Collection Framework
컬렉션
- 동일한 타입을 묶어서 관리하는 자료구조
- 저장공간의 크기를 동적으로 관리
프레임워크
- 클래스와 인터페이스의 모임(라이브러리)
- 클래스의 정의에 설계의 원칙 또는 구조가 존재
컬렉션 프레임워크
- 리스트, 스택, 큐, 트리 등의 자료구조에 정렬, 탐색 등의 알고리즘을 구조화 해 놓은 프레임워크
배열의 특징
- 동일한 타입만 묶어서 저장 가능
- 생성시 크기를 지정해야 하면 추후에 변경이 불가능하다. (컬렉션과의 차이점)
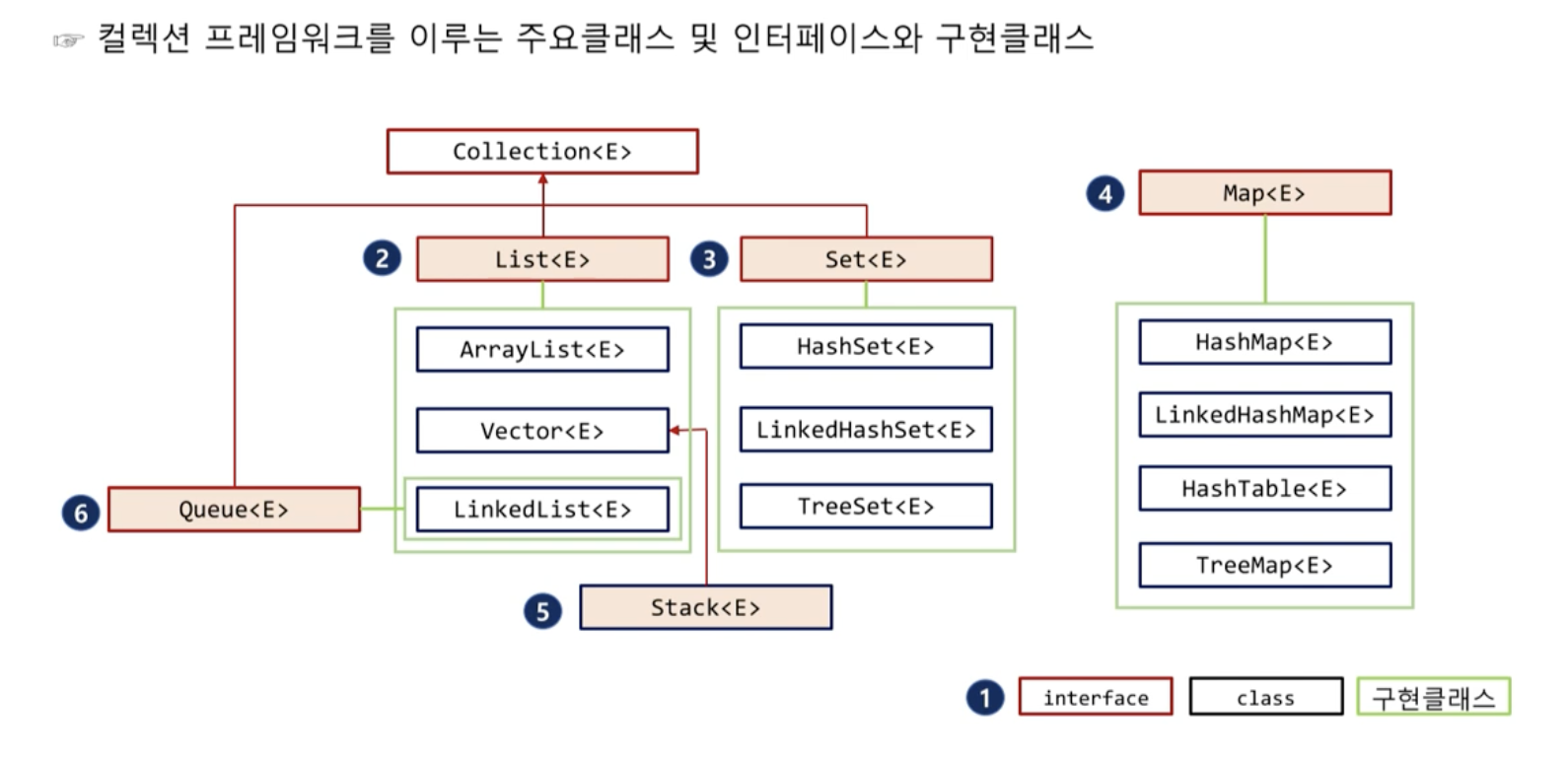
- 인터페이스는 객체 생성을 못한다. 고로 자식클래스를 가지고 상속해서 만든다. 아래에 구현해 놓은 클래스를 사용하면 됨
Stack< E >컬렉션
- List를 상속받아서 Vector 클래스를 구현 Vector를 상속받은 클래스가 Stack이다
- Vector< E >클래스의 자식 클래스
- List < E >의 기본 메서드의 사용과 더불어 LIFO Last-In-First-Out 구조.
