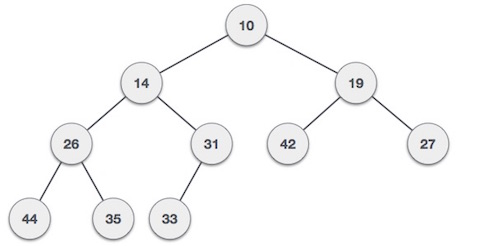
Heap(Heap Tree)이란?
- 여러 개의 값 중에서 가장 작은 값을(최대 힙의 경우는 큰 값) 빠르게 찾기 위해 만든 완전 이진 트리.
- 트리의 부모 노드는 자식 노드보다 항상 작은 값(최대 힙의 경우는 큰 값)을 가진다.
- 짧게 힙(Heap)이라고 줄여서 부르기도 한다.
- 우선 순위 큐를 구현하는 데에 사용된다.
이미지 출처: 나무위키
Heap의 데이터 삽입과 삭제
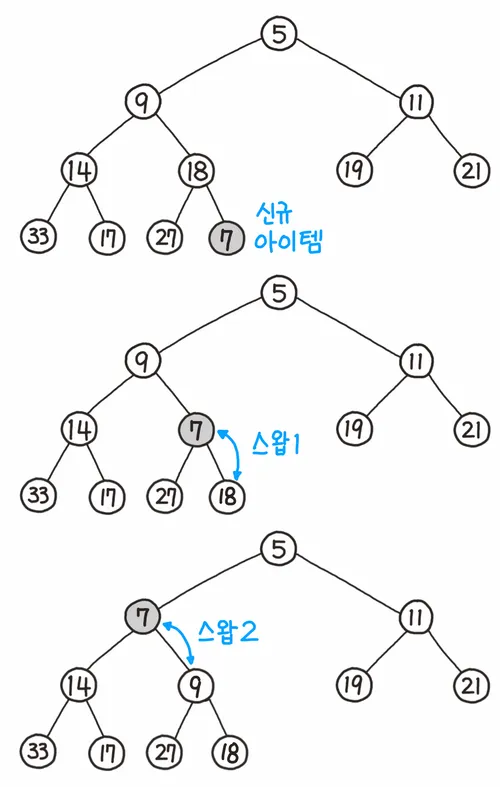
데이터 삽입
- 트리의 가장 끝에 노드를 삽입한다.
- 해당 노드와 부모 노드를 비교하여 규칙에 맞도록 교환한다.
- Heap의 규칙에 맞을 때까지 2번을 반복한다. (Bubble Up)
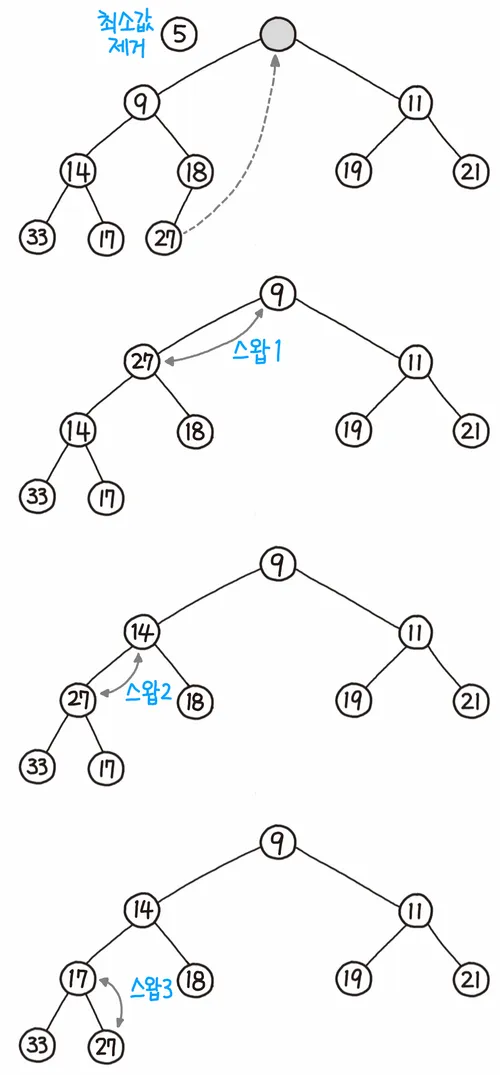
데이터 삭제
- 루트 노드를 삭제한다.
- 트리 가장 끝의 노드를 루트에 위치시킨다.
- 해당 노드와 자식 노드를 비교하여 규칙에 맞도록 교환한다.
- Heap의 규칙에 맞을 때까지 3번을 반복한다. (Bubble Down)
JavaScript의 Heap
C++, Python 등의 언어에는 Heap(또는 우선 순위 큐)를 간편하게 사용할 수 있는 라이브러리 등이 있지만, JavaScript에는 없다...
그래서 최소,최대 Heap을 직접 구현하여 사용해야 한다.
아래는 Class로 구현한 Heap이다.
주석 참고
class Heap {
// 최소, 최대 Heap 구분
constructor(isMinHeap = true) {
this.heap = [];
// Heap의 종류에 따라 다른 비교 연산
this.compare = isMinHeap ? (a, b) => a - b : (a, b) => b - a;
}
// 노드 교환
swap(index1, index2) {
[this.heap[index1], this.heap[index2]] = [this.heap[index2], this.heap[index1]];
}
// 데이터 삽입
insert(value) {
this.heap.push(value);
// 데이터 삽입 후 Heap 규칙에 맞게 정리
this.bubbleUp();
}
bubbleUp() {
// 트리 끝의 노드
let index = this.heap.length - 1;
while(index > 0) {
// 비교할 부모 노드
const parentIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
// 현재 노드의 값이 부모 노드의 값보다 크면(최대힙은 작으면) 끝
if(this.compare(this.heap[parentIndex], this.heap[index]) <= 0) break;
// 규칙에 맞지 않으면 두 노드를 교환
this.swap(parentIndex, index);
// 다음 bubbleUp연산을 위해 교환한 자리의 index를 할당
index = parentIndex;
}
}
// 데이터 삭제
remove() {
// 트리가 비어있으면 null 반환
if(this.heap.length === 0) return null;
// 트리에 노드가 하나이면 바로 삭제 및 반환
if(this.heap.length === 1) return this.heap.pop();
const root = this.heap[0];
// 트리 가장 끝의 노드를 루트로 이동
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop();
// 이동 후 Heap 규칙에 맞게 정리
this.bubbleDown();
// 삭제한 데이터 반환
return root;
}
bubbleDown() {
// 루트(로 이동한) 노드
let index = 0;
const length = this.heap.length;
// 노드가 리프로 갈 때까지 반복
while(index * 2 + 1 < length) {
let betterIndex = index * 2 + 1;
const rightIndex = index * 2 + 2;
// 오른쪽 자식이 존재할 때, 양쪽 자식 노드 중 작은(최대 힙은 큰) 값을 선택
if(rightIndex < length && this.compare(this.heap[rightIndex], this.heap[betterIndex]) < 0) {
betterIndex = rightIndex;
}
// 현재 노드의 값이 자식 노드의 값보다 작으면(최대 힙은 크면) 끝
if(this.compare(this.heap[index], this.heap[betterIndex]) <= 0) break;
// 규칙에 맞지 않으면 두 노드를 교환
this.swap(index, betterIndex);
// 다음 bubbleDown연산을 위해 교환한 자리의 index를 할당
index = betterIndex;
}
}
}
// 사용 예시
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const maxHeap = new Heap(false);
arr.forEach(el => maxHeap.insert(el));
arr.remove();