
이번 문제는 LeetCode의 1번 문제입니다. 한 번 살펴볼까요?
1. 오늘의 학습 키워드
- Brute Force
- Two Pointer
- Hash Table
2. 문제: 1. Two Sum
- 단계: Easy
- 주제: Array, Hash Table
- 출처: https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum/description/
1. Two Sum
Given an array of integers nums and an integer target, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to target.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution, and you may not use the same element twice.
You can return the answer in any order.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
Output: [0,1]
Explanation: Because nums[0] + nums[1] == 9, we return [0, 1].
Example 2:
Input: nums = [3,2,4], target = 6
Output: [1,2]
Example 3:
Input: nums = [3,3], target = 6
Output: [0,1]
Constraints:
2 <= nums.length <= 10^4-10^9 <= nums[i] <= 10^9-10^9 <= nums[i] <= 10^9- Only one valid answer exists.
Follow-up:
Can you come up with an algorithm that is less than time complexity?
3. 문제 풀이
이 문제는 배열에서 두 수를 찾아 합이 target이 되는 인덱스를 반환하는 문제로, 다양한 방법으로 접근할 수 있습니다.
Step1. 문제 이해하기
- Input:
- 정수 배열
nums와 정수target이 주어집니다.
- 정수 배열
- Output:
target합을 이루는 두 요소의 인덱스를 반환해야 하며, 가능한 답이 하나만 존재합니다.
- Constraints:
- nums[i]의 값이나
target값의 크기는 시간 복잡도에 큰 영향을 주지 않습니다.nums배열에서target이 되는 두 값의 인덱스를 찾기 때문에nums배열의 길이가 가장 중요합니다.
- nums[i]의 값이나
Step2. 접근 방법
- 문제 단순화 or 극한화 및 자료구조 선택:
-
일단 완전 탐색(Brute Force)로 풀 수 있는지 살펴보았습니다. 사실 이 문제를 보자마자 완전 탐색으로 풀 수 있다는 생각이 들었는데요.
nums배열에서target이 될 수 있는 두 값의 인덱스를 찾기 때문에 완전 탐색을 직관적으로 사용하기에 적합한 문제였습니다. 그리고nums배열의 길이가 10^4이므로 O(n^2)으로 된다면 간당간당하게 완전 탐색으로 풀 수 있는 문제입니다. -
또다른 방법을 파악하기 위해, 문제를 단순화 및 극한화를 해볼까요?
nums배열에서 두 지점을 잡고target이 될 수 있는지 없는지 해볼까? 이렇게 하면 O(n^2)이 아닌 O(n)으로 할 수 있지 않나?
-
마지막으로 자료구조를 활용할 수 없을끼요?
- 원하는 값이 어떤 자료구조에 있는지 확인할 때 파이썬에서 in 연산자를 사용하는데, 리스트에서 in 연산자를 사용하면 O(n)의 시간복잡도가 들지만, 해시 테이블은 O(1)의 시간복잡도가 나옵니다.즉, 투 포인터 방법과 해시 테이블을 사용하면 완전 탐색의 시간 복잡도인 O(n^2)보다 훨씬 효율적으로 진행할 수 있습니다.
-
Brute Force 풀이
class Solution(object):
def twoSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
for i in range(len(nums)):
for j in range(i+1,len(nums)):
if nums[i] + nums[j] == target:
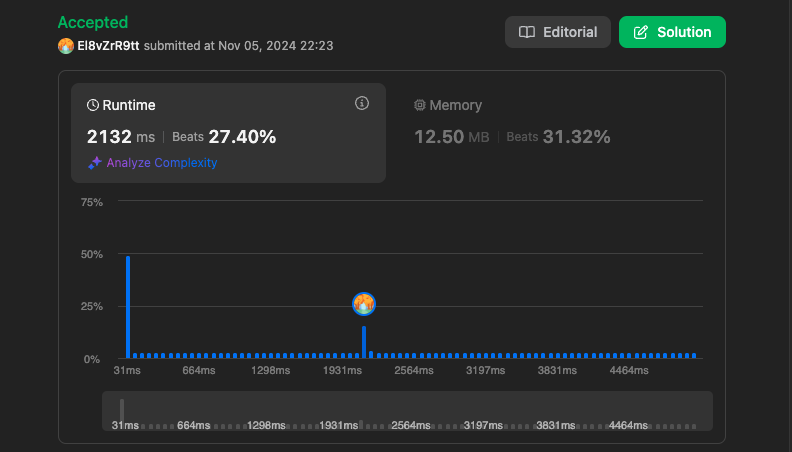
return [i, j]시간 복잡도
- 의 시간복잡도가 나옵니다.
