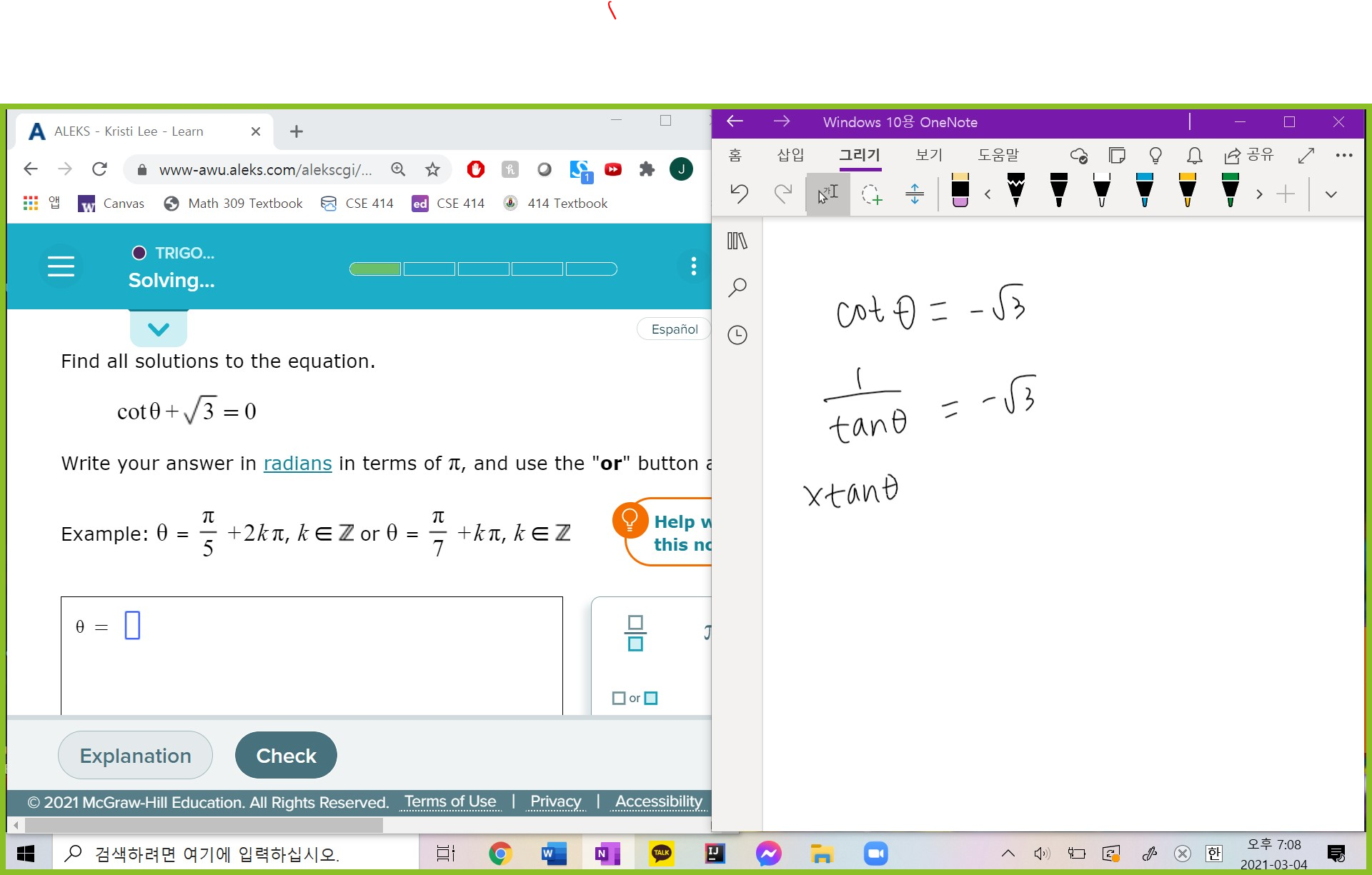
Sum of Two Integers
class Solution {
public int getSum(int a, int b) {
while (b != 0) {
int answer = a ^ b;
int carry = (a & b) << 1;
a = answer;
b = carry;
}
return a;
}
}냅. 다. 외. 워.
Runtime: 0 ms, faster than 100.00% of Java online submissions for Sum of Two Integers.
Memory Usage: 35.5 MB, less than 80.46% of Java online submissions for Sum of Two Integers.
class Solution:
def getSum(self, a: int, b: int) -> int:
x, y = abs(a), abs(b)
if (x < y):
return self.getSum(b, a)
sign = 1 if a > 0 else -1
if a * b >= 0:
while y:
answer = x ^ y
carry = (x & y) << 1
x, y = answer, carry
else:
while y:
answer = x ^ y
borrow = ((~x) & y) << 1
x, y = answer, borrow
return x * sign전에는 파이선으로 루션이 긁어왔엇네요^^
Evaluate Reverse Polish Notation
class Solution {
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
for (String token : tokens) {
if (!"+-*/".contains(token)) {
stack.push(Integer.valueOf(token));
continue;
}
int number2 = stack.pop();
int number1 = stack.pop();
int result = 0;
switch (token) {
case "+":
result = number1 + number2;
break;
case "-":
result = number1 - number2;
break;
case "*":
result = number1 * number2;
break;
case "/":
result = number1 / number2;
break;
}
stack.push(result);
}
return stack.pop();
}
}Stack을 이용하는 방식..
