JWT(Json Web Toekn)은 일반적으로 클라이언트와 서버 통신 시 권한 인가(Authorization)을 위해 사용한는 토큰이다.
- 웹 상에서 Form을 통해 로그인하는 것이 아닌, API 접근을 위해 프론트엔드에게 인증 토큰을 발급하고 싶을때, 적절한 인증 수단
Spring Security + JWT의 동작 과정
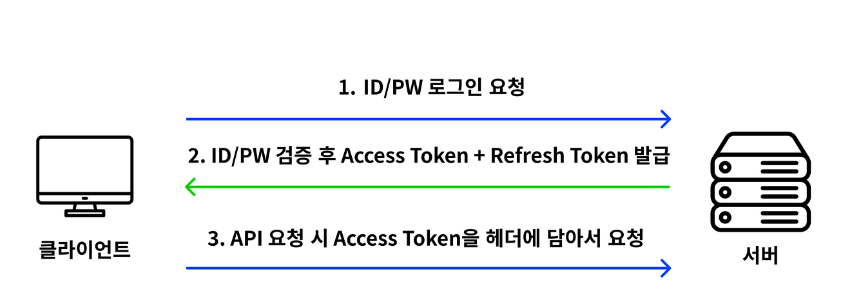
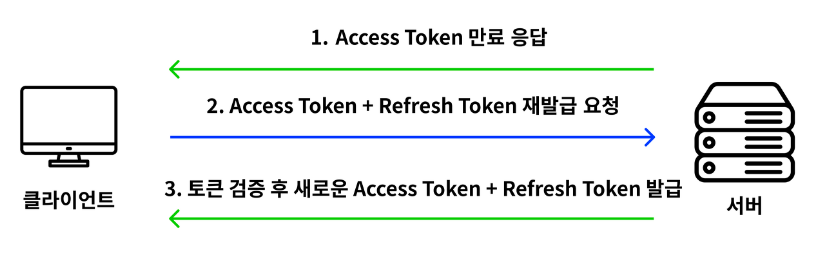
Refresh Token은 새로운 Access Token을 발급하기 위한 토큰이다. 보통 AccessToken은 외부 유출 문제로 인해 유효기간을 짧게 설정(30분)하는데, 정상적인 클라이언트는 유효기간이 끝난 Access Token에 대해 Refresh Token을 사용하여 새로운 Access Token을 발급 받을 수 있다. 따라서 Refresh Token의 유효기간은 Access Token의 유효기간보다 길게 설정해야 한다(2주). 그렇지만 Refresh Token이 유출되어서 다른 사용자가 이를 통해 새로운 Access Token을 발급받았다면? 이 경우 Access Token의 충돌이 발생하기 때문에, 서버 측에서는 두 토큰을 모두 폐기 시켜야한다. 따라서 국제 인터넷 표준화 기구에서는 이를 방지하기 위해 두 토큰을 같은 유효기간을 가지도록 권장하고 있다.
TokenDTO
먼저, 클라이언트에 토큰을 보내기 위한 DTO를 생성한다.
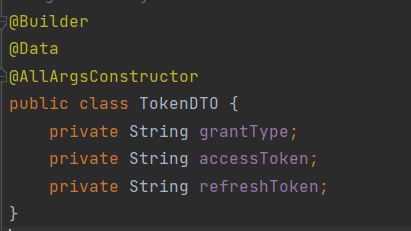
grantType은 JWT 대한 인증 타입으로, 여기서는 Bearer를 사용한다. 이후 HTTP 헤더에 prefix로 붙여주는 타입이기도 하다.
grantType
- OAuth 2.0 프레임워크의 핵심은 다양한 클라이언트 환경에 적합한 인증 및 권한의 위임 방법(grant_type)을 제공하고 그 결과로 클라이언트에게 access_token을 발급하는 것이다.
- 한 번 획득된 access_token은 만료 시점까지 모든 리소스 서버의 엔드포인트 요청 헤더에 Authorization: Bearer {ACCESS_TOKEN}로 첨부된다.
application.yml
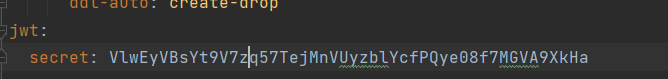
토큰의 암호화 복호화를 위한 secret key로서 이후 HS256 알고리즘을 사용하기 위해, 256비트보다 커야한다. 알파벳은 한 단어당 8bit이므로 32글자 이상이면된다.
