저번 시간에는 큐 자료구조에 대해 알아보았는데요.
오늘은 링크드 리스트에 대한 내용을 알아보도록 하겠습니다.
1. 링크드 리스트 개념
링크드 리스트(Linked List)는 각 요소(Node)가 데이터와 다음 요소를 가리키는 포인터를 가지고 있는 선형 데이터 구조입니다. 배열과 달리, 링크드 리스트의 요소들은 메모리상에서 연속적으로 위치하지 않으며, 각 요소는 다른 요소의 주소를 포함하여 리스트를 형성합니다.
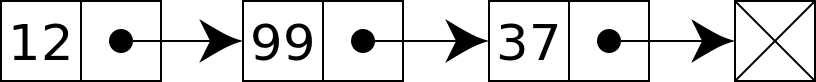
링크드 리스트의 장점
- 동적 크기 조절: 배열은 크기가 고정되어 있지만, 링크드 리스트는 필요에 따라 크기를 동적으로 조절할 수 있습니다.
- 효율적인 삽입/삭제: 배열의 경우 요소를 삽입하거나 삭제할 때 모든 요소를 이동해야 할 수도 있지만, 링크드 리스트는 단순히 포인터를 변경하는 것으로 가능합니다.
링크드 리스트의 단점
- 랜덤 접근 불가: 배열은 인덱스를 통해 O(1) 시간 복잡도로 요소에 접근할 수 있지만, 링크드 리스트는 O(n) 시간이 걸립니다.
- 추가 메모리 사용: 포인터를 저장하기 위한 추가 메모리가 필요합니다.
2. 파이썬으로 링크드 리스트 구현
이제 파이썬으로 단일 연결 리스트(Singly Linked List)를 구현하는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다.
class Node:
def __init__(self,data):
self.data = data # 노드가 저장하는 데이터
self.next = None # 다음 노드를 가리키는 포인터
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self,data):
self.head = Node(data) # 링크드 리스트의 첫번째 데이터
def append(self,data):
if self.head is None:
self.head = Node(data)
else:
node = self.head
while node.next:
node = node.next
node.next = Node(data)
def print_linked_list(self):
current = self.head
while current:
print(current.data,end=' -> ')
current = current.next
print('None')
def delete(self,data):
if self.head == '':
print('This data is not in our linked list')
return
if self.head.data == data:
tmp = self.head
self.head = self.head.next
tmp = None
else:
current = self.head
while current.next:
if current.next.data == data:
tmp = current.next
current.next = current.next.next
tmp = None
return
else:
current = current.next
def insert_before(self,target_data,data): # target_data 앞에 data를 삽입하는 메서드
if self.head is None:
print('Linked List is empty')
return
if self.head.data == target_data:
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
return
current = self.head
while current.next and current.next.data != target_data:
current = current.next
if current.next is None:
print(f"Node with data {target_data} not found.")
else: # current.next가 target_data일 때
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = current.next
current.next = new_node
def insert_after(self,target_data,data): # target_data 뒤에 data를 삽입하는 메서드
if self.head is None:
print('Linked List is empty')
return
current = self.head
while current is not None:
if current.data == target_data:
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = current.next
current.next = new_node
return
current = current.next
# target_data를 찾지 못한 경우
print(f'Node with data {target_data} not found.')
# 링크드 리스트 사용 예제
if __name__ == '__main__':
ll = LinkedList(0)
# 1부터 11 넣기
for i in range(1,11):
ll.append(i)
# 결과 출력
ll.print_linked_list() # 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> 9 -> 10 -> None
ll.delete(5)
ll.print_linked_list() # 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> 9 -> 10 -> None
# 5 앞에 99 삽입
ll.insert_before(5, 99) # Node with data 5 not found.
