문제
An array A consisting of N integers is given. Rotation of the array means that each element is shifted right by one index, and the last element of the array is moved to the first place. For example, the rotation of array A = [3, 8, 9, 7, 6] is [6, 3, 8, 9, 7] (elements are shifted right by one index and 6 is moved to the first place).
The goal is to rotate array A K times; that is, each element of A will be shifted to the right K times.
Write a function:
class Solution { public int[] solution(int[] A, int K); }
that, given an array A consisting of N integers and an integer K, returns the array A rotated K times.
For example, given
A = [3, 8, 9, 7, 6]
K = 3the function should return [9, 7, 6, 3, 8]. Three rotations were made:
[3, 8, 9, 7, 6] -> [6, 3, 8, 9, 7]
[6, 3, 8, 9, 7] -> [7, 6, 3, 8, 9]
[7, 6, 3, 8, 9] -> [9, 7, 6, 3, 8]For another example, given
A = [0, 0, 0]
K = 1the function should return [0, 0, 0]
Given
A = [1, 2, 3, 4]
K = 4the function should return [1, 2, 3, 4]
Assume that:
N and K are integers within the range [0..100];
each element of array A is an integer within the range [−1,000..1,000].
In your solution, focus on correctness. The performance of your solution will not be the focus of the assessment.
Copyright 2009–2025 by Codility Limited. All Rights Reserved. Unauthorized copying, publication or disclosure prohibited.
나의 초기 코드
class Solution {
public int[] solution(int[] A, int K) {
int size = A.length;
int temp[] = new int[size]; // 새로운 rotation 결과
// K번 반복
for(int i=0; i<K; i++){
// rotation
temp[0] = A[size-1]; //A의 맨 마지막 값이 temp의 첫번째 값이 된다.
// n번재 값은 n+1에 배치한다.(0번째 값은 1번째 값이 된다.)
for(int j=0; j<size-1; j++){
temp[j+1] = A[j];
}
// 변경된 배열 내용을 다시 A에 반영.
for(int j=0; j<size; j++){
A[j] = temp[j];
}
}
return A;
}
}결과
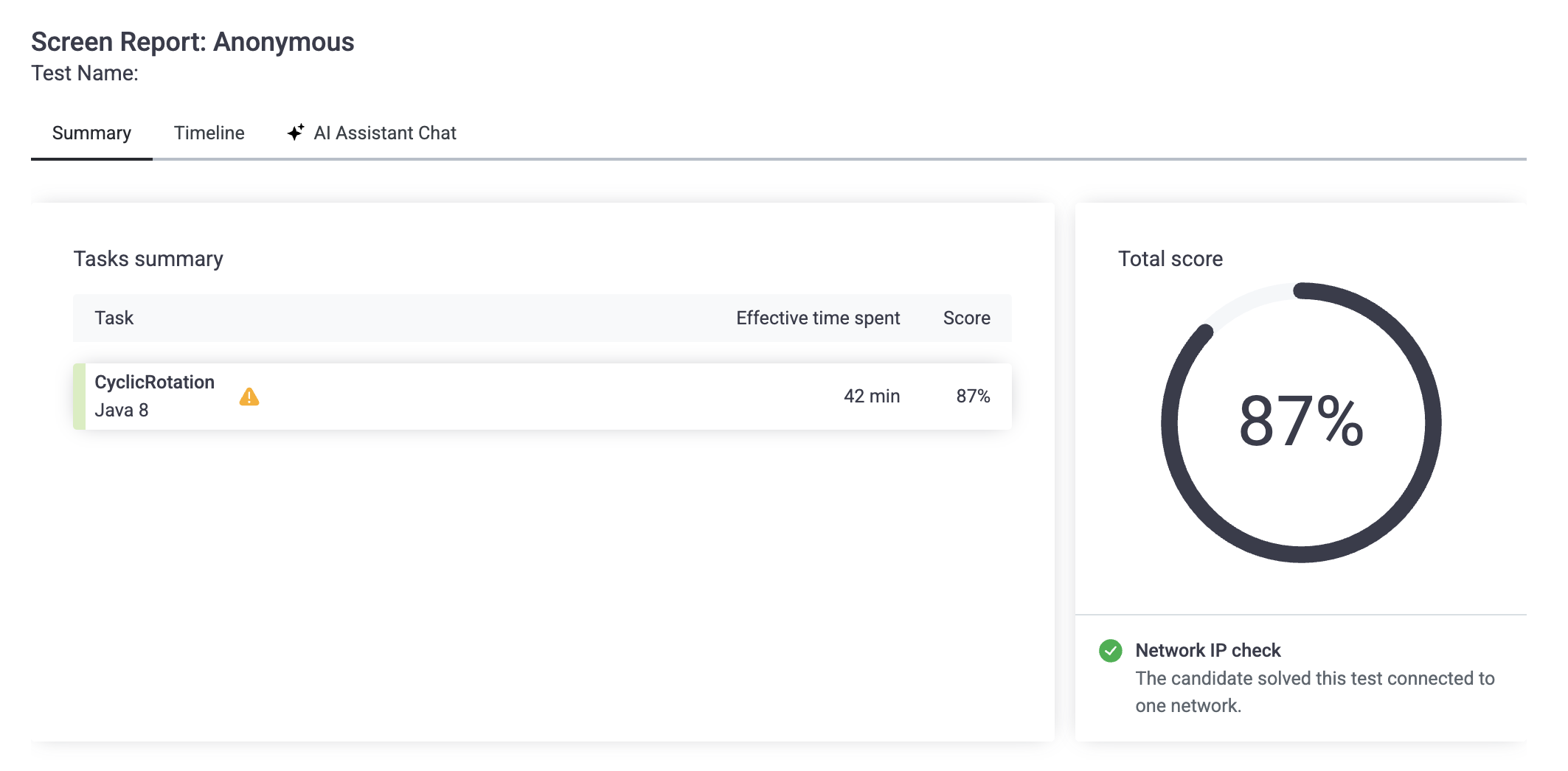
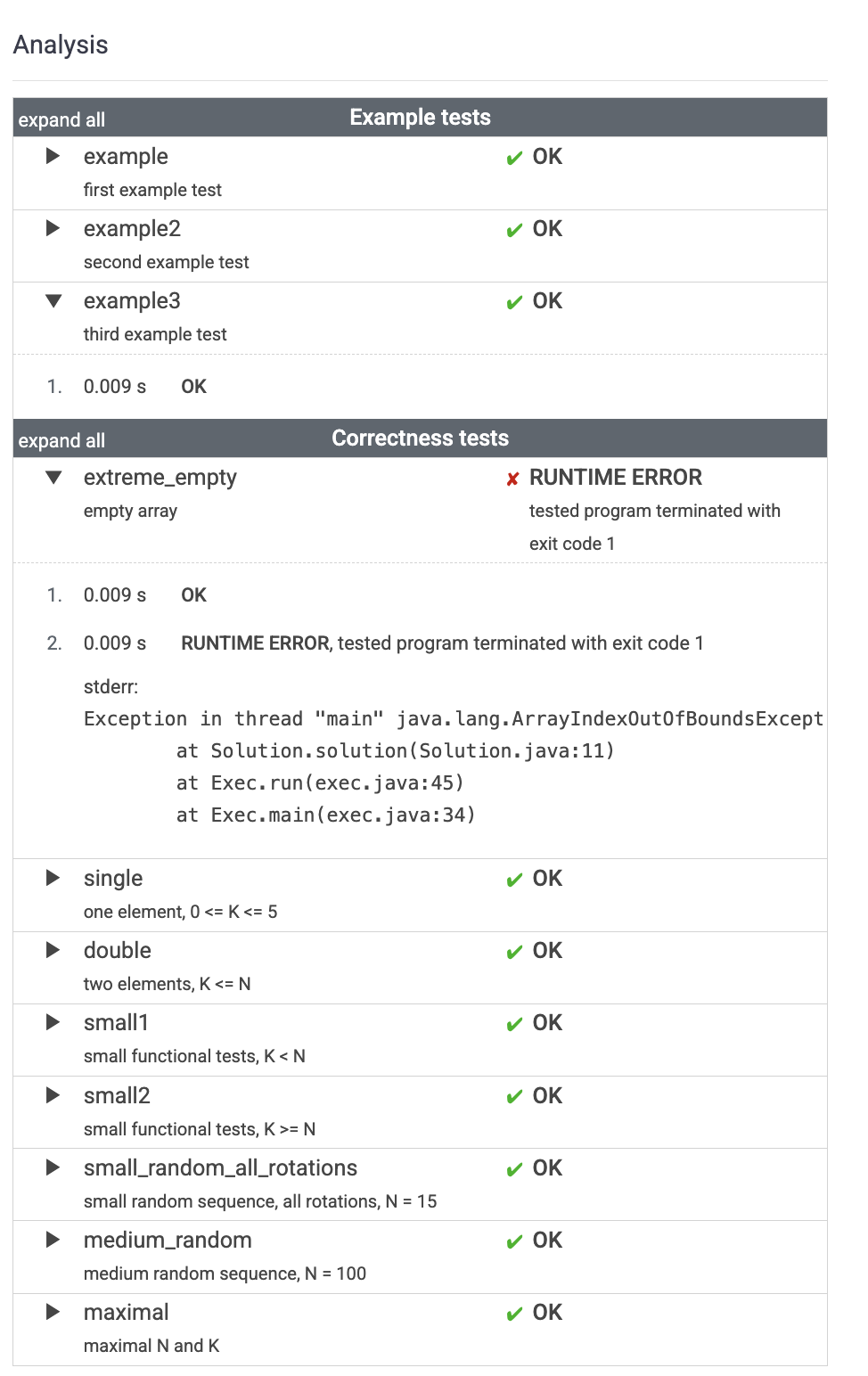
문제 포인트
- N and K are integers within the range [0..100]
: 배열의 크기가 0인 배열이 있는 가능성을 놓침.- N번째 rotation을 하고 난 후는 그 결과가 같다.
