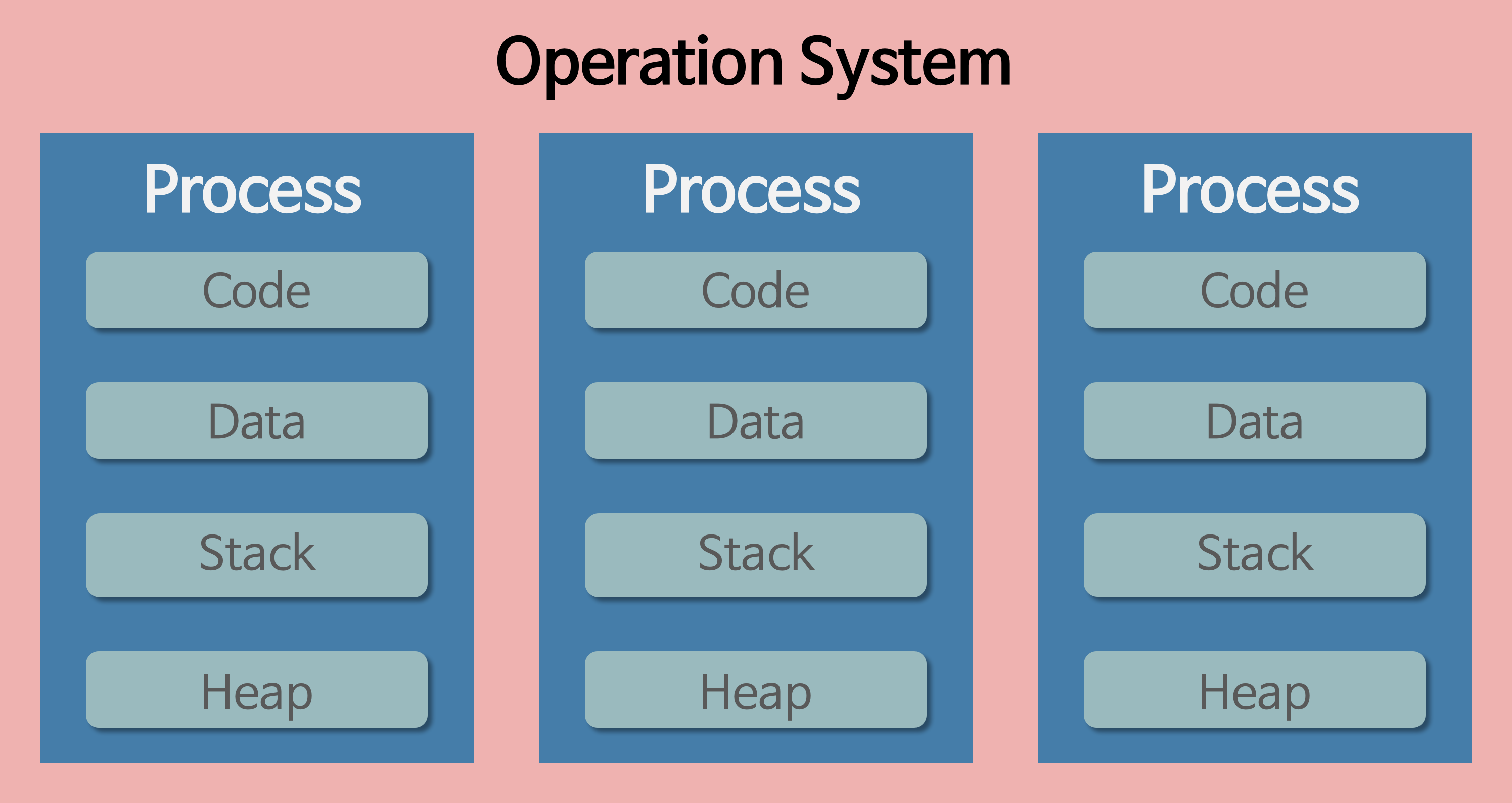
Process: One address space per process/ Each process has its own data(global variables), stack, heap

