예외(Exception) 계층
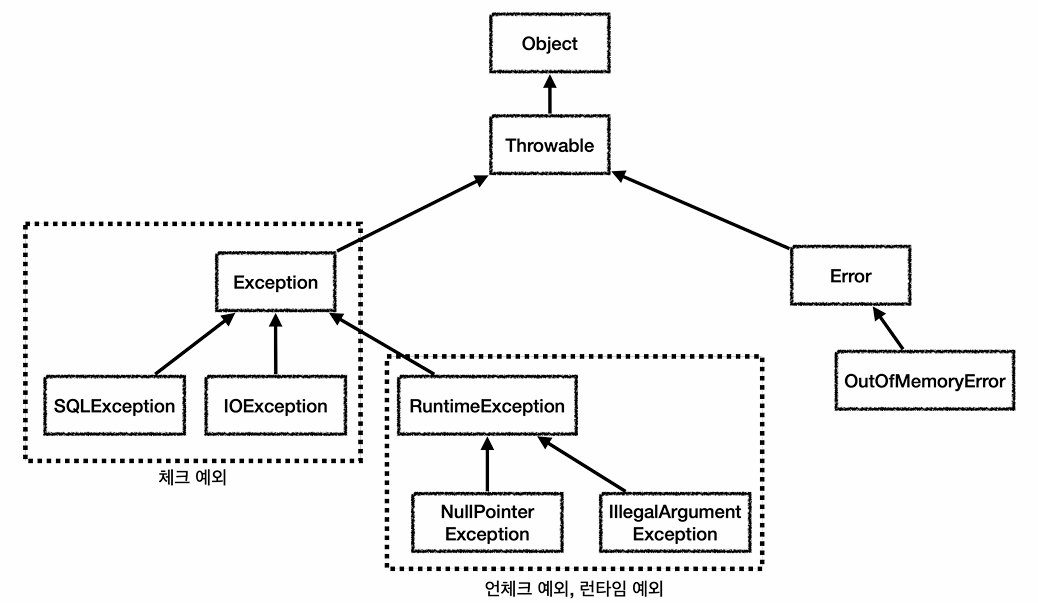
Object
- 예외도 객체임
- 모든 객체의 최상위 부모
Throwable
- 최상위 예외
- 상위 예외를 catch로 잡으면 하위 예외까지 잡기 때문에 애플리케이션에서 Throwable 예외를 잡으면 안됨 (Error 예외도 함께 잡을 수 있기 때문)
Error
- 메모리 부족이나 시스템 오류와 같이 애플리케이션에서 복구 불가능한 시스템 예외
- 애플리케이션 개발자는 이 예외를 잡으려고 해서는 안됨
Exception
- 애플리케이션 로직에서 사용할 수 있는 실질적인 최상위 예외
- RuntimeException을 제외하고 하위 예외까지 모두 컴파일러가 체크하는 체크 예외
RuntimeException
- 컴파일러가 체크하지 않는 언체크 예외
- 해당 예외와 그 하위 언체크 예외를 런타임 예외라고 부름
예외 기본 규칙
1. 예외는 잡아서 처리하거나 던져야 한다.
2. 예외를 잡거나 던진 때 지정한 예외 뿐만 아니라 해당 예외의 자식들도 함께 처리된다.
체크 예외 (Checked Exception)
- RuntimeException을 제외하고 Exception과 그 하위 예외는 모두 컴파일러가 체크하는 체크 예외
- 체크 예외는 잡아서 처리(try, catch)하거나, 밖으로 던지도록 선언(throws Exception)해야하고, 그렇지 않으면 컴파일 오류가 발생
Checked Exception 장단점
장점 : 개발자가 실수로 예외를 누락하지 않도록 컴파일러를 통해 문제를 잡아주는 훌륭한 안전 장치이다.
