1.문제
In a town, there are n people labeled from 1 to n. There is a rumor that one of these people is secretly the town judge.
If the town judge exists, then:
The town judge trusts nobody.
Everybody (except for the town judge) trusts the town judge.
There is exactly one person that satisfies properties 1 and 2.
You are given an array trust where trust[i] = [ai, bi] representing that the person labeled ai trusts the person labeled bi.
Return the label of the town judge if the town judge exists and can be identified, or return -1 otherwise.
1부터 n까지 숫자로 표현되는 사람 n명이 마을에 존재하고 그 중 한 명이 비밀리에 업무를 수행하는 마을 판사이다.
만약에 마을 판사가 존재한다고하면, 마을 판사는 아무도 믿지 않고, 마을 판사를 제외한 모든 사람은 마을 판사를 믿고, 앞의 두 조건을 만족하는 한 사람이 존재한다.
마을 사람의 수와 믿음을 나타내는 배열이 주어질 때 마을 판사가 존재하면 마을 판사의 숫자를, 그렇지 않으면 -1을 반환하는 문제이다.
모든 사람이 믿고있는 한 사람이 다른 사람을 아무도 믿지 않을 경우 마을 판사가 존재함을 알 수 있다.
Example 1:
Input: n = 2, trust = [[1,2]]
Output: 2Example 2:
Input: n = 3, trust = [[1,3],[2,3]]
Output: 3Example 3:
Input: n = 3, trust = [[1,3],[2,3],[3,1]]
Output: -1Constraints:
- 1 <= n <= 1000
- 0 <= trust.length <= 10^4
- trust[i].length == 2
- All the pairs of trust are unique.
- ai != bi
- 1 <= ai, bi <= n
2.풀이
- 마을판사는 모든이들의 신뢰를 받고 자신은 아무도 신뢰하지 않는 사람이다.
- 믿는 사람이 있는 사람의 label 을 a배열에 , 믿음을 받는 사람의 label을 b 배열에 저장한다.
- b 배열의 사람들 중 값이 n-1 (마을판사는 아무도 믿지 않기 때문) 인 인덱스를 찾아서 a 배열에서 그 인덱스의 값이 0이면 인덱스를 리턴
/**
* @param {number} n
* @param {number[][]} trust
* @return {number}
*/
const findJudge = function (n, trust) {
let a = new Array(n).fill(0);
let b = new Array(n).fill(0);
let result = -1;
for (let i = 0; i < trust.length; i++) {
// 믿는 사람이 있는 사람의 label 을 a배열에 , 믿음을 받는 사람의 label을 b 배열에 저장한다.
const [truster, trustee] = trust[i];
a[truster - 1]++;
b[trustee - 1]++;
}
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (b[i] === n - 1 && a[i] === 0) {
// trustee 배열에서 값이 n-1인 숫자중 truster 배열에서 값이 0인 index를 찾는다
result = i + 1;
return result;
}
}
return result;
};
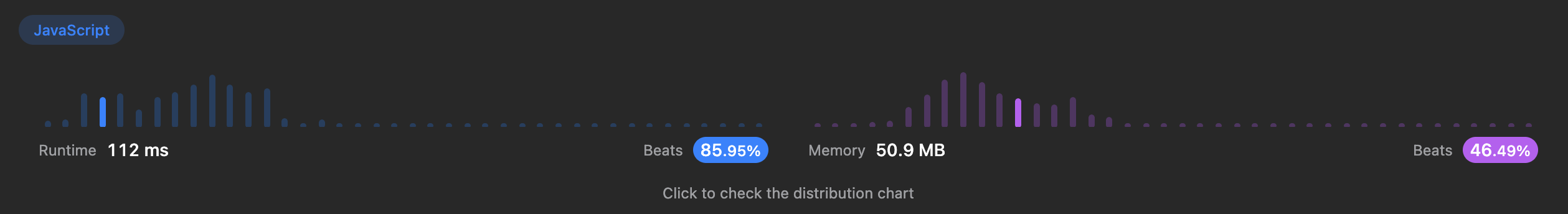
3.결과