ll.print_linked_list() # 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> 9 -> 10 -> None
# 6 앞에 99 삽입
ll.insert_before(6, 99)
ll.print_linked_list() # 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 99 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> 9 -> 10 -> None
# 0 뒤에 15 삽입 (헤드 노드 뒤에 삽입하는 경우)
ll.insert_after(0, 15)
ll.print_linked_list() # 0 -> 15 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 99 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> 9 -> 10 -> None
# 8 뒤에 77 삽입
ll.insert_after(8,77)
ll.print_linked_list() # 0 -> 15 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 99 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> 77 -> 9 -> 10 -> None
3. 링크드 리스트의 주요 연산
위의 코드에서 링크드 리스트의 기본 연산인 삽입(append)과 출력(print_list)을 구현했습니다. 다음으로 추가할 수 있는 연산은 다음과 같습니다:
- 삽입 연산: 원하는 위치에 노드를 삽입하는 방법 (예: 맨 앞, 중간, 끝)
- 삭제 연산: 특정 노드를 삭제하는 방법
- 탐색 연산: 특정 값을 가진 노드를 찾는 방법
- 길이 계산: 리스트의 길이를 계산하는 방법
4. 코드 상세 설명
위에서 파이썬으로 링크드 리스트를 구현하는 방법을 살펴보았습니다. 이제 각 메서드의 동작을 하나씩 자세히 설명하며, 어떻게 링크드 리스트가 작동하는지 이해해 보도록 하겠습니다.
Node 클래스
링크드 리스트는 Node라는 기본 단위로 구성됩니다. Node 클래스는 각 노드가 저장하는 데이터와 다음 노드를 가리키는 포인터를 가지고 있습니다.
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data # 노드가 저장하는 데이터
self.next = None # 다음 노드를 가리키는 포인터
data: 노드가 저장하는 실제 데이터입니다.next: 다음 노드를 가리키는 포인터입니다. 새 노드를 생성할 때는 이 포인터가None으로 설정됩니다.
LinkedList 클래스
LinkedList 클래스는 전체 리스트를 관리합니다. 이 클래스는 리스트의 첫 번째 노드인 헤드를 저장하고, 여러 가지 리스트 연산을 제공합니다.
__init__ 메서드
리스트의 첫 번째 노드를 초기화합니다. 이 메서드는 리스트가 생성될 때 호출됩니다.
def __init__(self, data):
self.head = Node(data) # 링크드 리스트의 첫 번째 노드
- 헤드 노드:
self.head는 리스트의 시작을 가리키는 중요한 포인터입니다. 초기화할 때 리스트의 첫 번째 데이터를 받아 이 데이터를 가지는 첫 번째 노드를 생성합니다.
append 메서드
리스트의 끝에 새로운 노드를 추가하는 메서드입니다.
def append(self, data):
if self.head is None:
self.head = Node(data)
else:
node = self.head
while node.next:
node = node.next
node.next = Node(data)
- 헤드 노드가 없는 경우: 리스트가 비어 있는 경우, 새로운 노드를 생성하고 이를 헤드 노드로 설정합니다.
- 리스트 순회 및 추가: 헤드 노드부터 시작하여 리스트의 끝까지 순회한 후, 마지막 노드의
next포인터를 새로운 노드로 설정합니다.
print_linked_list 메서드
리스트의 모든 노드를 출력하는 메서드입니다.
def print_linked_list(self):
current = self.head
while current:
print(current.data, end=' -> ')
current = current.next
print('None')
- 순회 및 출력: 리스트의 헤드부터 시작하여 각 노드의 데이터를 출력하고,
next포인터를 따라가며 리스트의 끝까지 출력합니다. 리스트의 마지막에는None을 출력하여 리스트의 끝임을 나타냅니다.
delete 메서드
특정 데이터를 가진 노드를 삭제하는 메서드입니다.
def delete(self, data):
if self.head is None:
print('This data is not in our linked list')
return
if self.head.data == data:
tmp = self.head
self.head = self.head.next
tmp = None
else:
current = self.head
while current.next:
if current.next.data == data:
tmp = current.next
current.next = current.next.next
tmp = None
return
else:
current = current.next
- 헤드 노드 삭제: 만약 삭제하려는 데이터가 헤드 노드에 있다면, 헤드를 다음 노드로 이동시켜 리스트에서 첫 번째 노드를 삭제합니다.