나중에 들어간 데이터가 먼저 나온다
- Vector< E > 클래스의 기본 메서드와 더불어 LIFO 구조를 위한 5개의 메서드
(push, peek, pop, search, empty)
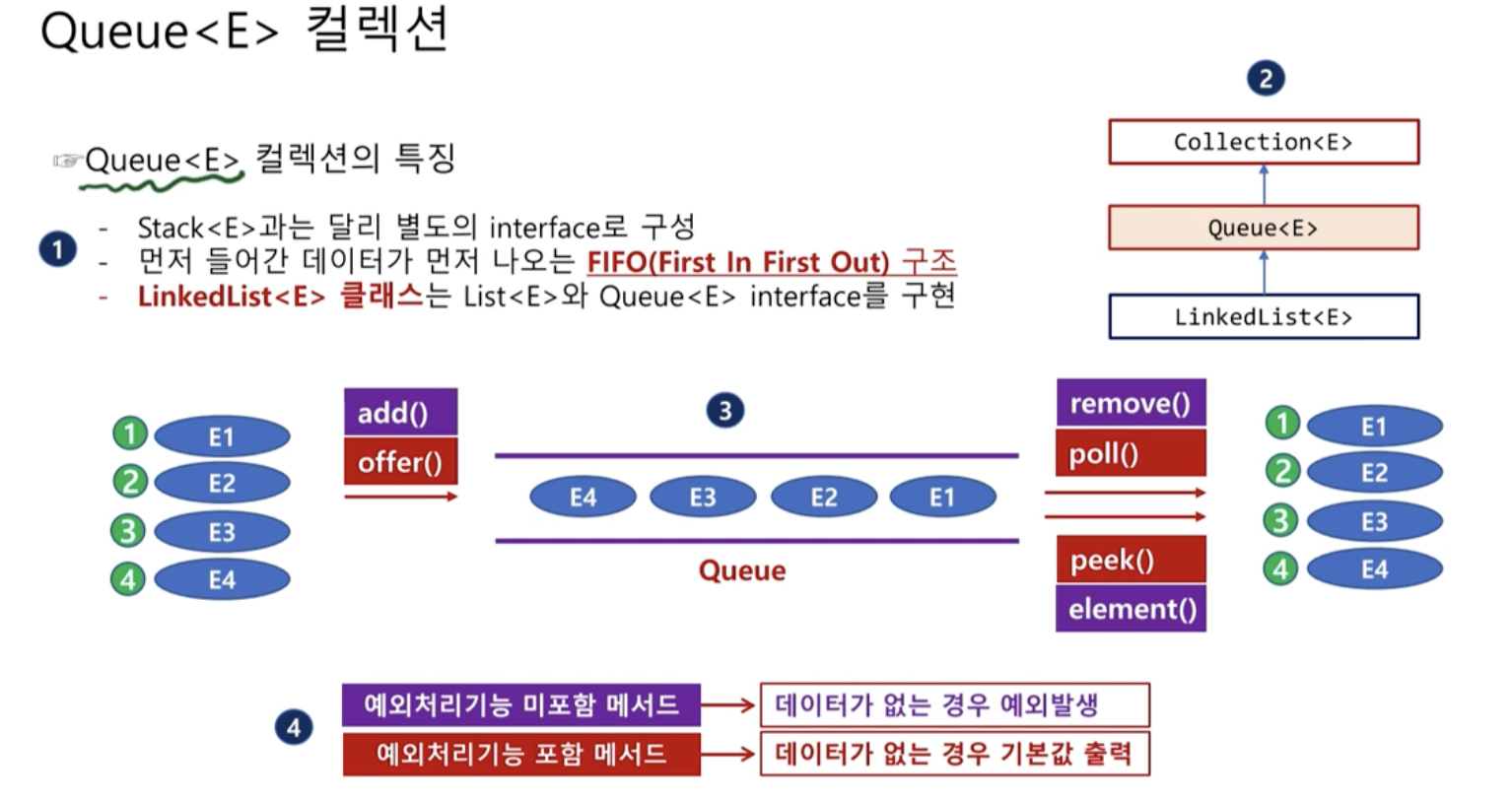
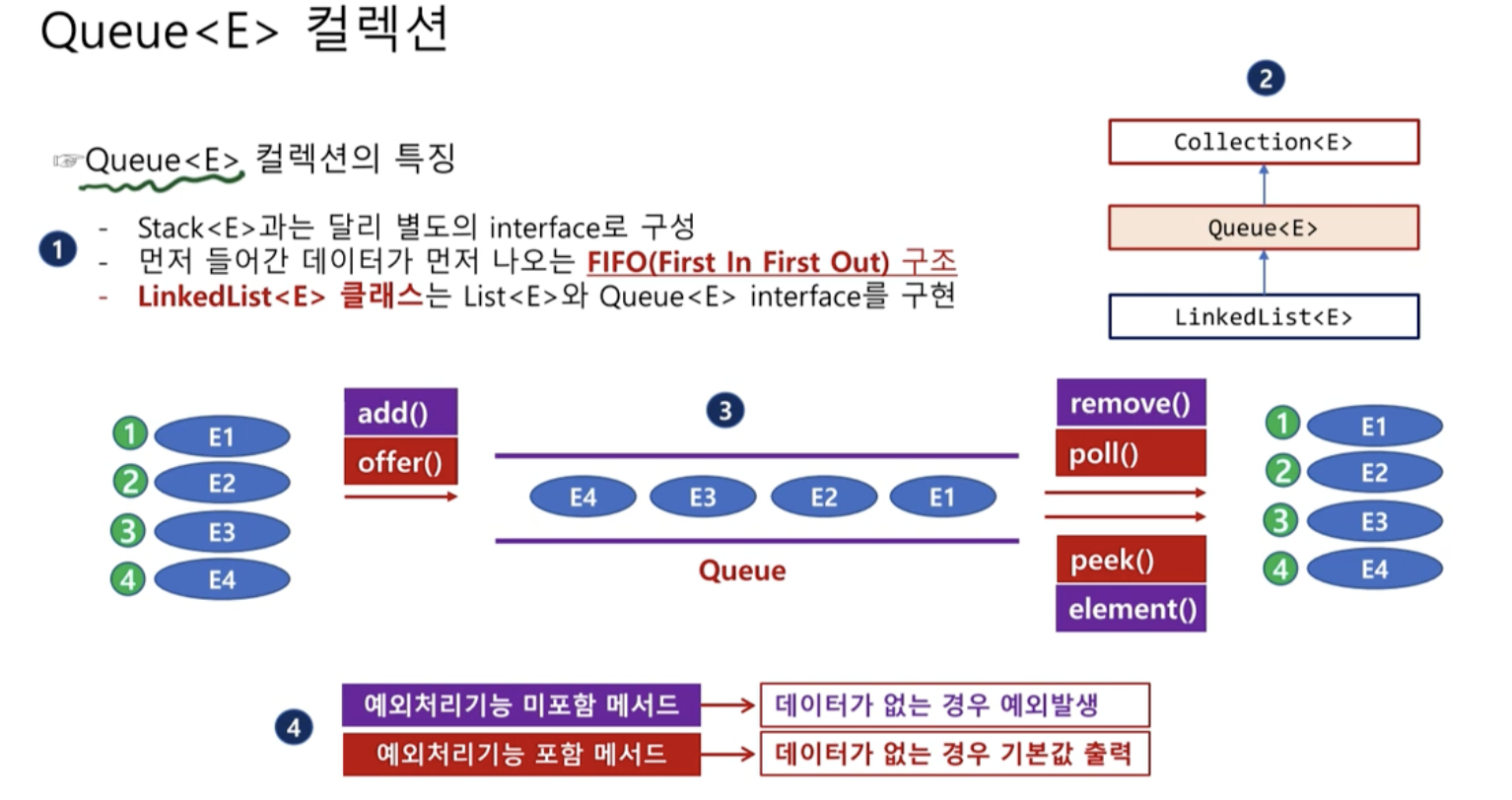
Queue < E >컬렉션
- 이벤트 처리할때 많이 사용
- Stack < E >과는 달리 별도의 interface로 구성
- 먼저 들어간 데이터가 먼저 나오는 FIFO 구조
선입선출 구조
- LinkedList< E >클래스는 List와 Queue 인터페이스를 구현
1. 올바른 괄호
package section05;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main01 {
public static String solution(String str){
String answer = "YES";
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for (char x : str.toCharArray()){
if (x== '(') stack.push(x);
else{
if (stack.isEmpty()) return "NO";
stack.pop();
}
}
if (!stack.isEmpty()) return "NO";
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = sc.next();
System.out.println(solution(str));
}
}
stack.pop() : 삭제stack.push() : 추가
2. 괄호 문자 제거
package section05;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main02 {
public static String solution(String str){
String answer = "";
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for (char x: str.toCharArray()){
if (x == ')'){
while(stack.pop()!='(');
}else stack.push(x);
}
for (int i=0; i<stack.size(); i++) answer+=stack.get(i);
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = sc.next();
System.out.println(solution(str));
}
}
3. 크레인 인형뽑기
package section05;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main03 {
public static int solution(int [][]board, int []moves){
int answer = 0;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int pos: moves){
for (int i=0; i<board.length; i++){
if (board[i][pos-1]!=0){
int tmp = board[i][pos-1];
board[i][pos-1]=0;
if (!stack.isEmpty() && tmp == stack.peek()){
answer +=2;
stack.pop();
}
else stack.push(tmp);
break;
}
}
}