사진 보니깐 이해 되네요
class Solution {
private static final Map<String, BiFunction<Integer, Integer, Integer>> OPERATIONS = new HashMap<>();
// Ensure this only gets done once for ALL test cases.
static {
OPERATIONS.put("+", (a, b) -> a + b);
OPERATIONS.put("-", (a, b) -> a - b);
OPERATIONS.put("*", (a, b) -> a * b);
OPERATIONS.put("/", (a, b) -> a / b);
}
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
for (String token : tokens) {
if (!OPERATIONS.containsKey(token)) {
stack.push(Integer.valueOf(token));
continue;
}
int number2 = stack.pop();
int number1 = stack.pop();
BiFunction<Integer, Integer, Integer> operation;
operation = OPERATIONS.get(token);
int result = operation.apply(number1, number2);
stack.push(result);
}
return stack.pop();
}
}Majority Element
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int length = nums.length;
return nums[length / 2];
}
}저 보자마자 이렇게 풀 생각했는데 저번에도 이렇게 풀어놨네요^^
사람은 변하지 않아~
Find the Celebrity
/* The knows API is defined in the parent class Relation.
boolean knows(int a, int b); */
public class Solution extends Relation {
public int findCelebrity(int n) {
//potential celebrities
// knows -> remove, one person doesn't know -> remove
Set<Integer> celebrity = new HashSet<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
celebrity.add(i);
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (Integer c : celebrity) {
if (j == c) continue;
if (! knows(j, c)) {
celebrity.remove(c);
}
if (knows(c, j)) {
celebrity.remove(c);
}
}
}
if (celebrity.size() != 0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}문제를 잘못읽음..웁스~^^
/* The knows API is defined in the parent class Relation.
boolean knows(int a, int b); */
public class Solution extends Relation {
private int n;
public int findCelebrity(int n) {
//potential celebrities
// knows -> remove, one person doesn't know -> remove
this.n = n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (isCeleb(i)) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
private boolean isCeleb(int c) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.n; i++) {
if (i == c) continue;
if (! knows(i, c) || knows(c,i)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}Runtime: 21 ms, faster than 49.66% of Java online submissions for Find the Celebrity.
Memory Usage: 39.2 MB, less than 85.41% of Java online submissions for Find the Celebrity.
public class Solution extends Relation {
private int numberOfPeople;
public int findCelebrity(int n) {
numberOfPeople = n;
int celebrityCandidate = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (knows(celebrityCandidate, i)) {
celebrityCandidate = i;
}
}
if (isCelebrity(celebrityCandidate)) {
return celebrityCandidate;
}
return -1;
}
private boolean isCelebrity(int i) {
for (int j = 0; j < numberOfPeople; j++) {
if (i == j) continue; // Don't ask if they know themselves.
if (knows(i, j) || !knows(j, i)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}Runtime: 18 ms, faster than 96.55% of Java online submissions for Find the Celebrity.
Memory Usage: 39.2 MB, less than 75.20% of Java online submissions for Find the Celebrity.
루션이 보니 머리 쬠만 더 굴리면 훨씬 빨라지네요!^^
Task Scheduler
class Solution {
public int leastInterval(char[] tasks, int n) {
// frequencies of the tasks
int[] frequencies = new int[26];
for (int t : tasks) {
frequencies[t - 'A']++;
}
Arrays.sort(frequencies);
// max frequency
int f_max = frequencies[25];
int idle_time = (f_max - 1) * n;
for (int i = frequencies.length - 2; i >= 0 && idle_time > 0; --i) {
idle_time -= Math.min(f_max - 1, frequencies[i]);
}
idle_time = Math.max(0, idle_time);
return idle_time + tasks.length;
}
}Runtime: 2 ms, faster than 99.79% of Java online submissions for Task Scheduler.
Memory Usage: 40.2 MB, less than 73.69% of Java online submissions for Task Scheduler.
dp를 쓰기!!!
class Solution {
public int leastInterval(char[] tasks, int n) {
// frequencies of the tasks
int[] frequencies = new int[26];
for (int t : tasks) {
frequencies[t - 'A']++;
}
// max frequency
int f_max = 0;
for (int f : frequencies) {
f_max = Math.max(f_max, f);
}
// count the most frequent tasks
int n_max = 0;
for (int f : frequencies) {
if (f == f_max) n_max++;
}
return Math.max(tasks.length, (f_max - 1) * (n + 1) + n_max);
}
}Runtime: 2 ms, faster than 99.79% of Java online submissions for Task Scheduler.
Memory Usage: 40.3 MB, less than 66.79% of Java online submissions for Task Scheduler.
비슷한듯 다른듯~~