Thread: Multiple thread share on address space/ its own stack and register context/ Threads within the same address space share data(global variables), heap

In GNU Compiler, add -lpthread to compile pthread programs
-> Makefile도 그래서 다음과 같이 구성됨
TARGET=p12
OBJECT=main.o
CXX=gcc
CXXFLAGS=-w
$(TARGET): $(OBJECT)
$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) -o $@ $(OBJECT) -lpthread
main.o: main.c
$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) -c main.c
clean:
rm $(OBJECT) $(TARGET)int pthread_create (pthread_t thread, pthread_attr_t attr, void (start_routine)(void ), void arg)
void pthread_exit (void *retval)
-> It does not close files
int pthread_cancel (pthread_t thread)
int pthread_join (pthread_t thread, void **retval)
#define NUM_THREADS 4
void *thread(void *arg) {
long id = (long)arg;
printf("thread#%ld: Hello Thread!\n", id);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid[NUM_THREADS];
long t;
for (t = 0; t < NUM_THREADS; t++){
printf("main: creating thread#%ld\n", t);
if (pthread_create(&tid[t], NULL, thread, (void*)t)){
printf("ERROR: pthread creation failed.\n");
exit(1);
}
}
for (t = 0; t < NUM_THREADS; t++){
pthread_join(tid[t], NULL);
}
printf("main: bye bye!\n");
return 0;
}과제 내용
- Multiplication result of M N matrix and N 1 vector is M * 1 vector
- Row size(M), column size(N) of matrix are received by command line argument
- Elements of matrix and vector are randomly assigned between 0~9 (data type is int)
- Create threads as much as the row size(M)
- Each thread performs a calculation on one row of the matrix
- thread_id and calculation results are deliverd through the struct thread_data
- Main function must wait other threads to terminate
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct{
//define return struct for thread_exit
long id;
int x;
}thread_data;
int **matrix;
int *vector;
int M, N;
void *thread(void *arg){
long tmp = (long)arg;
//Calculate matrix[t] * vector and return result using thread_data struct
thread_data *result = (thread_data *)malloc(sizeof(thread_data));
int value, sum = 0;
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
value = matrix[tmp][i] * vector[i];
sum += value;
}
result->id = tmp;
result->x = sum;
pthread_exit((void*)result);
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
M = (*argv[1]) - '0';
N = (*argv[2]) - '0';
pthread_t *tid = (pthread_t *)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * M);
printf(" *** Matrix ***\n");
matrix = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*)*M);
for(int i=0; i<M; i++){
matrix[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*N);
for(int j=0; j<N; j++){
matrix[i][j] = rand()%10;
printf("[ %d ] ", matrix[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf(" *** Vector ***\n");
vector = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*N);
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
vector[i] = rand()%10;
printf("[ %d ] \n", vector[i]);
}
// Create new thread to calculate Rows
long t;
for(t = 0; t < M; t++){
if(pthread_create(&tid[t], NULL, thread, (void*)t)){
printf("ERROR: pthread creation failed.\n");
exit(1);
}
}
printf(" *** Result ***\n");
// print the result, get thread_data struct from threads using thread_join() function.
for(t = 0; t < M; t++){
thread_data *res;
pthread_join(tid[t], (void**)&res);
printf("[ %d ]\n", res->x);
}
return 0;
}-> matrix랑 vector, M이랑 N은 전역변수로 선언
-> pthread_create()로 M만큼 thread 생성
-> pthread_exit()의 반환값을 받기 위해 thread_data 구조체를 위와 같이 선언
-> void thread()는 thread 함수 (주소값 == 8byte -> long으로 선언된 tmp에 할당)
-> pthread_exit()에서 thread_data를 void 로 cast하여 값을 반환함
-> pthread_join()을 이용해 (multi process에서 wait()랑 비슷) 값 받기

실행결과