- 리스트 순회 및 삭제: 삭제하려는 데이터를 가진 노드를 찾을 때까지 리스트를 순회하고, 해당 노드를 삭제하여 리스트에서 제거합니다.
insert_before 메서드
특정 노드 앞에 새로운 노드를 삽입하는 메서드입니다.
def insert_before(self, target_data, data): # target_data 앞에 data를 삽입하는 메서드
if self.head is None:
print('Linked List is empty')
return
if self.head.data == target_data:
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
return
current = self.head
while current.next and current.next.data != target_data:
current = current.next
if current.next is None:
print(f"Node with data {target_data} not found.")
else: # current.next가 target_data일 때
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = current.next
current.next = new_node
- 리스트가 비어 있는 경우: 리스트가 비어 있으면 삽입할 수 없으므로 함수는 종료됩니다.
- 헤드 노드 앞에 삽입: 만약
target_data가 헤드 노드의 데이터와 일치하면, 새로운 노드를 헤드로 설정합니다. - 리스트 순회 및 삽입:
target_data를 가진 노드를 찾을 때까지 리스트를 순회하고, 해당 노드 앞에 새로운 노드를 삽입합니다.
insert_after 메서드
특정 노드 뒤에 새로운 노드를 삽입하는 메서드입니다.
def insert_after(self, target_data, data): # target_data 뒤에 data를 삽입하는 메서드
if self.head is None:
print('Linked List is empty')
return
current = self.head
while current is not None:
if current.data == target_data:
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = current.next
current.next = new_node
return
current = current.next
print(f'Node with data {target_data} not found.')
- 리스트가 비어 있는 경우: 리스트가 비어 있으면 삽입할 수 없으므로 함수는 종료됩니다.
- 리스트 순회 및 삽입:
target_data를 가진 노드를 찾을 때까지 리스트를 순회하고, 해당 노드 뒤에 새로운 노드를 삽입합니다.
5. 링크드 리스트 예제
마지막으로, 구현한 메서드들을 활용하여 링크드 리스트를 어떻게 사용하는지 예제를 통해 살펴보겠습니다.
# 링크드 리스트 사용 예제
if __name__ == '__main__':
ll = LinkedList(0)
# 1부터 10까지 데이터를 삽입
for i in range(1, 11):
ll.append(i)
# 리스트 출력
ll.print_linked_list() # 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> 9 -> 10 -> None
# 특정 노드 삭제
ll.delete(5)
ll.print_linked_list() # 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> 9 -> 10 -> None
# 특정 노드 앞에 데이터 삽입
ll.insert_before(6, 99)
ll.print_linked_list() # 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 99 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> 9 -> 10 -> None
# 특정 노드 뒤에 데이터 삽입
ll.insert_after(8, 77)
ll.print_linked_list() # 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 99 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> 77 -> 9 -> 10 -> None
이 코드는 링크드 리스트의 다양한 연산을 보여주는 좋은 예제입니다. 삽입, 삭제, 그리고 리스트 출력과 같은 기본적인 연산들이 어떻게 작동하는지 확인할 수 있습니다.
흐음,, 좀 복잡하죠? 하지만 한 발 더 남았습니다.😔
할 수 있습니다!! 다시 집중해볼까요?

6. 이중 연결 리스트(Doubly Linked List)란?
이중 연결 리스트는 단일 연결 리스트와 비슷하지만, 각 노드가 두 개의 포인터(next와 prev)를 가지는 구조로, 양방향으로 리스트를 순회할 수 있습니다. 이중 연결 리스트는 삽입과 삭제 작업이 양쪽 방향에서 모두 가능하기 때문에 더 유연한 데이터 구조를 제공합니다.