수정 코드
class Solution {
public int[] solution(int[] A, int K) {
int size = A.length;
if(size==0){
return A;
}
int temp[] = new int[size]; // 새로운 rotation 결과
// K번 반복
for(int i=0; i<K%size; i++){
// rotation
temp[0] = A[size-1]; //A의 맨 마지막 값이 temp의 첫번째 값이 된다.
// n번재 값은 n+1에 배치한다.(0번째 값은 1번째 값이 된다.)
for(int j=0; j<size-1; j++){
temp[j+1] = A[j];
}
// 변경된 배열 내용을 다시 A에 반영.
for(int j=0; j<size; j++){
A[j] = temp[j];
}
}
return A;
}
}
결과
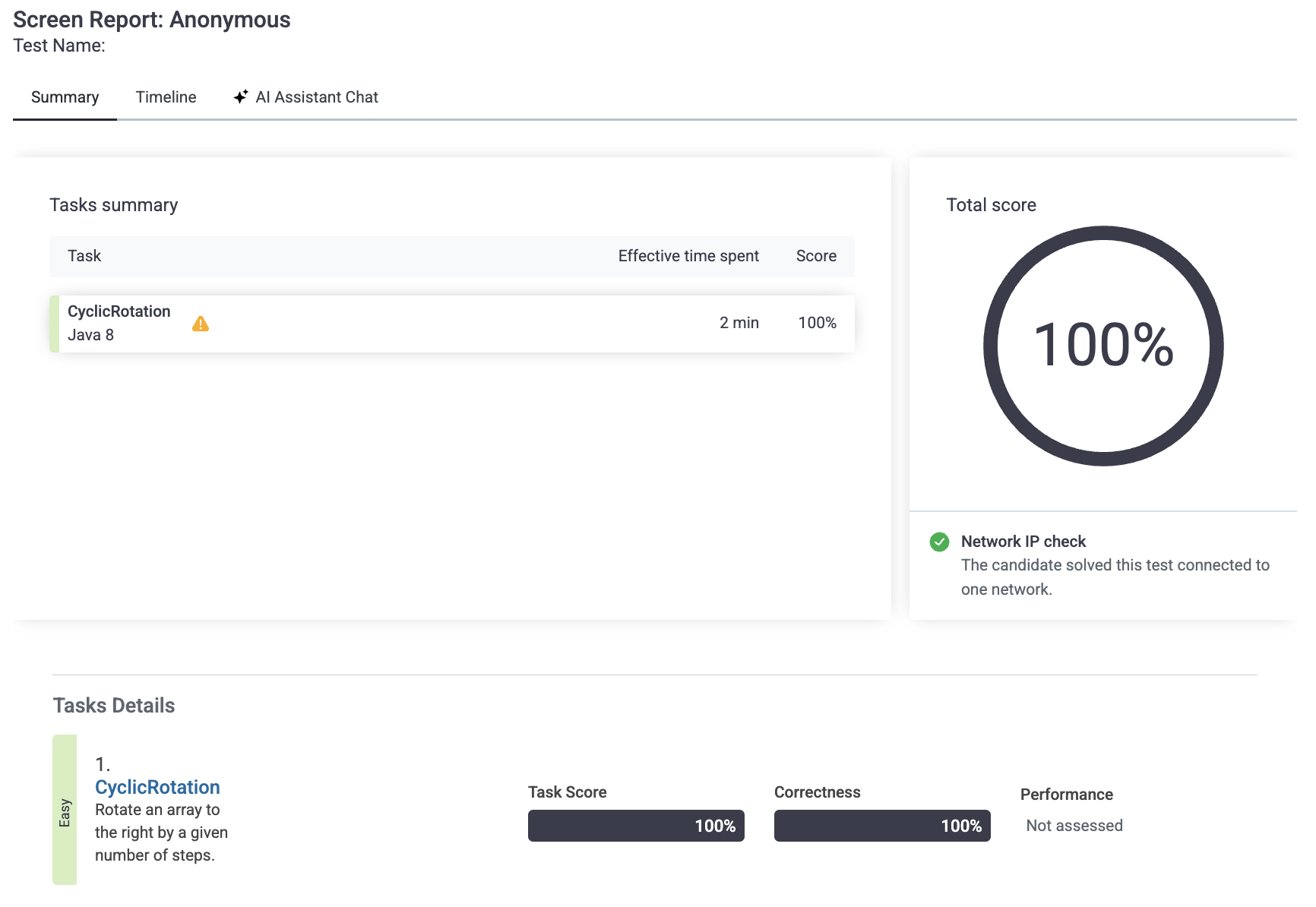
수정코드2
class Solution {
public int[] solution(int[] A, int K) {
int N = A.length;
int result[]= new int[N];
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
result[(i+K)%N] = A[i];
}
return result;
}
}% 개념을 활용해서 좀 더 간단하게 코드를 짜보았다.
