from collections import deque
N = int(input()); board = [[0] * N for _ in range(N)]
K = int(input())
for i in range(K):
tmp = list(map(int, input().split(' ')))
board[tmp[0]-1][tmp[1]-1] = 2
L = int(input()); turn = {}
for i in range(L):
tmp = input().split(' ')
turn[int(tmp[0])] = tmp[1]
x, y = 0, 0
snake = deque(()); snake.append((x, y))
board[x][y] = 1
dx = [0, 1, 0, -1]
dy = [1, 0, -1, 0]
direction = 0
def rotate(value):
global direction
if value == 'L':
direction = (direction - 1) % 4
else:
direction = (direction + 1) % 4
cnt = 0
while True:
cnt += 1
x += dx[direction]; y += dy[direction]
if x < 0 or x >= N or y < 0 or y >= N:
break
if board[x][y] == 2:
board[x][y] = 1
snake.append((x, y))
if cnt in turn:
rotate(turn[cnt])
elif board[x][y] == 0:
board[x][y] = 1
snake.append((x, y))
tmp_x, tmp_y = snake.popleft()
board[tmp_x][tmp_y] = 0
if cnt in turn:
rotate(turn[cnt])
else:
break
print(cnt)
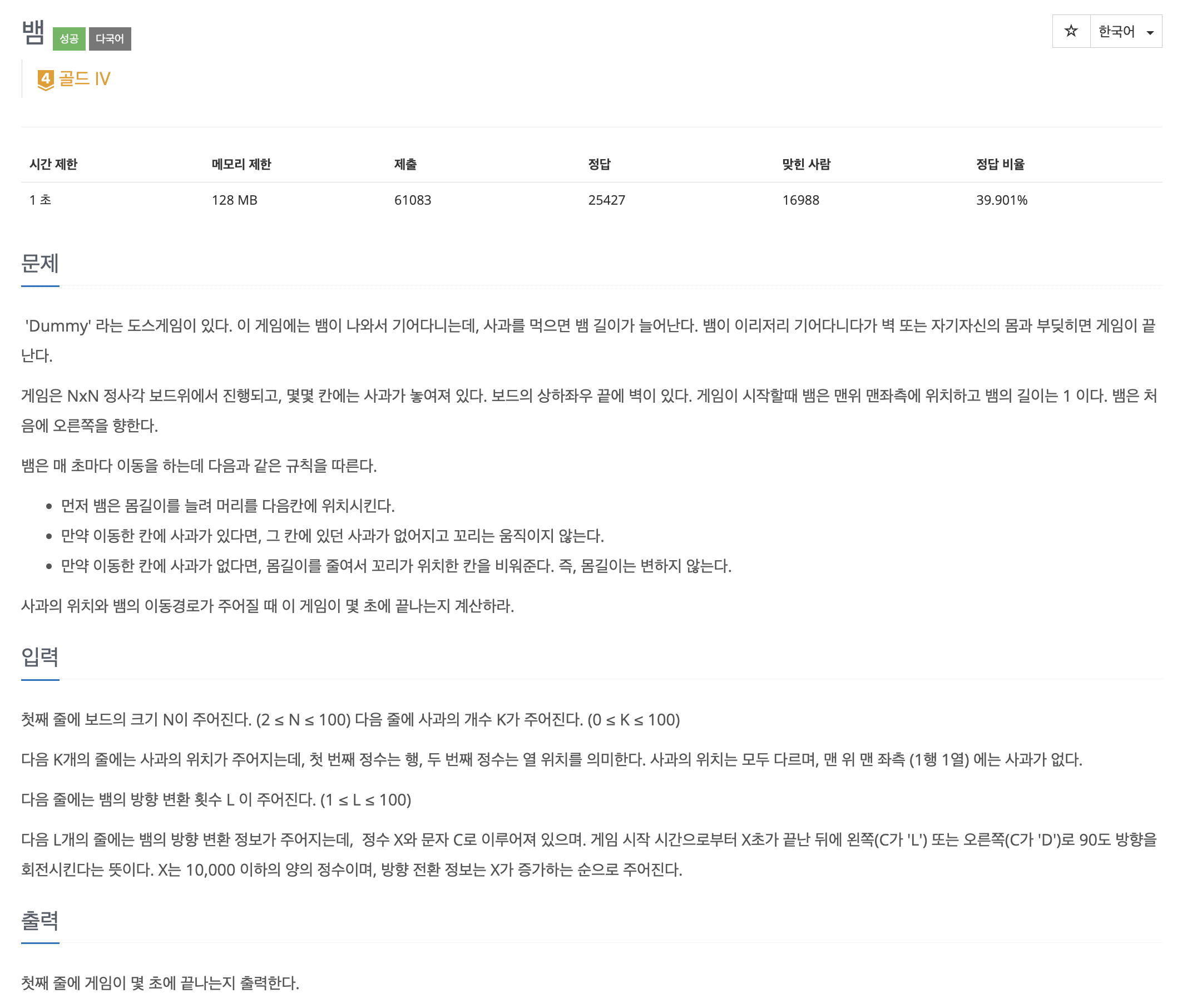
- 보드를 나타내기 위해 board라는 이름의 2차원 list를 정의함
- 기본값: 0, 뱀의 위치: 1, 사과 위치: 2
- snake의 좌표를 저장하기 위해 depue(())를 사용함
- 뱀의 머리는 snake[-1], 뱀의 꼬리는 snake[0]임
- 회전하는 시각을 저장하기 위해 turn이라는 이름의 dictionary를 사용함
- x, y는 현재 x, y 좌표임
x, y = 0, 0
dx = [0, 1, 0, -1]; dy = [1, 0, -1, 0]
direction = 0
def rotate(value):
global direction
if value == 'L';
direction = (direction - 1) % 4
else:
direction = (direction + 1) % 4
- dx = [0, 1, 0, -1], dy = [1, 0, -1, 0], direction = 0을 이용하여 회전하는 경우를 구현함 (x += dx[direction], y += dy[direction])
- ex) direction == 0일 때, x += 0, y += 1이 되므로,
-> 처음 기준 직진
- 1) 이동한 뱀의 머리가 벽에 닿는다면 break
- 2) 이동한 board의 위치에 사과가 있다면 꼬리를 popleft() 하지 않음
- 3) 이동한 board의 위치에 사과가 없다면 꼬리를 popleft() 해줌
- 4) 이동한 board의 위치에 뱀의 몸이 있다면 break


