)들이 서로 연결된 physical arrangement:
Bus
– Single central cable로 여러 장치를 연결
Tree
– root node 존재, 다른 모든 노드가 연결되어 계층을 구성
Ring
– closed loop에 다수의 장치가 연결
Star
– 모든 컴퓨터가 허브(hub)라는 중앙 장치에 연결
Storage
기본 저장 장치
– Disk trays(head,magnetic으로 접근), SSD & NVM flash
Storage array
– 대용량의 스토리지를 가진 simply powerful computer
– arrays는 central management system하에서 최대 petabytes of data까지 저장할 수 있는 series of drives를 하나의 시스템으로 결합
– storage arrays는 dedicated network를 통해 여러 server에 storage를 제공할 수 있도록 구성됨

Cluster 크기 고민
많은 Rack이 cluster를 형성
– interconnection이 밀접한 유사한 machines이 많음
Datacenter
Large server, storage farms이 함께 연결됨
– 각각 100 cores를 가진 50-200K racks
– 소비전력 10-100MW
– Several zettabytes (10^21) of storage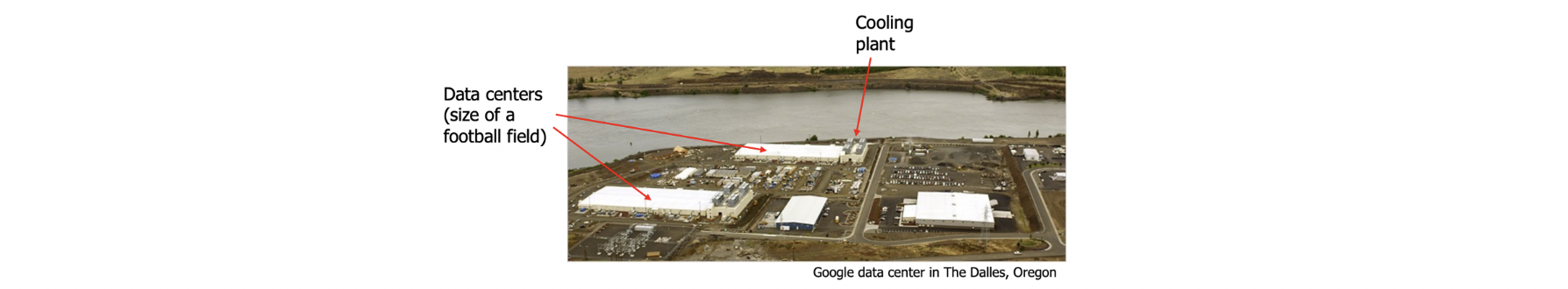
Inside a Datacenter
Giant warehouse(창고) filled with: Racks of servers, Network switches,Storage arrays
Air conditioning (Cooling)
Redundant(여분의) power: UPS/Generators, Multiple power feeds (다중 전원 공급 장치)
Fire protection
Physical security
Monitoring systems
Global Datacenter Distribution
데이터 센터는 전 세계에 분산
ex Google 데이터 센터 위치(inferred)
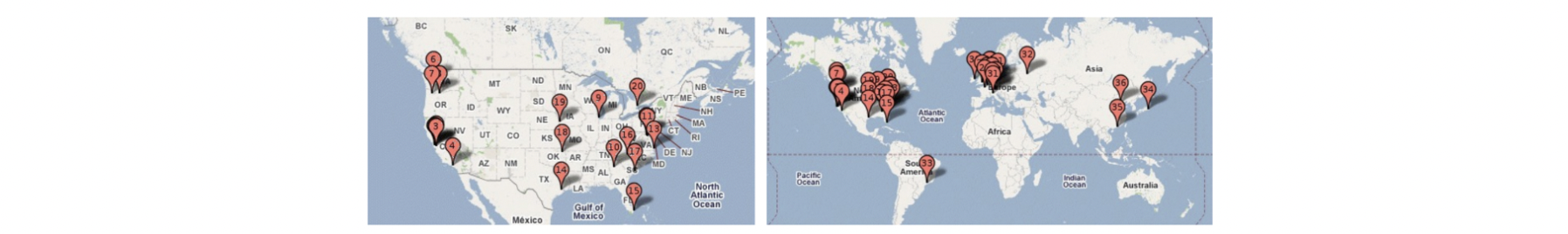
Why?
– 물리적으로 사용자와 가까워야함
– cheaper resources (countryside에 설치)
– failures(장애)로부터 보호 (ex Japan datacenter 무너지면 바로 Korea연결)
Power and Cooling(크기)
clusters에 많은 전력이 필요
ex 서버당 140와트, Rack with 32 servers → 4.5kW ⇒ heat(열)로 변환
Large clusters need massive cooling
ex 랙 1개 - 4.5kW: 약 3 space heaters
많은 energy소비

On-Site Power Generation for Datacenters
Alabama의 Google's datacenter는 전용 발전소(dedicated power plant)를 가짐
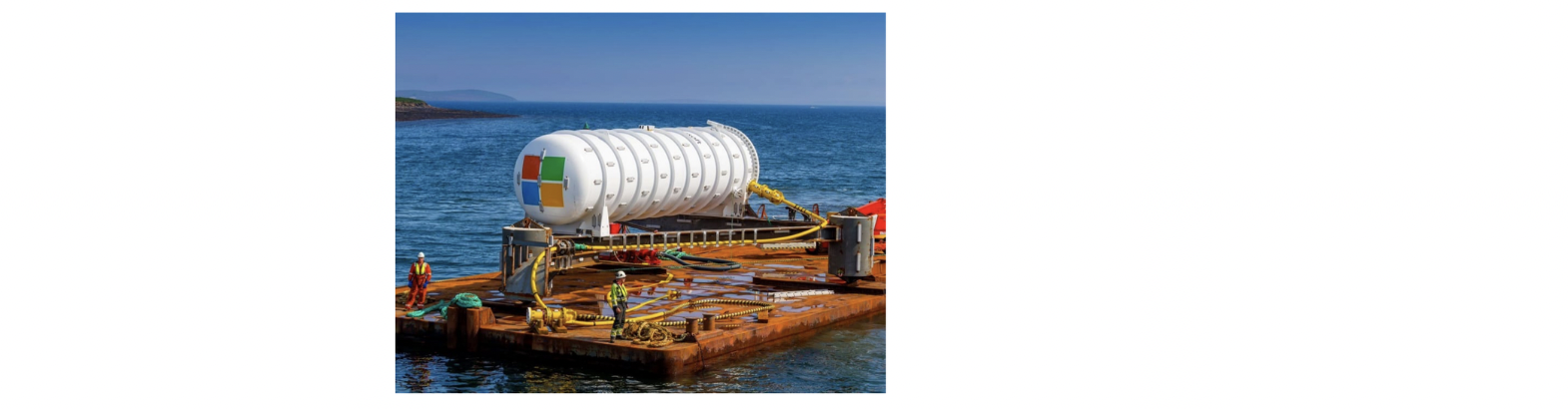
Underwater Datacenter
Microsoft's underwater datacenter(실험용)
– 연안 인구(coastal populations)에 대한 quick cloud services
– For cooling
