문제설명

생각하기
- ArrayList를 이용해 return값을 저장하기
- 반복문과 조건문을 적절히 사용하기
내 풀이
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Solution {
public int[] solution(int[] progresses, int[] speeds) {
int cnt =0; // 현재 작업중인 위치
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
while(cnt !=progresses.length){
if(progresses[cnt] <= 99){
for(int i =cnt; i<progresses.length; i++){
progresses[i] += speeds[i];
}
}
if( progresses[cnt] >= 100){
int res =0; // 배포되는 개수
while(progresses[cnt] >= 100){
cnt++;
res++;
if(cnt ==progresses.length) break;
}
list.add(res);
}
}
int[] ans = new int[list.size()];
int num =0;
for(Integer i : list) ans[num++] = i;
return ans;
}
}두번째 while문을 빠져나가는 break 조건을 잘못설정해서 outofbound메모리오류가 1시간동안 났다..
문제가 풀리지 않을 땐 내 코드를 차분히 다시 읽어보자.
ArrayList를 int[]로 바꾸는 코드를 한줄로 쓸 수 있다.
int[] ans = new int[list.size()];
int num =0;
for(Integer i : list) ans[num++] = i;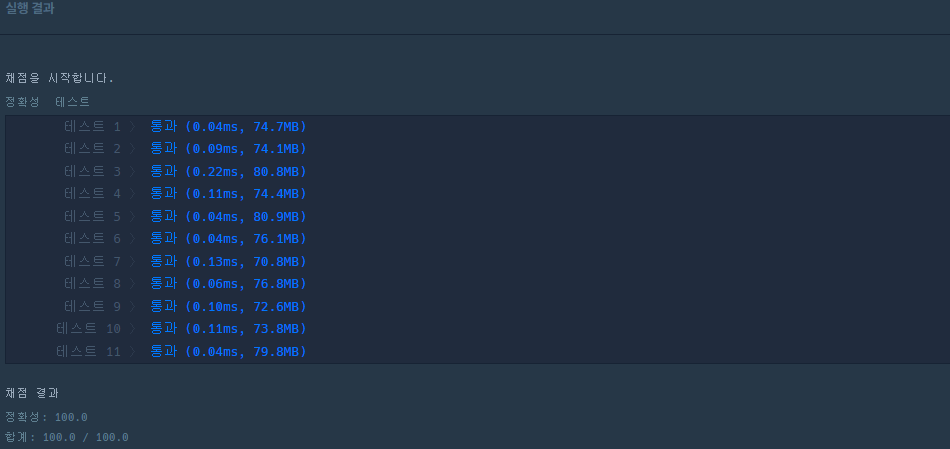
int[] ans = {};
ans = list.stream().mapToInt(i->i).toArray();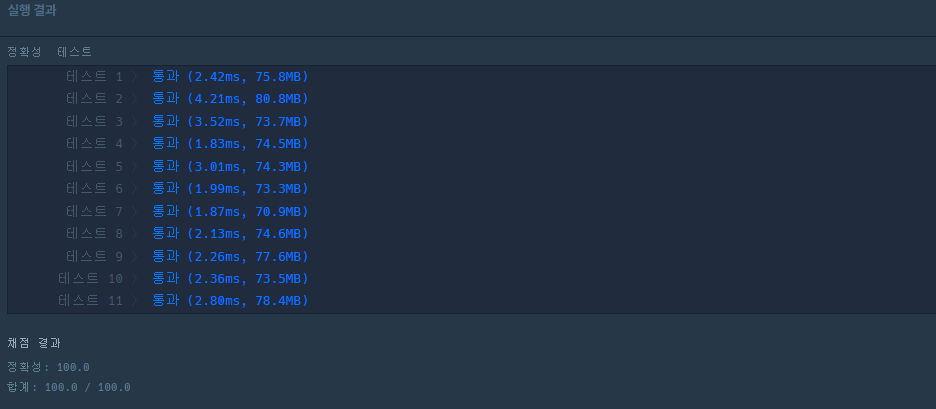
코드는 간결해 졌지만 속도면에서 느려지기 때문에 for문을 사용한 변환이 더 효율적이다.
