TCP Reliability
SACK(Selective Acknowledgment)
TCP Flow Control
- Window Size
- Window scale
- Acknowledgments
- (MSS)Maximum Segment Size
- Congestion Avoidance
DHCP
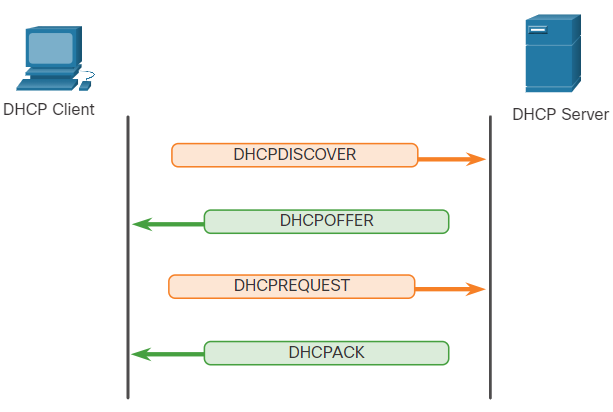
- DHCP가 여러개 있을 경우 Broadcast 통신, Default는 unicast 통신
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPREQUEST
- DHCPACK
1. DHCP 메시지 종류와 흐름
DHCP 클라이언트와 DHCP 서버 간의 통신은 4가지 주요 메시지를 통해 이루어집니다: DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPOFFER, DHCPREQUEST, 그리고 DHCPACK. 이들은 DHCP의 IP 주소 할당 절차를 구성합니다.
1.1 DHCPDISCOVER (클라이언트 -> 서버)
DHCP 클라이언트가 네트워크에 연결되면, IP 주소를 할당받기 위해 DHCPDISCOVER 메시지를 전송합니다.
이 메시지는 브로드캐스트(broadcast) 방식으로 전송되며, 네트워크 내의 모든 DHCP 서버에게 전달됩니다.
브로드캐스트 주소(255.255.255.255)로 전송되기 때문에, 네트워크에 여러 개의 DHCP 서버가 있을 경우 모두가 이 메시지를 수신하고 응답할 수 있습니다.
1.2 DHCPOFFER (서버 -> 클라이언트)
DHCP 서버는 DHCPDISCOVER 메시지를 수신한 후, 사용 가능한 IP 주소와 네트워크 설정을 포함하여 DHCPOFFER 메시지로 응답합니다.
이 단계에서는 서버가 클라이언트에게 할당할 IP 주소와 그 외 필요한 네트워크 정보를 제안합니다.
일반적으로 브로드캐스트 방식으로 전송되지만, 서버가 클라이언트의 MAC 주소를 사용하여 유니캐스트로 보내기도 합니다. 네트워크 구성에 따라 다릅니다.
네트워크에 여러 개의 DHCP 서버가 있다면, 여러 서버로부터 각각 DHCPOFFER 메시지를 받을 수 있습니다.
1.3 DHCPREQUEST (클라이언트 -> 서버)
클라이언트는 여러 개의 DHCPOFFER 중 하나를 선택하여 해당 서버에게 DHCPREQUEST 메시지를 전송합니다. 이 메시지를 통해 제안된 IP 주소와 설정을 받아들이겠다는 의사를 표시합니다.
DHCPREQUEST 메시지는 클라이언트가 선택하지 않은 다른 DHCP 서버들에게도 전송되어 이들이 제안한 IP 주소를 해제하도록 합니다.
이 단계에서는 기본적으로 유니캐스트(unicast) 방식으로 서버에게 직접 응답이 전달됩니다.
1.4 DHCPACK (서버 -> 클라이언트)
DHCP 서버는 클라이언트의 요청을 확인하고, 최종적으로 IP 주소와 네트워크 설정 정보를 클라이언트에게 전달하는 DHCPACK 메시지를 전송합니다.
이 메시지는 유니캐스트 방식으로 클라이언트에게 전달됩니다.
클라이언트는 이 메시지를 수신함과 동시에 IP 주소를 활성화하고 네트워크 연결을 완료합니다.