JWtTokenProvider
JWT 토큰 생성, 토큰 복호화 및 정보 추출, 토큰 유효성 검증의 기능이 구현된 클래스이다.
package com.cbu.backend.member.security.jwt;
import io.jsonwebtoken.*;
import io.jsonwebtoken.io.Decoders;
import io.jsonwebtoken.security.Keys;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.security.Key;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class JwtTokenProvider {
private final Key key;
private final Long ACCESS_TOKEN_VALIDATION_PERIOD = 60L * 60 * 24 * 1000;
private final Long REFRESH_TOKEN_VALIDATION_PERIOD = 60L * 60 * 24 * 14 * 1000;
public JwtTokenProvider(@Value("${jwt.secret}") String secretKey) {
byte[] keyBytes = Decoders.BASE64.decode(secretKey);
this.key = Keys.hmacShaKeyFor(keyBytes);
}
// 유저 정보를 가지고 AccessToken, RefreshToken 을 생성하는 메서드
public TokenDTO generateToken(Authentication authentication) {
// 권한 가져오기
String authorities = getAuthorities(authentication);
long now = getNow();
// Access Token 생성
Date accessTokenExpiresIn = getAccessTokenExpiresIn(now);
String accessToken = getAccessToken(authentication, authorities, accessTokenExpiresIn);
// Refresh Token 생성
String refreshToken = getRefreshToken(now);
return getTokenDTO(accessToken, refreshToken);
}
// JWT 토큰을 복호화하여 토큰에 들어있는 정보를 꺼내는 메서드
public Authentication getAuthentication(String accessToken) {
// 토큰 복호화
Claims claims = parseClaims(accessToken);
if (claims.get("auth") == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("권한 정보가 없는 토큰입니다.");
}
// 클레임에서 권한 정보 가져오기
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities =
Arrays.stream(claims.get("auth").toString().split(","))
.map(SimpleGrantedAuthority::new)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// UserDetails 객체를 만들어서 Authentication 리턴
UserDetails principal = new User(claims.getSubject(), "", authorities);
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(principal, "", authorities);
}
// 토큰 정보를 검증하는 메서드
public boolean validateToken(String token) {
try {
Jwts.parserBuilder().setSigningKey(key).build().parseClaimsJws(token);
return true;
} catch (io.jsonwebtoken.security.SecurityException | MalformedJwtException e) {
log.info("Invalid JWT Token", e);
} catch (ExpiredJwtException e) {
log.info("Expired JWT Token", e);
} catch (UnsupportedJwtException e) {
log.info("Unsupported JWT Token", e);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
log.info("JWT claims string is empty.", e);
}
return false;
}
private Claims parseClaims(String accessToken) {
try {
return Jwts.parserBuilder().setSigningKey(key).build().parseClaimsJws(accessToken).getBody();
} catch (ExpiredJwtException e) {
return e.getClaims();
}
}
private static long getNow() {
return (new Date()).getTime();
}
private static String getAuthorities(Authentication authentication) {
return authentication.getAuthorities().stream()
.map(GrantedAuthority::getAuthority)
.collect(Collectors.joining(","));
}
private static TokenDTO getTokenDTO(String accessToken, String refreshToken) {
return TokenDTO.builder()
.grantType("Bearer")
.accessToken(accessToken)
.refreshToken(refreshToken)
.build();
}
private String getRefreshToken(long now) {
return Jwts.builder()
.setExpiration(getRefreshTokenExpires(now))
.signWith(key, SignatureAlgorithm.HS256)
.compact();
}
private Date getRefreshTokenExpires(long now) {
return new Date(now + REFRESH_TOKEN_VALIDATION_PERIOD);
}
private Date getAccessTokenExpiresIn(long now) {
return new Date(now + ACCESS_TOKEN_VALIDATION_PERIOD);
}
private String getAccessToken(Authentication authentication, String authorities, Date accessTokenExpiresIn) {
return Jwts.builder()
.setSubject(authentication.getName())
.claim("auth", authorities)
.setExpiration(accessTokenExpiresIn)
.signWith(key, SignatureAlgorithm.HS256)
.compact();
}
}
클래스가 너무 길어져서 토큰 유효성 검증의 기능을 JWTvalidaotr로 따로 빼고 싶지만 일단 보류.
