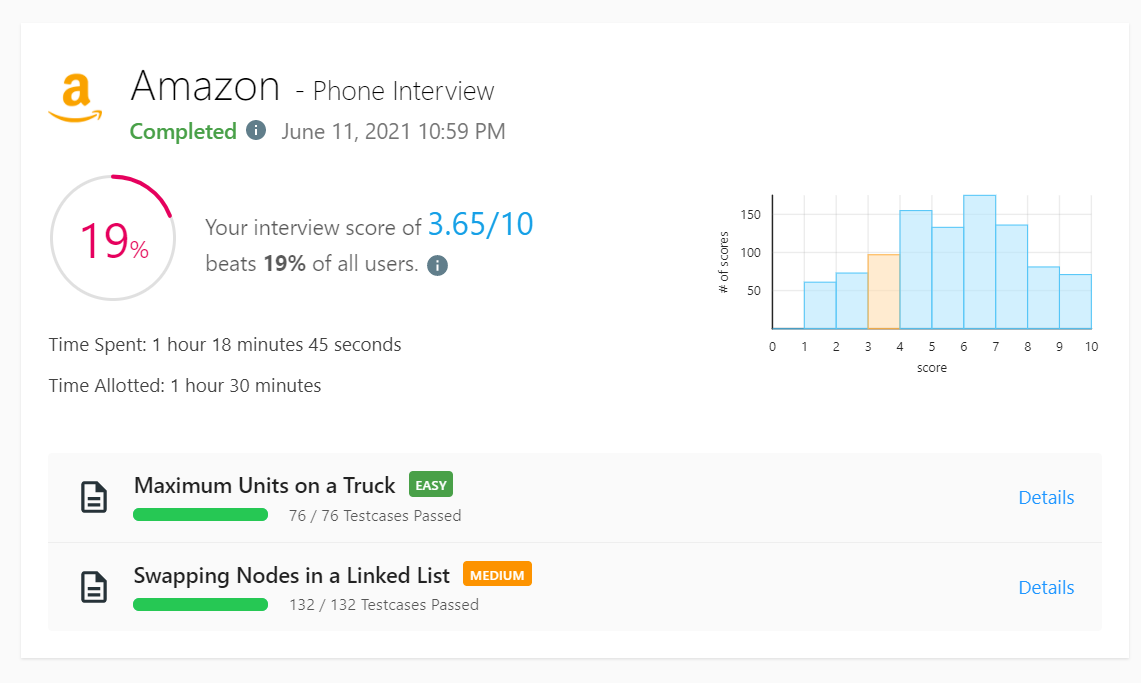
1710. Maximum Units on a Truck
class Solution {
public int maximumUnits(int[][] boxTypes, int truckSize) {
//keep something of size truckSize that holds the largest values
//maxheap
Queue<int[]> q = new PriorityQueue<int[]>((n1, n2) -> n2[1] - n1[1]);
for (int i = 0; i < boxTypes.length; i++) {
q.add(boxTypes[i]);
}
int left = truckSize;
int result = 0;
while (left > 0 && q.size() > 0) {
int[] input = q.poll();
int nums = Integer.min(left, input[0]);
result += nums * input[1];
left -= nums;
}
return result;
}
}Runtime: 6 ms, faster than 93.72% of Java online submissions for Maximum Units on a Truck.
Memory Usage: 38.8 MB, less than 91.32% of Java online submissions for Maximum Units on a Truck.
PriorityQueue를 사용해서 쉽게 풀었읍니다~
순서대로 정렬 해 준 후 앞에서 뺄만큼 빼주면 됨
1721. Swapping Nodes in a Linked List
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapNodes(ListNode head, int k) {
List<Integer> l = new ArrayList<Integer>();
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
l.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.next;
}
Integer[] al = new Integer[l.size()];
al = l.toArray(al);
int second = al[k-1];
al[k-1] = al[al.length - k];
al[al.length -k] = second;
ListNode result = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode resultcur = result;
for (int i = 0; i < al.length; i++) {
resultcur.next = new ListNode(al[i]);
resultcur = resultcur.next;
}
return result.next;
}
}Runtime: 10 ms, faster than 9.52% of Java online submissions for Swapping Nodes in a Linked List.
Memory Usage: 60.4 MB, less than 84.78% of Java online submissions for Swapping Nodes in a Linked List.
머리 굴려보려고 했는데 영 안굴러가서..
진심 믿기지 않을 만큼 저렴한 방법으로 풀었읍니다~
이렇게 푸느니 안푸는게 인터뷰 볼 때 나을 정도..ㅎㅎ
class Solution {
public ListNode swapNodes(ListNode head, int k) {
int listLength = 0;
ListNode frontNode = null;
ListNode endNode = null;
ListNode currentNode = head;
// find the length of list and set the front node
while (currentNode != null) {
listLength++;
if (listLength == k) {
frontNode = currentNode;
}
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// set the end node at (listLength - k)th node
endNode = head;
for (int i = 1; i <= listLength - k; i++) {
endNode = endNode.next;
}
// swap front node and end node values
int temp = frontNode.val;
frontNode.val = endNode.val;
endNode.val = temp;
return head;
}
}Runtime: 3 ms, faster than 66.10% of Java online submissions for Swapping Nodes in a Linked List.
Memory Usage: 64.6 MB, less than 75.44% of Java online submissions for Swapping Nodes in a Linked List.
투패스
class Solution {
public ListNode swapNodes(ListNode head, int k) {
int listLength = 0;
ListNode frontNode = null;
ListNode endNode = null;
ListNode currentNode = head;
// set the front node and end node in single pass
while (currentNode != null) {
listLength++;
if (endNode != null)
endNode = endNode.next;
// check if we have reached kth node
if (listLength == k) {
frontNode = currentNode;
endNode = head;
}
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// swap the values of front node and end node
int temp = frontNode.val;
frontNode.val = endNode.val;
endNode.val = temp;
return head;
}
}Runtime: 2 ms, faster than 100.00% of Java online submissions for Swapping Nodes in a Linked List.
Memory Usage: 65.1 MB, less than 43.93% of Java online submissions for Swapping Nodes in a Linked List.
원패스 방식