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int [][] board = new int[n][n];
for (int i=0; i<n; i++ ){
for (int j=0; j<n; j++){
board[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
int m = sc.nextInt();
int [] moves = new int[m];
for (int i=0; i<m; i++){
moves[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println(solution(board, moves));
}
}
4. 호위식 연산
package section05;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main04 {
public static int solution(String str){
int answer = 0;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
for (char x : str.toCharArray()){
if( Character.isDigit(x)) stack.push(x -48);
else{
int rt = stack.pop();
int lt = stack.pop();
if (x== '+') stack.push(lt +rt);
else if (x == '-') stack.push(lt -rt);
else if (x == '*') stack.push(lt *rt);
else if (x == '/') stack.push(lt /rt);
}
}
answer = stack.get(0);
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = sc.next();
System.out.println(solution(str));
}
}
Character.isDigit(x) : char값이 숫자인지 여부를 판단하여 true,false 리턴- 아스키코드의 숫자 값을 구하기 위해서는 ‘0’ = 48을 빼줘야 한다.
5. 쇠막대기
package section05;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main05 {
public static int solution(String str){
int answer = 0;
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i=0; i<str.length(); i++){
if (str.charAt(i) == '(') stack.push('(');
else{
stack.pop();
if (str.charAt(i-1) == '(') answer += stack.size();
else answer ++;
}
}
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = sc.next();
System.out.print(solution(str));
}
}
6. 공주구하기
package section05;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class reMain07 {
public static int solution(int n, int k){
int answer = 0;
Queue<Integer> Q = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
Q.offer(i);
}