원래는 AccessToken과 RefreshToken의 만료 기간을 같게 하라했지만 내 수준의 보안은 다 뚤리게 되어있고 30분 2주가 국룰이라기에 그냥 그렇게 했다 ㅋㅋ.
JwtAuthenticationFilter
클라이언트 요청시 JWT인증을 하기 위해 설치하는 커스텀 필터로 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter이전에 실행된다. 이전에 실행된다는 뜻은 JwtAuthenticationFilter를 통과하면 UsernamePasswordAuhenticationFilter 이후의 필터는 통과한 것으로 본다는 뜻이다.
package com.cbu.backend.member.security.jwt;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.filter.GenericFilterBean;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.io.IOException;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class JwtAuthenticationFilter extends GenericFilterBean {
private final JwtTokenProvider jwtTokenProvider;
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
// 1. Request Header 에서 JWT 토큰 추출
String token = resolveToken((HttpServletRequest) request);
// 2. validateToken 으로 토큰 유효성 검사
if (token != null && jwtTokenProvider.validateToken(token)) {
// 토큰이 유효할 경우 토큰에서 Authentication 객체를 가지고 와서 SecurityContext 에 저장
Authentication authentication = jwtTokenProvider.getAuthentication(token);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
// Request Header 에서 토큰 정보 추출
private String resolveToken(HttpServletRequest request) {
String bearerToken = request.getHeader("Authorization");
if (StringUtils.hasText(bearerToken) && bearerToken.startsWith("Bearer")) {
return bearerToken.substring(7);
}
return null;
}
}여기서 잠깐 필터란..?
필터 : 말 그대로 요청과 응답을 거른뒤 정제하는 역할을 한다.
- Disoatcher Servlet에 요청이 전달되기 전/후에 url패턴에 맞는 모든 요청에 대한 부가 작업을 처리할 수 있는 기능을 제공한다.
- 즉, 스프링 컨테이너가 아닌 톰캣과 같은 웹 컨테이너에 의해 관리가 되는 것이고, 스프링 범위 밖에서 처리되는 것이다.
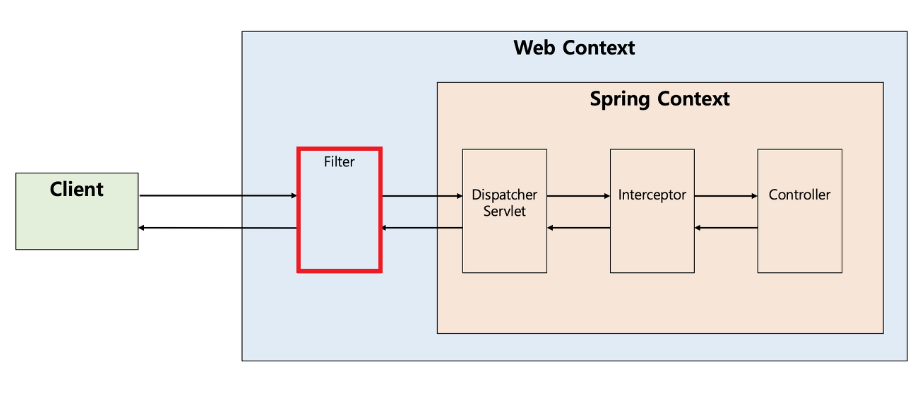
필터의 메소드 종류
- init() : 필터 객체를 초기화하고 서비스에 추가하기 위한 메소드
- 웹 컨테이너가 1회 init()을 호출하여 필터 객체를 초기화하면 이후 요청들은 doFilter()를 통해 처리된다.
- doFilter() : url-pattern에 맞는 모든 HTTP 요청이 디스패처 서블릿으로 전달되기 전에 웹 컨테이너에 의해 실행되는 메소드
- doFilter의 파라미터로 FilterChain이 있는데, FilterChain의 doFilter 통해 다음 대상으로 요청을 전달할 수 있게 된다.
- chain.doFilter()로 전, 후에 우리가 필요한 처리 과정을 넣어줌으로써 원하는 처리를 진행할 수 있다.
- destroy() : 필터 객체를 제거하고 사용하는 자원을 반환하기 위한 메소드이다.
- 웹 컨테이너가 1회 destroy()를 호출하여 필터 객체를 종료하면 이후에는 doFilter에 의해 처리되지 않는다.
