단순히 공부와 정리용으로 적은 글 입니다!
3.1 transport-layer services
transport service protocol
send side : application layer에서 온 message를 쪼개 segment로 만들고 network layer로 보낸다.
receive side : segments를 reassemble하여 message로 만들어서 application layer로 보낸다.
transport VS network layer
network layer는 IP address로 host를 구분하여 host간의 communication을 한다.
transport layer는 port#로 process를 구분하여 process간의 communication을 한다.
Internet transport layer protocol
TCP : reliable(error, loss X), in-order, congestion control, flow control, connection setup
UDP : unreliable, unordered, not guarantee delay, bandwidth
3.2 multiplexing and demultiplexing
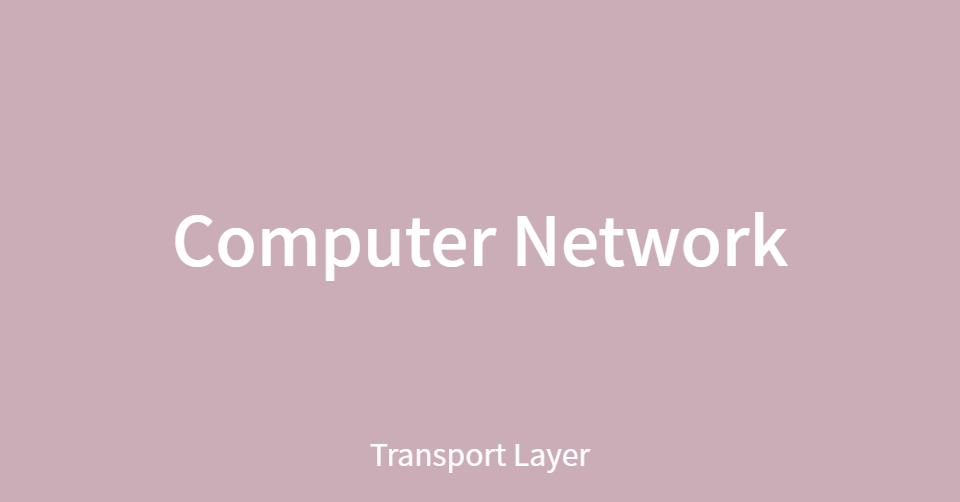
TCP/UCP segment format
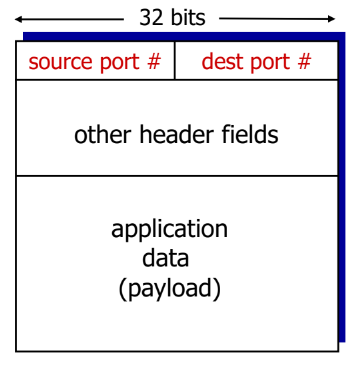
Multiplexing And Demultiplexing
multiplexing : sender에서 segment(header)에 port#를 더한다
demultiplexing : receiver에서 segment를 알맞은 소켓으로 전달한다
How demltiplexing works
- 각각의 datagram (network layer)은 source IP, destination IP를 가짐
- 각각의 datagram은 하나의 transport layer segment를 옮김
- segment는 source, destination port#를 가짐
- host는 IP와 port#를 이용하여 segment를 알맞은 소켓으로 보냄
Connectionless demultiplexing(UDP)
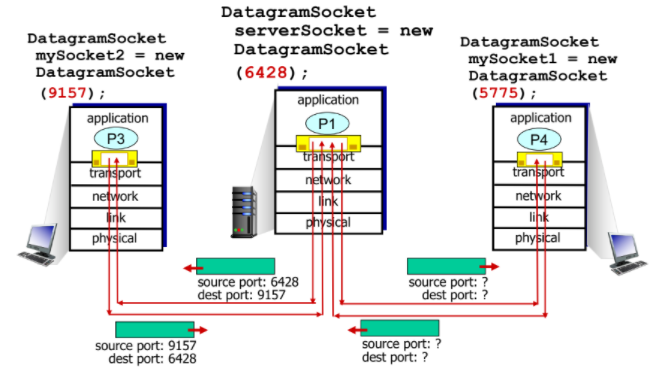
- destination의 IP와 port#를 이용하여 소켓을 구분함
- connection이 없으므로 (프로세스를?)구별을 하지않고 보내고 끝임
- host가 UDP segment를 받으면 destination port#를 받고 해당 process를 찾아서 보냄
- source IP와 port#에 상관 없이 destination은 IP와 port#이 같으면 같은 소켓으로 전달됨
Connection-oriented demultiplexing(TCP)
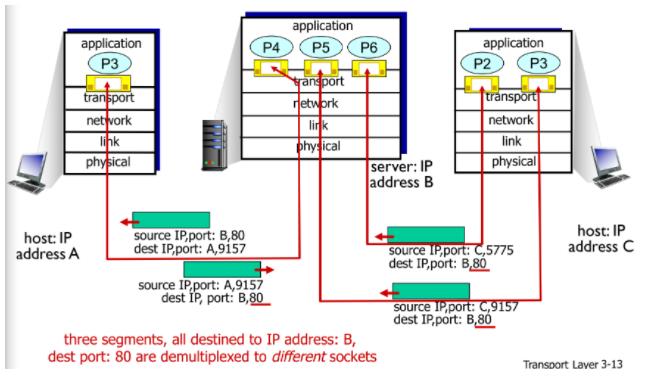
- source의 IP와 port#, destination의 IP와 port#를 이용하여 소켓을 구분함
- 웹 서버는 각각의 connection client마다 다른 socket을 사용함(non-persistent HTTP방식도{이건 더 찾아 보기~})
- destination은 IP와 port#이 같아도 source IP와 port#가 다르면 다른 socket으로 전달함
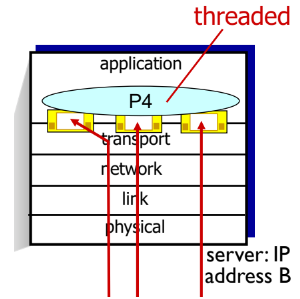
- 이렇게 thread로 소켓을 만들어서 서버를 만들어도 됨