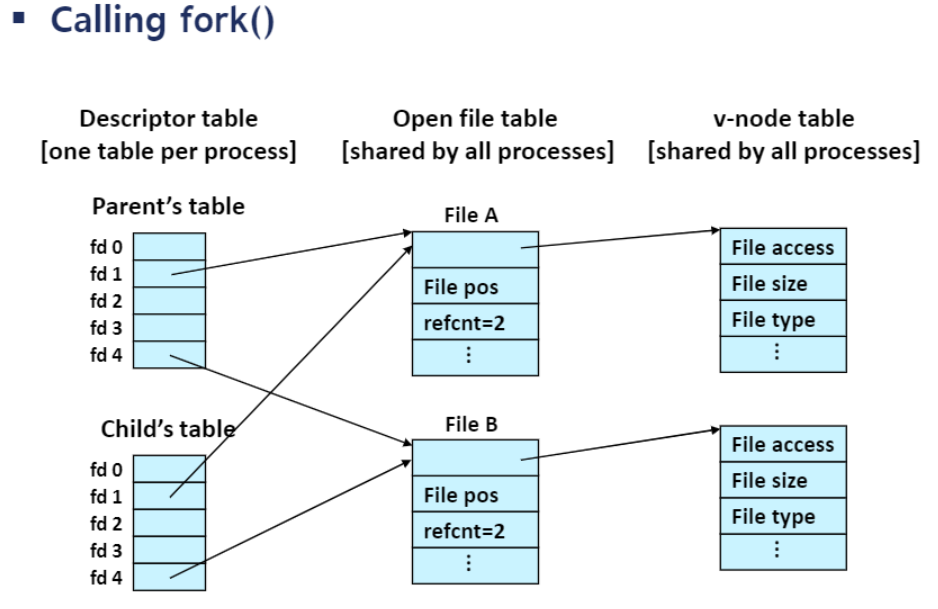
Inter-Process Communication
-> Mechanism for communication between process
-> Signals, I/O redirection, Anonymous pipe, Named pipe (FIFO), Shared Memory, Message Queue ...



int main(void){
char c;
int fd = open(“temp.txt", O_RDONLY);
if (fork() == 0) {
read(fd, &c, 1);
exit(0);
}
else {
wait(NULL);
read(fd, &c, 1);
printf(“c=%c\n”,c); //c=y
}
return 0;
}Q. How does a shell implement I/O redirection?
A. dup2(oldfd, newfd)
-> Copies (per-process) descriptor table entry oldfd to entry newfd
int main()
{
printf("ls > out.txt example\n");
int f = open("out.txt", O_WRONLY|O_CREAT, 0666);
if(fork() == 0){
dup2(f, 1);
execl("/bin/ls","/bin/ls",NULL);
}
wait(NULL);
return 0;
}int pipe (int fd[2]);
fd[0]: open for reading
fd[1]: open for writing
-> The output of fd[1] is the input for fd[0]

Anonymous pipe
parent -> child:
parent closes fd[0];
child closes fd[1];
or
parent <- child:
parent closes fd[1];
child closes fd[0];
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXLINE 80
int main(void)
{
int n, fd[2];
pid_t pid;
char line[MAXLINE];
if(pipe(fd) < 0) exit(1);
if((pid = fork()) < 0) exit(2);
if (pid> 0) { /* parent */
close(fd[0]);
write(fd[1], "hello world\n", 12);}
else { /* child */
close(fd[1]);
n = read(fd[0], line, MAXLINE);
write(1, line, n);
}
exit(0);
}Make mini shell which supports I/O redirection & pipes
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int main()
{
char *cmd = NULL;
size_t size = 0;
char *arg[11];
while(1){
int i = 0;
getline(&cmd, &size, stdin);
cmd[strlen(cmd) - 1] = '\0';
if(strlen(cmd) == 0)
continue;
char *ptr = strtok(cmd, " ");
while(ptr != NULL){
arg[i++] = ptr;
ptr = strtok(NULL, " ");
}
arg[i] = NULL;
if(strcmp("quit", arg[0]) == 0) //"quit"
break;
char path[100];
sprintf(path, "/bin/%s", arg[0]);
for(int x = 0; x < i; x++){
if(strcmp(">", arg[x]) == 0){ //output redirection
int fd = open(arg[x+1], O_RDWR|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC, 0644);
if(fork() == 0){
dup2(fd, STDOUT_FILENO);
arg[x] = NULL;
execv(path, arg);
}
wait(NULL);
close(fd);
break;
}
else if(strcmp(">>", arg[x]) == 0){ //output redirection (appending)
int fd = open(arg[x+1], O_RDWR|O_APPEND, 0644);
if(fork() == 0){
dup2(fd, STDOUT_FILENO);
arg[x] = NULL;
execv(path, arg);
}
wait(NULL);
close(fd);
break;
}
else if(strcmp("<", arg[x]) == 0){ //input redirection
int fd = open(arg[x+1], O_RDONLY);
if(fork() == 0){
dup2(fd, STDIN_FILENO);
arg[x] = NULL;
execv(path, arg);
}
wait(NULL);
close(fd);
break;
}
else if(strcmp("|", arg[x]) == 0){ //pipeline
int fd[2];
pid_t pid1, pid2;
if(pipe(fd) < 0) exit(1);
if((pid1 = fork()) == 0){ //parent
close(fd[0]);
dup2(fd[1], STDOUT_FILENO);
arg[x] = NULL;
execv(path, arg);
}
wait(NULL);
if((pid2 = fork()) == 0){ //child
close(fd[1]);
char **arg2 = &arg[x + 1];
sprintf(path, "/bin/%s", arg2[0]);
dup2(fd[0], STDIN_FILENO);
execv(path, arg2);
}
close(fd[0]);
close(fd[1]);
wait(NULL);
break;
}
else if(strcmp("exit", arg[x]) == 0){ //exit
if(arg[x+1] != NULL){
int no = atoi(arg[x+1]);
printf("%d\n", no);
exit(no);
}
else{
printf("%d\n", 0);
exit(0);
}
}
} //for loop end
}