단점 : 개발자가 모든 체크 예외를 반드시 잡거나 던지도록 처리해야 하기 때문에, 너무 번거로운 일이 된다. 크게 신경쓰고 싶지 않은 예외까지 모두 챙겨야 한다.
public class CheckedAppTest {
@Test
void checked() {
Controller controller = new Controller();
assertThatThrownBy(() -> controller.request())
.isInstanceOf(Exception.class);
}
static class Controller {
Service service = new Service();
public void request() throws SQLException, ConnectException {
service.logic();
}
}
static class Service {
Repository repository = new Repository();
NetworkClient networkClient = new NetworkClient();
public void logic() throws SQLException, ConnectException {
repository.call();
networkClient.call();
}
}
static class NetworkClient {
public void call() throws ConnectException {
throw new ConnectException("연결 실패");
}
}
static class Repository {
public void call() throws SQLException {
throw new SQLException("ex");
}
}
}- 처리할 수 있는 체크 예외라면 서비스나 컨트롤러에서 처리하겠지만, 데이터베이스나 네트워크 통신과 같이 시스템 레벨에서 올라온 예외들은 대부분 복구가 불가능하다. 그리고 실무에서 발생하는 대부분의 예외들은 이런 시스템 예외들이다.
- 이런 경우에 체크 예외를 사용하면 아래에서 올라온 복구 불가능한 예외를 서비스, 컨트롤러 같은 각각의 클래스가 모두 알고 있어야 (throws SQLException, ConnectException) 한다. 그래서 불필요한 의존관계 문제가 발생 (SQLException은 JDBC 기술)하게 된다.
Unchecked Exceptioin를 통해 이러한 문제를 해결해보자.
언체크 예외 (Unchecked Exception)
- RuntimeException과 그 하위 예외는 언체크 예외로 분류
- 컴파일러가 예외를 체크하지 않는다는 뜻
- 예외를 던지는
throws를 선언하지 않고 생략할 수 있고, 이 경우 자동으로 예외를 던짐 - 비즈니스 로직상 너무 중요해서 의도적으로 예외를 던지는 경우를 제외하고 기본적으로 언체크 예외를 사용함
Unchecked Exception 장단점
장점 : 신경쓰고 싶지 않은 언체크 예외를 무시할 수 있다
단점 : 개발자가 실수로 예외를 누락할 수 있다.
public class UncheckedAppTest {
@Test
void unchecked() {
Controller controller = new Controller();
assertThatThrownBy(() -> controller.request())
.isInstanceOf(Exception.class);
}
static class Controller {
Service service = new Service();
public void request() {
service.logic();
}
}
static class Service {
Repository repository = new Repository();
NetworkClient networkClient = new NetworkClient();
public void logic() {
repository.call();
networkClient.call();
}
}
static class NetworkClient {
public void call() {
throw new RuntimeConnectException("연결 실패");
}
}
static class Repository {
public void call() {
try {
runSQL();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeSQLException(e);
}
}
public void runSQL() throws SQLException {
throw new SQLException("ex");
}
}
static class RuntimeConnectException extends RuntimeException {
public RuntimeConnectException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
static class RuntimeSQLException extends RuntimeException {
public RuntimeSQLException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
}
}- 리포지토리에서 체크 예외인
SQLException이 발생하면 런타임 예외인RuntimeSQLException으로 전환해서 (스택 트레이스와 관련) 예외를 던진다. - 체크 예외 처럼 예외를 강제로 의존하지 않아도 된다.
- 런타임 예외를 사용하면 서비스나 컨트롤러가 이런 복구 불가능한 예외를 신경쓰지 않아도 된다. 이렇게 복구 불가능한 예외는
Filter,Interceptor,서블릿 오류 페이지나ControllerAdvice를 통해 공통으로 처리하면 된다.
예외 포함과 스택 트레이스
예외를 전환할 때는 꼭 기존 예외를 포함해야 한다. 그렇지 않으면 스택 트레이스를 확인할 때 심각한 문제가 발생한다.
