계수 정렬 구현
public class Main2 {
public static void countingSort(int[] arr) {
// # 1 일반 배열 사용
// 최대값 구해서 배열 설정
int max = Arrays.stream(arr).max().getAsInt();
int[] cntArr = new int[max + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
cntArr[arr[i]]++;
}
int idx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < cntArr.length; i++) {
while (cntArr[i] > 0) {
arr[idx++] = i;
cntArr[i] -= 1;
}
}
// # 2 Hashmap 사용
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int item: arr) {
map.put(item, map.getOrDefault(item, 0) + 1);
}
int idx2 = 0;
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList(map.keySet());
Collections.sort(list);
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
int cnt = map.get(list.get(i));
while (cnt > 0) {
arr[idx2++] = list.get(i);
cnt--;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
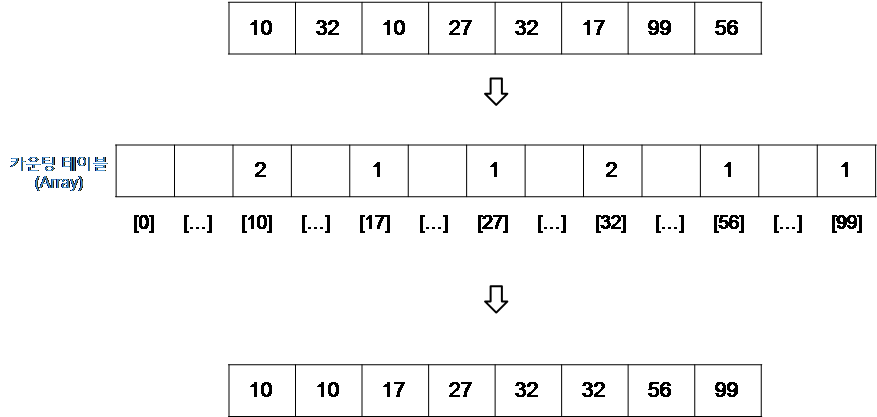
int[] arr = {10, 32, 10, 27, 32, 17, 99, 56};
countingSort(arr);
System.out.println("계수 정렬: " + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
//출력
계수 정렬: [10, 10, 17, 27, 32, 32, 56, 99]