DHCP 통신 방식: 브로드캐스트와 유니캐스트
기본적으로 DHCP는 브로드캐스트 방식으로 시작하여, 설정이 완료되기 전까지 클라이언트가 IP 주소가 없기 때문에, 모든 장치에게 도달할 수 있도록 합니다.
DHCP 서버가 클라이언트의 네트워크 정보를 파악할 수 있는 경우, 유니캐스트 통신 방식으로 전환하여 특정 서버와 클라이언트 간의 통신이 가능합니다.
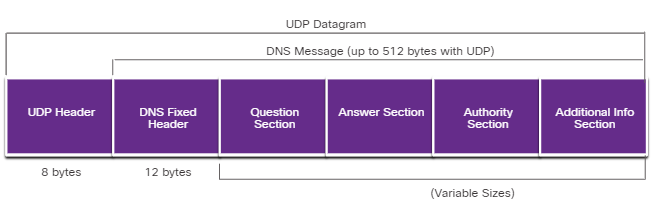
DNS
-
UDP 53
-
Data가 큰 경우 TCP 53을 사용할수도 있다.
-
Recursive queries
- Cache
- Host
- DNS Server
- DDNS(Dynamic DNS)
NAT
FTP & TFTP
Active mode : Control connection (TCP 21), Data Connection(TCP 20)
passive mode : Control connection (TCP 21), Data Connection(Random)
HTTP
-
Hypertext Tansfer Protocol And Hypertext Markup Language
- HTTP Operation
GET - A client request for data. A client (web browser) sends the GET message to the web server to request HTML pages, as shown in the figure.
POST - Submits data to be processed by a resource.
PUT - Uploads resources or content to the web server such as an image.
DELETE - Deletes the resource specified.
OPTIONS - Returns the HTTP methods that the server supports.
CONNECT - Requests that an HTTP proxy server forwards the HTTP TCP session to the desired destination.
- HTTP Operation
-
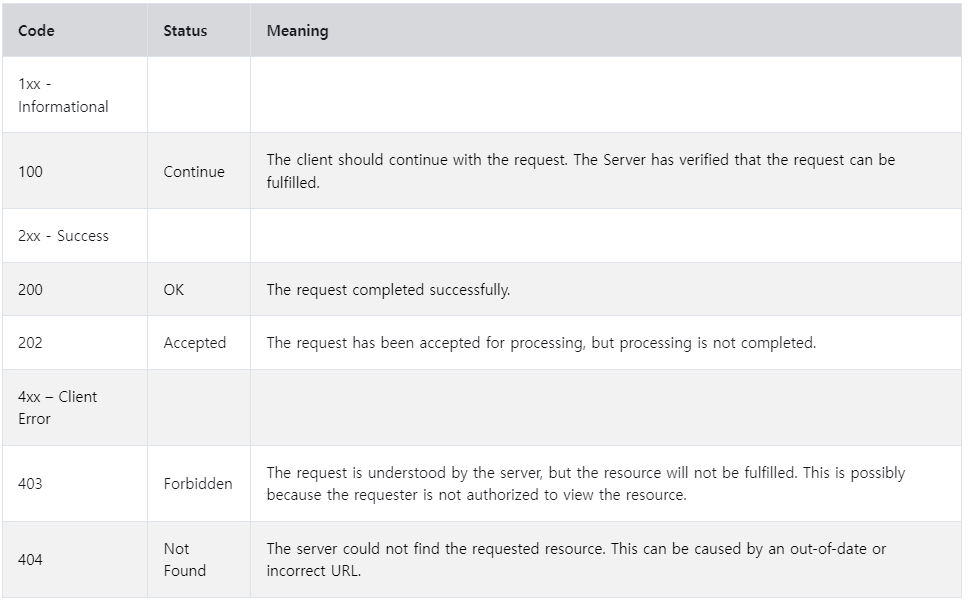
HTTP Status Codes
1xx - Informational
2xx - Success
3xx - Redirection
4xx - Client Error
5xx - Server Error
-
HTTPS
SSL(Secure Socket Layer) : 현재는 많이 사용하지 않음
TLS(Transport Layer Security)
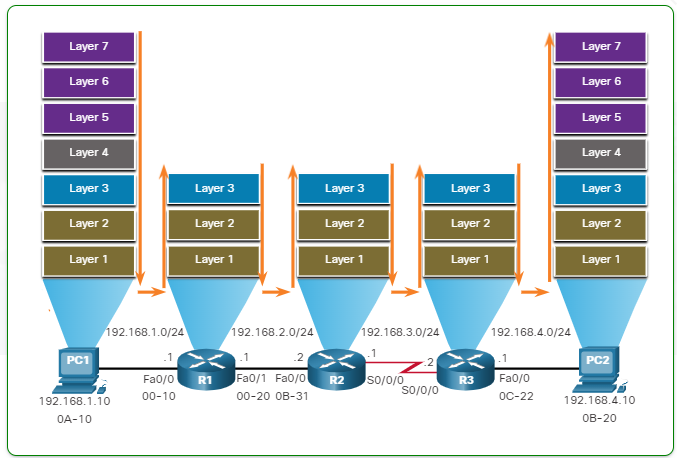
End-Devices
- Router
- MAC : Own
- Destination IP : RIB(routing) -> best-path를 찾는다.