<기존 예외를 포함하는 경우>
static class Repository {
public void call() {
try {
runSQL();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeSQLException(e); //기존 예외(e) 포함
}
}
public void runSQL() throws SQLException {
throw new SQLException("ex");
}
}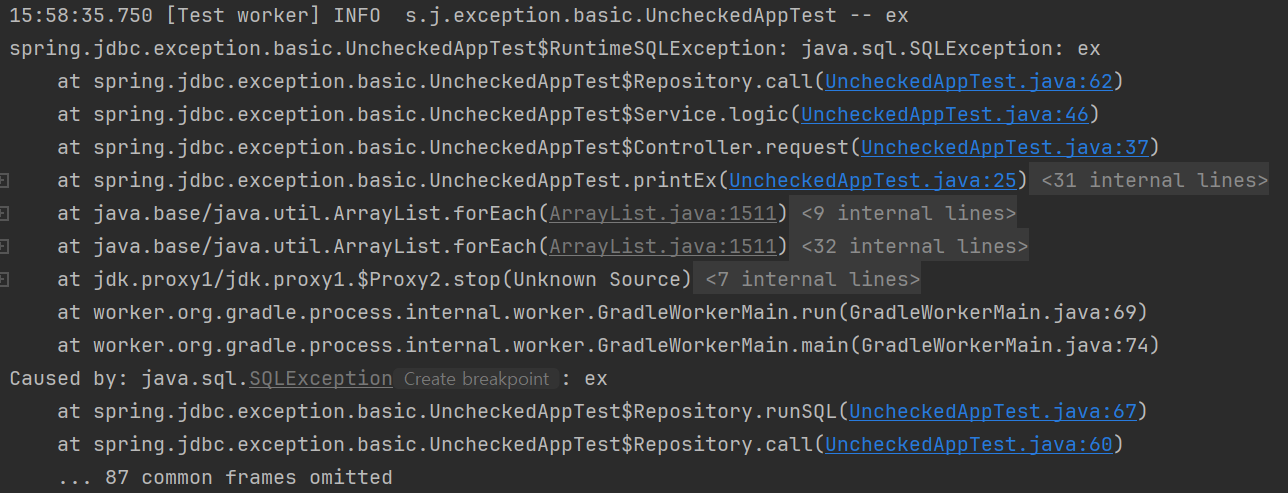
로그를 찍어서 확인해보면 RuntimeSQLException 예외를 포함해서 기존에 발생한 SQLException과 스택 트레이스를 확인할 수 있다.
<기존 예외를 포함하지 않는 경우>
static class Repository {
public void call() {
try {
runSQL();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeSQLException(); //기존 예외(e) 제외
}
}
public void runSQL() throws SQLException {
throw new SQLException("ex");
}
}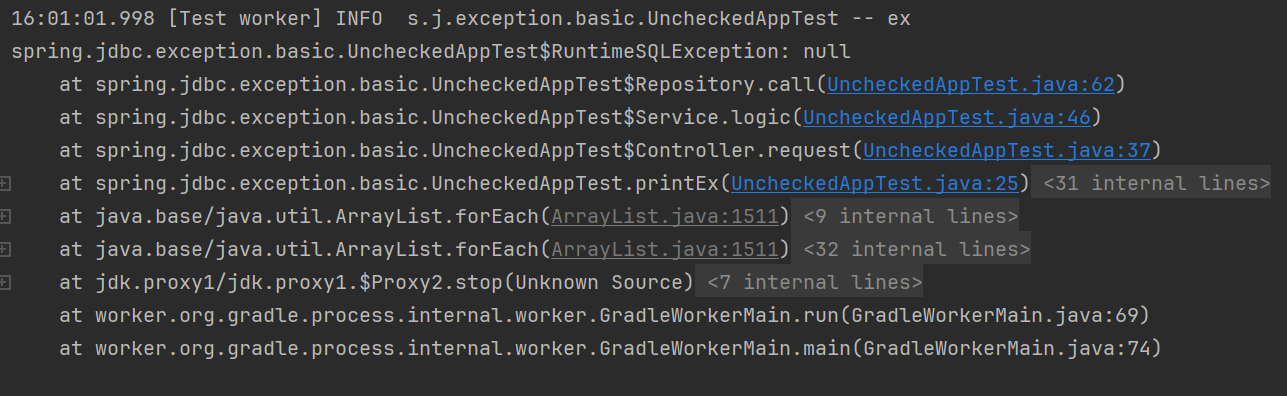
로그를 찍어보면 기존에 발생한 java.sql.SQLException과 스택 트레이스를 확인할 수 없고 변환한 RuntimeSQLException 예외만 확인할 수 있다. 만약 실제 DB에 연동했다면 DB에서 발생한 예외를 확인할 수 없는 심각한 문제가 발생한다.