이중 연결 리스트의 장점
- 양방향 순회 가능: 리스트의 앞쪽과 뒤쪽 모두로 이동할 수 있습니다.
- 더 빠른 삽입/삭제: 특정 위치에서의 삽입 및 삭제 작업이 양쪽에서 모두 가능하여 더 효율적입니다.
이중 연결 리스트의 단점
- 추가 메모리 사용: 각 노드가 두 개의 포인터(
next와prev)를 가지기 때문에 메모리 사용이 더 큽니다. - 구현 복잡성: 포인터가 두 개이기 때문에 코드가 복잡해질 수 있습니다.
7. 파이썬으로 이중 연결 리스트 구현
이제 이중 연결 리스트를 파이썬으로 구현하는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다.
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data # 노드가 저장하는 데이터
self.next = None # 다음 노드를 가리키는 포인터
self.prev = None # 이전 노드를 가리키는 포인터
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self, data):
self.head = Node(data) # 리스트의 첫 번째 노드
def append(self, data):
if self.head is None:
self.head = Node(data)
else:
node = self.head
while node.next:
node = node.next
new_node = Node(data)
node.next = new_node
new_node.prev = node # 새 노드의 prev를 마지막 노드로 설정
def print_linked_list(self):
current = self.head
while current:
print(current.data, end=' <-> ')
current = current.next
print('None')
def delete(self, data):
if self.head is None:
print('This data is not in our linked list')
return
if self.head.data == data:
tmp = self.head
self.head = self.head.next
if self.head:
self.head.prev = None # 헤드 노드의 prev를 None으로 설정
tmp = None
else:
current = self.head
while current.next:
if current.next.data == data:
tmp = current.next
current.next = current.next.next
if current.next:
current.next.prev = current # 삭제된 노드의 다음 노드의 prev를 현재 노드로 설정
tmp = None
return
else:
current = current.next
def insert_before(self, target_data, data):
if self.head is None:
print('Linked List is empty')
return
if self.head.data == target_data:
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head.prev = new_node
self.head = new_node
return
current = self.head
while current.next and current.next.data != target_data:
current = current.next
if current.next is None:
print(f"Node with data {target_data} not found.")
else:
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = current.next
new_node.prev = current
current.next.prev = new_node
current.next = new_node
def insert_after(self, target_data, data):
if self.head is None:
print('Linked List is empty')
return
current = self.head
while current is not None:
if current.data == target_data:
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = current.next
new_node.prev = current
if current.next:
current.next.prev = new_node
current.next = new_node
return
current = current.next
print(f'Node with data {target_data} not found.')
8. 이중 연결 리스트의 주요 연산
위 코드에서는 이중 연결 리스트의 기본 연산을 구현했습니다. 이제 각 메서드가 어떻게 작동하는지 살펴보겠습니다.
append 메서드
리스트의 끝에 새로운 노드를 추가합니다.
def append(self, data):
if self.head is None:
self.head = Node(data)
else:
node = self.head
while node.next:
node = node.next
new_node = Node(data)
node.next = new_node
new_node.prev = node # 새 노드의 prev를 마지막 노드로 설정
- 리스트가 비어 있으면 헤드 노드를 설정하고, 비어 있지 않으면 리스트 끝까지 순회한 후 새로운 노드를 추가합니다. 새 노드의
prev포인터는 마지막 노드를 가리킵니다.
print_linked_list 메서드
리스트의 모든 노드를 출력합니다.
def print_linked_list(self):
current = self.head
while current:
print(current.data, end=' <-> ')
current = current.next
print('None')
- 노드를 순회하면서 양방향 연결을 시각적으로 보여주기 위해
<->를 사용합니다.
delete 메서드
특정 데이터를 가진 노드를 삭제합니다.