- Filtering : L4
->router(control plane) : Prefix-list - 다양한 Protocol을 지원한다.
Packet Forwarding Decision Process
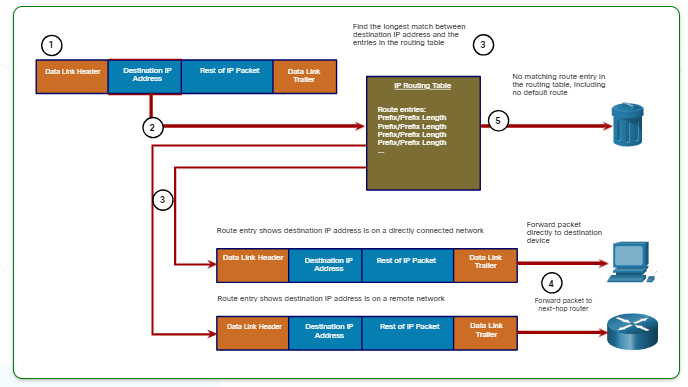
The following steps describe the packet forwarding process shown in the figure:
1. The data link frame with an encapsulated IP packet arrives on the ingress interface.
2. The router examines the destination IP address in the packet header and consults its IP routing table.
3. The router finds the longest matching prefix in the routing table.
4. The router encapsulates the packet in a data link frame and forwards it out the egress interface. The destination could be a device connected to the network or a next-hop router.
5. However, if there is no matching route entry the packet is dropped.
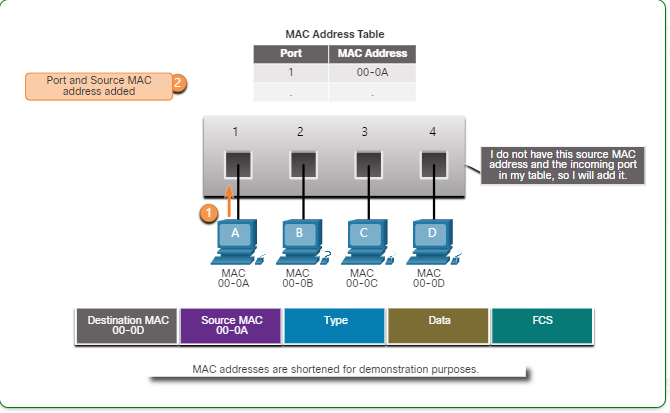
Switching Operation
- Learn - Examining the Source MAC Address
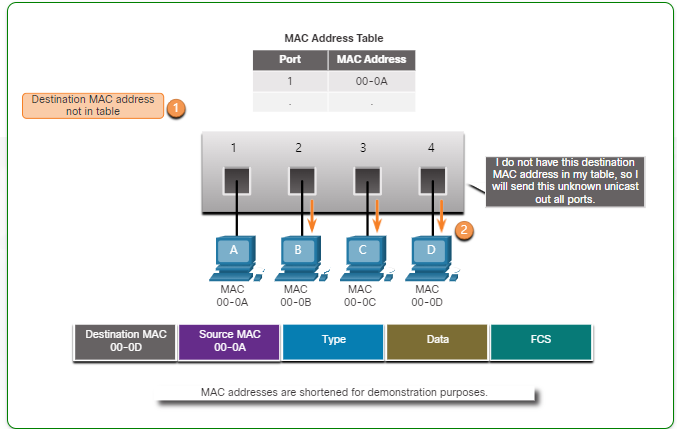
- Forward - Examining the Destination MAC Address
VLAN
STP(Spanning Tree Protocol)
Wireless
- wireless 와 LAN의 차이점
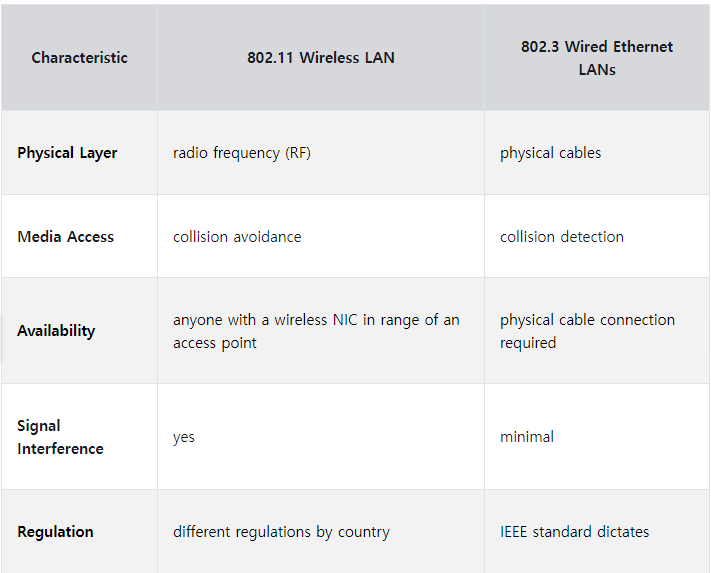
- 공유기를 wireless Router 라고 부른다.
- AP(Access Point)
802.11 Frame Structure
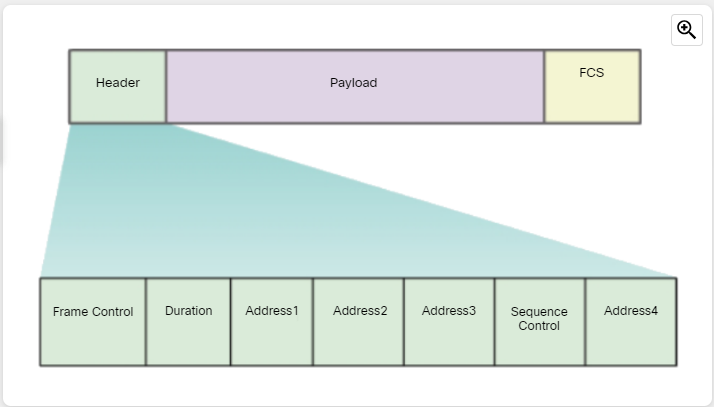
- Frame Control - This identifies the type of wireless frame and contains subfields for protocol version, frame type, address type, power management, and security settings.
- Duration - This is typically used to indicate the remaining duration needed to receive the next frame transmission.
- Address1 - This usually contains the MAC address of the receiving wireless device or AP.(Destination MAC)
- Address2 - This usually contains the MAC address of the transmitting wireless device or AP.(Source MAC)
- Address3 - This sometimes contains the MAC address of the destination, such as the router interface (default gateway) to which the AP is attached.(Router MAC)
Sequence Control - This contains information to control sequencing and fragmented frames. - Address4 - This usually missing because it is used only in ad hoc mode.
- Payload - This contains the data for transmission.
- FCS - This is used for Layer 2 error control.
CSMA/CA
- CSMA(Carrier Sense Multiple Access)/CA(Collision Avoidance)
: 예약제로 사용해서 Collision의 방지한다.
Security Services
- ACL
- SNMP
- NetFlow
- Port Mirroring
- Syslog Servers
- NTP
- AAA Server
- VPN