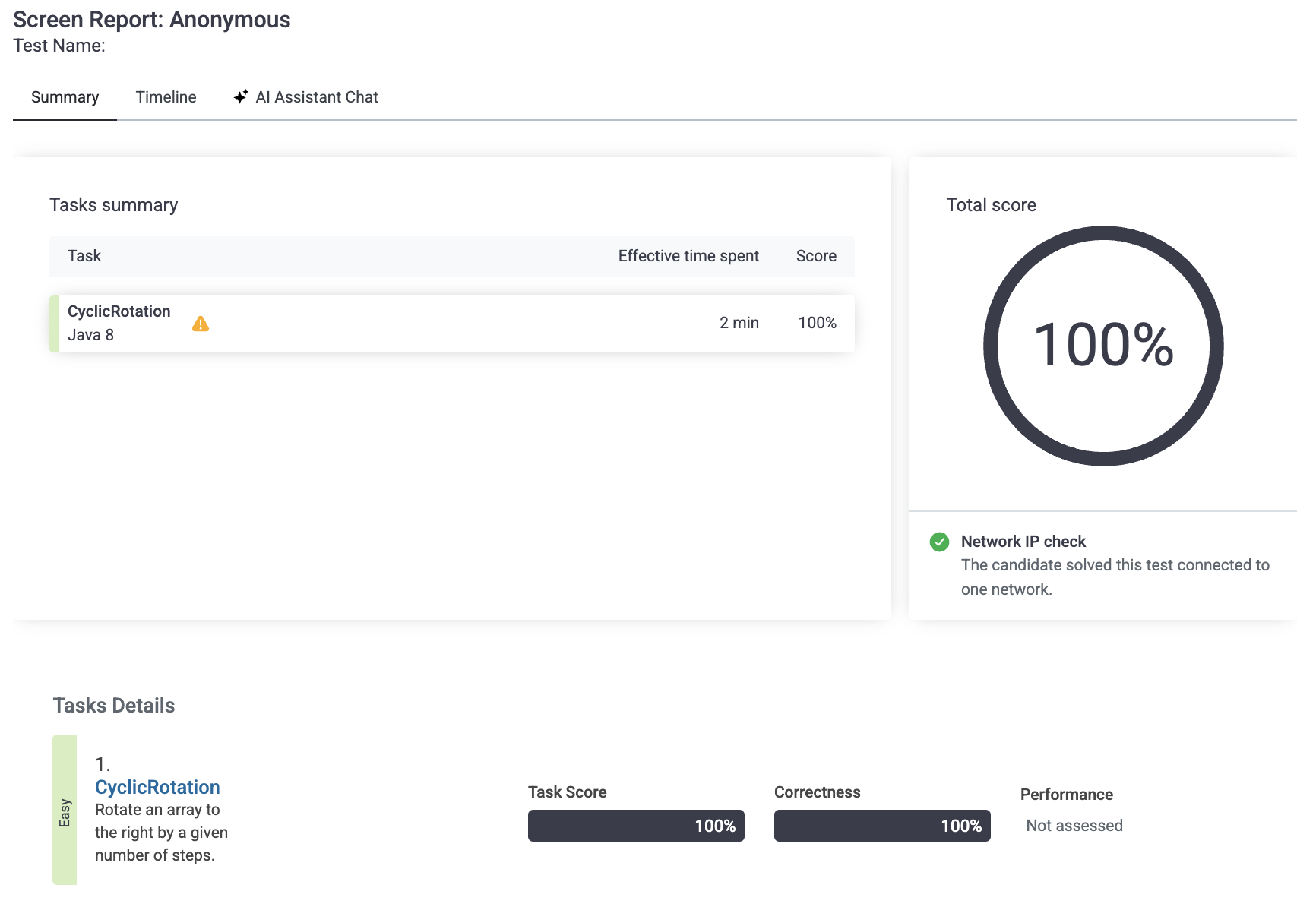

좀 비효율 적인 부분이 많이 들어갔는데 추가 배열 없이 A 만으로 푸는게 가능하실지.
힌트 : A 배열 부분적으로 reverse 시도