def delete(self, data):
if self.head is None:
print('This data is not in our linked list')
return
if self.head.data == data:
tmp = self.head
self.head = self.head.next
if self.head:
self.head.prev = None # 헤드 노드의 prev를 None으로 설정
tmp = None
else:
current = self.head
while current.next:
if current.next.data == data:
tmp = current.next
current.next = current.next.next
if current.next:
current.next.prev = current # 삭제된 노드의 다음 노드의 prev를 현재 노드로 설정
tmp = None
return
else:
current = current.next
- 헤드 노드를 삭제하거나, 리스트의 다른 부분에서 노드를 삭제할 때
next와prev포인터를 적절히 업데이트하여 노드를 리스트에서 제거합니다.
insert_before 메서드
특정 노드 앞에 새로운 노드를 삽입합니다.
def insert_before(self, target_data, data):
if self.head is None:
print('Linked List is empty')
return
if self.head.data == target_data:
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head.prev = new_node
self.head = new_node
return
current = self.head
while current.next and current.next.data != target_data:
current = current.next
if current.next is None:
print(f"Node with data {target_data} not found.")
else:
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = current.next
new_node.prev = current
current.next.prev = new_node
current.next = new_node
target_data를 가진 노드를 찾아 그 앞에 새로운 노드를 삽입합니다.next와prev포인터를 적절히 설정하여 새로운 노드를 연결합니다.
insert_after 메서드
특정 노드 뒤에 새로운 노드를 삽입합니다.
def insert_after(self, target_data, data):
if self.head is None:
print('Linked List is empty')
return
current = self.head
while current is not None:
if current.data == target_data:
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = current.next
new_node.prev = current
if current.next:
current.next.prev = new_node
current.next = new_node
return
current = current.next
print(f'Node with data {target_data} not found.')
target_data를 가진 노드를 찾아 그 뒤에 새로운 노드를 삽입합니다. 마찬가지로next와prev포인터를 설정하여 연결합니다.
9. 이중 연결 리스트 사용 예제
마지막으로, 구현한 이중 연결 리스트를 사용하는 예제를 살펴보겠습니다.
# 이중 연결 리스트 사용 예제
if __name__ == '__main__':
dll = DoublyLinkedList(0)
# 1부터 10까지 데이터를 삽입
for i in range(1, 11):
dll.append(i)
# 리스트 출력
dll.print_linked_list
() # 0 <-> 1 <-> 2 <-> 3 <-> 4 <-> 5 <-> 6 <-> 7 <-> 8 <-> 9 <-> 10 <-> None
# 특정 노드 삭제
dll.delete(5)
dll.print_linked_list() # 0 <-> 1 <-> 2 <-> 3 <-> 4 <-> 6 <-> 7 <-> 8 <-> 9 <-> 10 <-> None
# 특정 노드 앞에 데이터 삽입
dll.insert_before(4, 99)
dll.print_linked_list() # 0 <-> 1 <-> 2 <-> 3 <-> 99 <-> 4 <-> 6 <-> 7 <-> 8 <-> 9 <-> 10 <-> None
# 특정 노드 뒤에 데이터 삽입
dll.insert_after(7, 77)
dll.print_linked_list() # 0 <-> 1 <-> 2 <-> 3 <-> 99 <-> 4 <-> 6 <-> 7 <-> 77 <-> 8 <-> 9 <-> 10 <-> None
이중 연결 리스트는 단일 연결 리스트보다 더 유연한 데이터 구조를 제공합니다. 양방향으로 리스트를 순회할 수 있기 때문에, 리스트의 양 끝에서 삽입과 삭제가 더 효율적으로 이루어질 수 있습니다. 이중 연결 리스트를 구현하면서 포인터(next, prev)를 올바르게 관리하는 것이 중요합니다.
이중 연결 리스트와 단일 연결 리스트의 차이점을 이해하고, 각각의 장단점을 고려하여 상황에 맞는 데이터 구조를 선택하는 것이 중요합니다.