while(!Q.isEmpty()){
for (int i=1; i<k; i++) {
Q.offer(Q.poll());
}
Q.poll();
if (Q.size()==1) answer= Q.poll();
}
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int k = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(solution(n, k));
}
}
q.add(x) : 해당 큐 맨뒤에 값 삽입, 성공시 true 반환q.offer(x) : 해당 큐 맨뒤에 값 삽입, 성공시 trueq.poll() : 큐 맨 앞에 있는 값 반환후 삭제, 비어있을경우 null 반환q.peek() : 큐의 맨 앞에 있는 값 반환, 비어있을경우 null 반환
7. 교육과정설계
package section05;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main07 {
public static String solution (String str1, String str2){
String answer = "YES";
Queue<Character> Q = new LinkedList<>();
for (char x : str1.toCharArray()) Q.offer(x);
for (char y : str2.toCharArray()){
if (Q.contains(y)){
if (Q.poll() != y) return "NO";
}
}
if (!Q.isEmpty()) return "NO";
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String str1 = sc.next();
String str2 = sc.next();
System.out.println(solution(str1, str2));
}
}
8. 응급실
package section05;
import java.util.*;
class Person{
int id;
int priority;
public Person(int id, int priority) {
this.id = id;
this.priority = priority;
}
}
public class Main08 {
public int solution(int n, int m, int[] arr){
int answer = 0;
Queue<Person> Q = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i=0; i<n; i++){
Q.offer(new Person(i, arr[i]));
}
while (!Q.isEmpty()){
Person tmp = Q.poll();
for (Person x : Q){
if (x.priority > tmp.priority){
Q.offer(tmp);
tmp =null;
break;
}
}
if (tmp!=null){
answer++;
if (tmp.id == m) return answer;
}
}
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main08 T = new Main08();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int []arr = new int[n];
for (int i=0; i<n; i++){
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println(T.solution(n, m, arr));
}
}