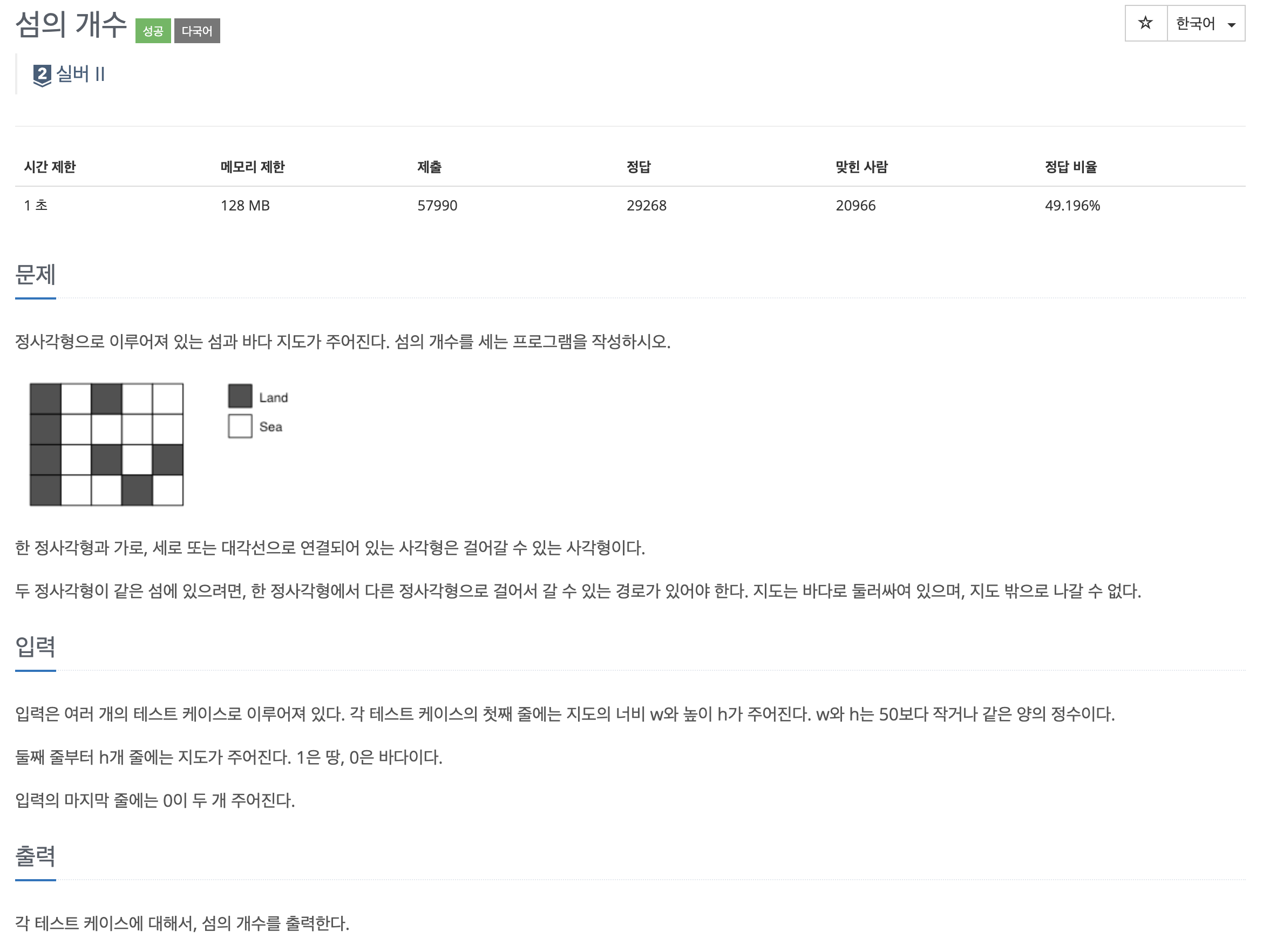
import sys
dx = [0, 0, -1, 1, 1, -1, 1, -1]
dy = [-1, 1, 0, 0, 1, -1, -1, 1]
def dfs(x, y):
global count
if x < 0 or y < 0 or x >= h or y >= w:
return
if Map[x][y] == 1:
count += 1
Map[x][y] = 0
for i in range(8):
dfs(x + dx[i], y + dy[i])
while True:
w, h = map(int, input().split(' ')); Map = []
if w == 0 and h == 0: break
else:
for _ in range(h):
tmp = list(map(int, sys.stdin.readline()[:-1].split(' ')))
Map.append(tmp)
count = 0; count_list = []
for x in range(h):
for y in range(w):
if Map[x][y] == 1:
dfs(x, y)
count_list.append(count)
count = 0
print(len(count_list))
- 2중 for문을 돌며 Map이 1인 경우 dfs 순회 시작
- Map 밖을 접근하는 경우 return
- Map에서 해당 위치의 값이 1인 경우 count +=1을 해주고 해당 위치를 0으로 바꿔줌. 그 후 주변 (dx = [0, 0, -1, 1, 1, -1, 1, -1], dy = [-1, 1, 0, 0, 1, -1, -1, 1]) 탐색 시작