참고 : 필터와 인터셉터
SecurityConofig
SpringSecurity 설정을 위한 클래스이다.
package com.cbu.backend.member.security;
import com.cbu.backend.member.security.jwt.JwtAuthenticationFilter;
import com.cbu.backend.member.security.jwt.JwtTokenProvider;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.http.SessionCreationPolicy;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.factory.PasswordEncoderFactories;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class SecurityConfig {
private final JwtTokenProvider jwtTokenProvider;
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.httpBasic().disable()
.csrf().disable()
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("").permitAll()
.antMatchers("").hasRole("USER")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.addFilterBefore(jwtAuthenticationFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
return http.build();
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return PasswordEncoderFactories.createDelegatingPasswordEncoder();
}
@Bean
public JwtAuthenticationFilter jwtAuthenticationFilter() {
return new JwtAuthenticationFilter(jwtTokenProvider);
}
}
과거에는 Security 설정을 WebSecurityConfigureAdapter 클래스를 상속받아서 구현했지만, SpringBoot 버전이 올라가면서 해당 방식이 Deprecated 되었다. 따라서 이제는 빈 등록을 통해 Security를 설정한다. 코드 하나하나를 분석해보자.
- httpBasic().disable()
- Http basic Auth 기반으로 로그인 인증창이 뜸. 기본 인증 로그인을 이용하지 않으면 disable
- csrf().disable()
CSRf: 정상적인 사용자가 의도치 않은 위조요청을 보내는 것을 의미한다.
ex) A라는 도메인에서, 인증된 사용자 H가 위조된 request를 포함한 link, email을 사용하였을 경우(클릭, 또는 사이트 방문만으로도), A 도메인에서는 이 사용자가 일반 유저인지, 악용된 공격인지 구분할 수가 없다. CSRF protection은 spring security에서 default로 설정된다. 즉 protection을 통해 GET요청을 제외한 상태를 변화시킬 수 있는 POST, PUT, DElETE 요청으로부터 보호한다. 그렇다면 이렇게 보안 수준을 향상시키는 CSRF를 왜 disable할까?
그 이유는 rest api를 이용한 서버라면, session 기반 인증과는 다르게 stateless하기 때문에 서버에 인증정보를 보관하지 않는다. rest api에서 client는 권한이 필요한 요청을 하기 위해서는 요청에 필요한 인증정보를(OAuth2, jwt토큰 등)을 포함시켜야한다. 따라서 서버에 인증정보를 저장하지 않기 때문에 굳이 불필요한 csrf코드들을 작성할 필요가 없다.
- sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
- JWT를 사용하기 때문에 세션을 사용하지 않는다는 설정이다.
- antMatchers().permitAll()
- antMatchers() : 특정 리소스에 대해서 권한을 설정합니다.
- permitAll() : antMatchers 설정한 리소스의 접근을 인증절차없이 허용한다는 의미입니다.
- antMatchers().hasRole("USER"): USER 권한이 있어야 요청할 수 있다는 설정이다.
- anyRequest().authenticated()
- 이 밖에 모든 요청에 대해서 인증을 필요로 한다는 설정이다.
- addFilterBefore(jwtAuthenticationFilter(),UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
- JWT 인증을 위하여 직접 구현한 필터를 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 전에 실행하겠다는 설정이다.
- passwordEncoder
-
JWT를 사용하기 위해서는 기본적으로 password encoder가 필요한데, 여기서는 Bycrypt encoder를 사용했다.
ex) 대부분 여러 웹 사이트르 이용하는데 이때 동일한 패스워드를 사용하다가 어느 한 웹사이트에서 비밀번호가 유출되면 이 사람이 가입된 모든 웹 사이트가 해킹된 일이 벌어질 수 있다. 따라서 암호화를 해두면 설사 서버가 털려서 패스워드가 유출된다 하더라도 괜찮다. PasswordEncoder를 통해 비밀번호를 암호화한다. PasswordEncoder은 인터페이스 객체이므로 구현체들이 하는 역할은 바로 이 암호화를 어떻게 할지, 암호화 알고리즘에 해당한다. PasswordEncoder의 구현체를 대입해주고 이를 스프링 빈으로 등록한다.
- JwtAuthenticationFilter
- 필터는 스프링 컨테이너 외부에 있으므로 Bean으로 등록해서 주입할 수 있게 한다.
출처 : 스프링 시큐리티, jwt 예제