마무리
이번 글에서는 단일 연결 리스트와 이중 연결 리스트의 개념과 파이썬 구현 방법을 자세히 살펴보았습니다. 링크드 리스트는 데이터 구조의 기본적인 개념 중 하나로, 메모리 효율성과 삽입/삭제의 유연성에서 큰 장점을 가지고 있습니다. 단일 연결 리스트는 구조가 간단하여 이해하기 쉽고, 이중 연결 리스트는 양방향으로 리스트를 순회할 수 있어 더욱 강력한 기능을 제공합니다.
링크드 리스트의 장점과 단점을 이해하고, 상황에 맞게 적절한 자료 구조를 선택하는 것은 매우 중요합니다. 예를 들어, 빠른 삽입과 삭제가 중요한 경우에는 링크드 리스트가 좋은 선택이 될 수 있습니다. 반면, 인덱스를 통한 빠른 접근이 필요하다면 배열과 같은 다른 자료 구조가 더 적합할 수 있습니다.
링크드 리스트의 개념을 확실히 이해하고 직접 구현해보면서, 자료 구조의 기초를 탄탄히 다지는 계기가 되었기를 바랍니다. 앞으로 더 복잡한 자료 구조를 배울 때도 링크드 리스트의 기본 개념이 중요한 역할을 할 것입니다.
하지만! 코딩테스트에서 링크드 리스트 자체를 직접 구현하거나 사용하는 경우는 드뭅니다.
그래도, 링크드 리스트의 개념을 이해하는 것은 여전히 중요합니다. 그 이유는 덱(Deque)과 같은 고수준 자료 구조가 링크드 리스트의 이점을 활용하고 있기 때문입니다.
Tips) 링크드 리스트와 덱(Deque)
파이썬에서 collections 모듈의 deque는 덱(Deque, Double-ended Queue)을 제공하는데, 이 자료 구조는 링크드 리스트의 장점을 일부 가지고 있습니다. 덱은 양쪽 끝에서 삽입과 삭제가 O(1) 시간 복잡도로 이루어질 수 있기 때문에, 효율적인 연산이 필요한 상황에서 매우 유용합니다.
덱은 다음과 같은 경우에 유용합니다:
- 양쪽에서 삽입과 삭제가 빈번할 때: 링크드 리스트처럼 덱도 양쪽 끝에서 삽입과 삭제가 빠르게 이루어질 수 있습니다.
- 큐와 스택의 결합된 형태: 덱은 큐와 스택의 기능을 모두 제공하므로, 상황에 따라 다양한 방식으로 사용할 수 있습니다.
코딩테스트에서의 활용
코딩테스트에서는 덱이 링크드 리스트의 역할을 대신할 수 있는 자료 구조로 자주 사용됩니다. 예를 들어:
- 슬라이딩 윈도우 문제: 덱을 사용해 효율적으로 윈도우 내에서 최대값이나 최소값을 추적할 수 있습니다.
- BFS/DFS 탐색: 덱을 큐 또는 스택처럼 사용하여 효율적인 탐색을 수행할 수 있습니다.
- 큐와 스택을 동시에 사용해야 하는 경우: 덱을 사용하면 한쪽 끝에서 삽입하고 다른 쪽 끝에서 삭제하는 작업을 쉽게 처리할 수 있습니다.
코딩테스트에서 링크드 리스트는 직접적으로 사용되지 않지만, 덱과 같은 고수준 자료 구조가 링크드 리스트의 장점을 활용하는 경우가 많습니다. 따라서 링크드 리스트의 개념을 이해하고 덱을 사용하는 방법을 익히는 것은 매우 유용합니다. 덱을 잘 활용하면 코딩테스트에서 다양한 문제를 효율적으로 해결할 수 있습니다.
전체 코드는 아래 링크에서 확인하실 수 있습니다:
Python/자료구조/구현/Linked_List at main · jw9603/Python
다음 시간은 해쉬 테이블에 대해 알아보도록 하겠습니다.
많은 기대 부탁드립니다. 🙏

긴 글 읽어주셔서 감사합니다!