결과
https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum/submissions/1443828948
Two Pointer 풀이
class Solution(object):
def twoSum(self,nums,target):
nums = [[n,i] for i,n in enumerate(nums)]
nums.sort(key=lambda x:x[0])
l = 0
r = len(nums)-1
while l < r:
num_sum = nums[l][0] + nums[r][0]
if num_sum == target:
return [nums[l][1],nums[r][1]]
elif num_sum < target:
l += 1
else:
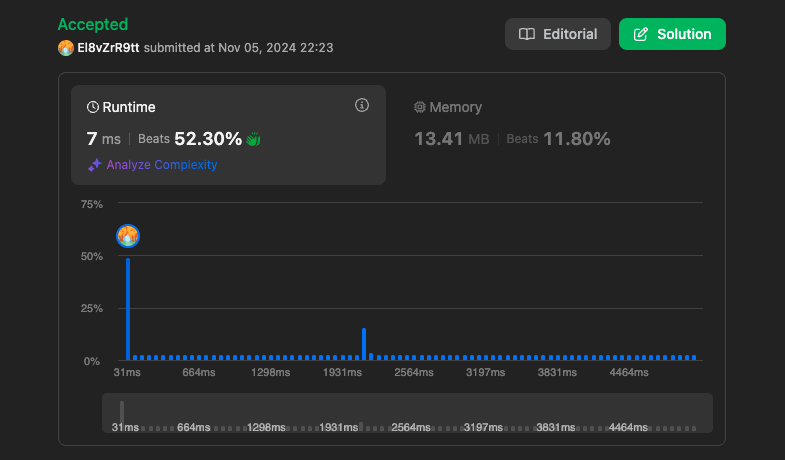
r -= 1시간 복잡도
결과
https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum/submissions/1443829444
Hash Table 풀이
class Solution(object):
def twoSum(self,nums,target):
hash_table = {}
for i,num in enumerate(nums):
needed = target - num
if needed in hash_table:
return [i,hash_table[needed]]
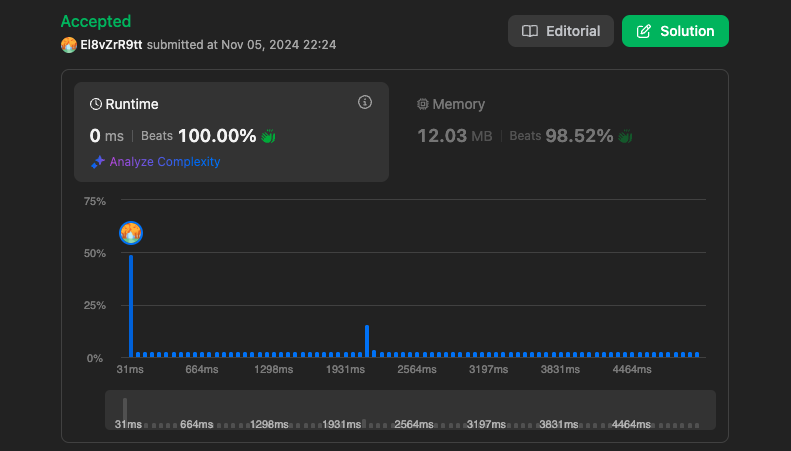
hash_table[num] = i시간 복잡도
결과
https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum/submissions/1443829967
4. 마무리
Two Sum 문제는 여러 알고리즘으로 접근할 수 있으며, 특히 해시 테이블을 사용하면 시간 복잡도를 크게 개선할 수 있습니다. 이 문제는 실무에서도 자주 등장하는 알고리즘 문제로, 배열 내 요소 간 합 문제에 효율적으로 접근하는 방법을 배울 수 있습니다.
전체 코드는 다음 링크에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
읽어주셔서 감사합니다!!
계속 발전하는 개발자가 되기를!!

