무한 스크롤을 구현할때 가장 아래 요소를 관찰하는 방법이다.(리플로우가 안일어 나서 성능이 좋다.)
처음에 관찰자를 만들자 교차로 관찰자를 만들고 2개의 인수로 콜백과 옵션이 필요하다.
const observer = new IntersectionObserver(function (entries, observer) {
entries.forEach((entry) => {
console.log(entry);
});
}, options);그리고 무엇을 관찰하고 싶을 거를 설정하자.
// 뭘관찰하고 싶은지
observer.observe($container);
console에 찍히는것은 $container의 전체 내용이다.
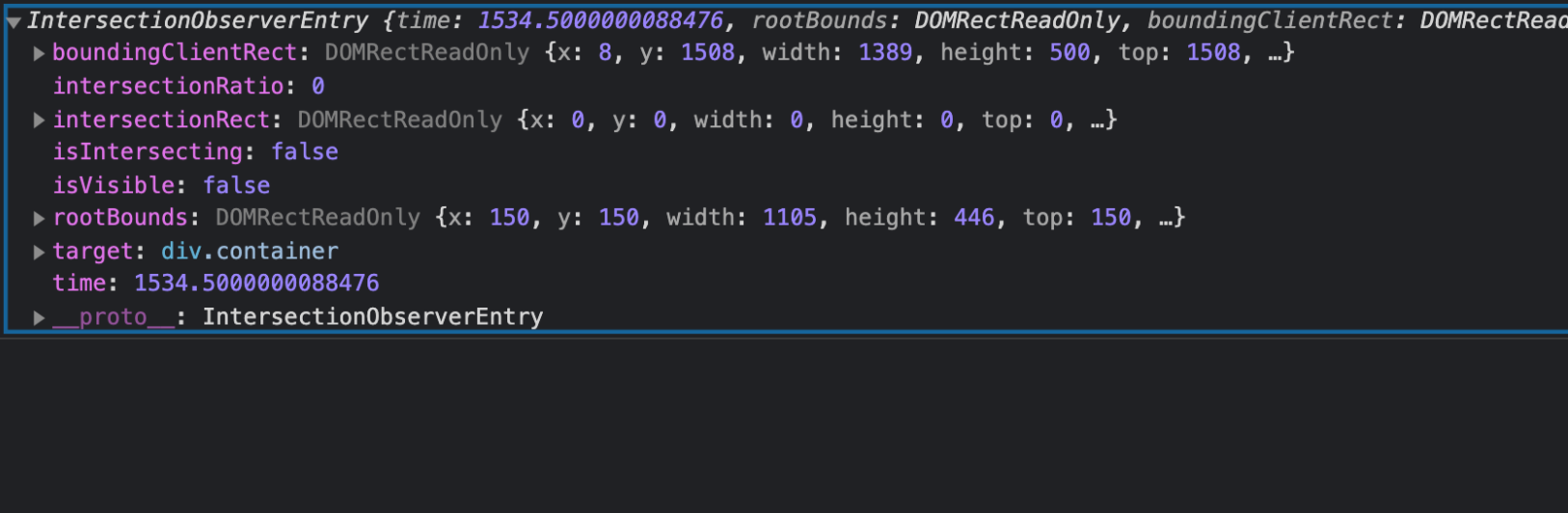
이 안에 isIntersecting은 교차 했는지 않했는지 알수 있다.
이제 option을 설정하자.
const options = {
root: null, // 이것은 view 포트이다.
threshold: 0, // 임계값이라고 한다.
rootMargin: '-150px', // css 여백을 설정하면
};rootMargin은 처음에 이해가 안됐는데 $container 공간 선에 도달할때 마진으로 뷰포트에 들어가면 언제인지 알 수 있다.

이 지점에서 교차 되었다고 나올 것이다.
threshold는 임계값이라고 하는데 실제로 페이지에 얼마나 많이 있는지 설정하는 것이다.
이것이 100%가 페이지에 있어야 하지만 0에 있으면 작은 조각이 들어가자 마자 0.25로 변경한다.
0.25%로 설정하면 25%가 보이는 것을 알고 있다.
마진값이 -150px 이여도 임계값이 도달하지 않았기 때문에 발사 되지 않는다.
다수의 요소를 관찰해 보자.
Container 를 3개정도 만들고
const $container1 = document.querySelectorAll('.container1');
observer.observe($container1);이렇게 해보자 그러면 에러가 발생할 것이다. 이게 작동하지 않은 이유는 노드 목록이 있으면 실행할 수 없다 전체에 대해
한명의 관찰자를 가질 수 없기 때문이다. 그래서 순회하면서 달아줘야한다.
$container1.forEach((section) => {
observer.observe(section);
});이제 콘솔로 말고 entry.target으로 보자.
const observer = new IntersectionObserver(function (entries, observer) {
entries.forEach((entry) => {
entry.target.classList.toggle('inverse');
});
}, options);css
body {
height: 3000px;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: flex-end;
}
.container {
width: 100%;
height: 500px;
background-color: red;
}
.container1 {
width: 100%;
height: 500px;
background-color: blue;
}
.container.inverse {
background-color: #eee;
}
.container1.inverse {
background-color: #eee;
}교차 돼면 하얀색으로 바꿔보자.
const observer = new IntersectionObserver(function (entries, observer) {
entries.forEach((entry) => {
console.log(entry.isIntersecting);
if (!entry.isIntersecting) {
entry.target.classList.remove('inverse');
return;
}
console.log(entry.target);
entry.target.classList.add('inverse');
});
}, options);전체 코드
const $container = document.querySelector('.container');
const $container1 = document.querySelectorAll('.container1');
const options = {
root: null, // 이것은 view 포트이다.
threshold: 0, // 임계값이라고 한다.
rootMargin: '-150px', // css 여백을 설정하면
};
// 1관찰자를 만들자
// 교차로 관찰자. .? 콜백함수가 필요하고 옵션이 필요하다,
const observer = new IntersectionObserver(function (entries, observer) {
entries.forEach((entry) => {
console.log(entry.isIntersecting);
if (!entry.isIntersecting) {
entry.target.classList.remove('inverse');
return;
}
console.log(entry.target);
entry.target.classList.add('inverse');
});
}, options);
// 뭘관찰하고 싶은지
// observer.observe($container);
$container1.forEach((section) => {
observer.observe(section);
});
// $container의 전체 내용을 알 수 있다.
// 이 안에서 inIntersecting은 교차 했는지 알 수 있다.
이러면 교차 되는 순간 색이 바뀌고 요소가 사라질때 원래 상태로 돌아간다.
이것을 이용해서 뷰 맨 아래에다 요소를 숨긴 후 그 요소가 교차하면 요소가 더 생긴다는지 무한 스크롤이 가능하다.
