💡 ScheduledExecutorService과 SpringBoot의 @Scheduled로 스케줄링을 설정할 수 있다.
- ScheduledExecutorService은 인수있는 메서드에도 적용할 수 있지만 @Scheduled는 인수있는 메서드에 적용이 불가하다.
ScheduledExecutorService
-
Java 1.5부터 지원되는 스케줄링이 가능한 Executor 서비스로 인터페이스이며, 구현체로 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor()가 있다.
-
예제 코드
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Transactional
public class BattleRivalService {
private final BattleRepository battleRepository;
private final BattleRivalRepository battleRivalRepository;
private final TeamRepository teamRepository;
private final BattleService battleService;
private final ScheduledExecutorService scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
public BattleRivalResponseDTO saveBattleRival(Battle battle, TeamMember teamMember) {
LocalDate lc = LocalDate.now();
LocalDateTime finishTime = LocalDateTime.now().plusDays(7);
BattleRival result = battleRivalRepository.findByTeamId(teamMember.getTeam().getId());
// 팀이 대결에 참여하지 않은 경우
if(result == null) {
BattleRival battleRival = new BattleRival(battle, teamMember.getTeam());
battleRivalRepository.save(battleRival);
battle.update(lc);
battleRepository.save(battle);
Team team = teamRepository.findById(battle.getBattleRivals().get(0).getTeam().getId()).orElse(null);
team.updateState("대결 진행 중");
teamRepository.save(team);
team = teamRepository.findById(teamMember.getTeam().getId()).orElse(null);
team.updateState("대결 진행 중");
teamRepository.save(team);
scheduler.schedule(() -> {
try {
battleService.finishBattle(battle.getId());
} catch (ParseException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, ChronoUnit.SECONDS.between(LocalDateTime.now(), finishTime), TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return BattleRivalResponseDTO.builder()
.teamId(battleRival.getTeam().getId())
.teamName(battleRival.getTeam().getName())
.peopleNum(battleRival.getTeam().getPeopleNum())
.step(battleRival.getStep())
.build();
} else {
// 팀이 대결에 참여한 경우
return null;
}
}@Scheduled
- 스프링 부트에서는 스케줄링 인터페이스를 직접 구현할 필요가 없다.
- @EnableScheduling 어노테이션으로 스케줄링을 사용하겠다는 것을 명시하고, @Scheduled 어노테이션으로 스케줄링 할 함수를 지정해주면 된다.
@EnableScheduling
@SpringBootApplication
public class WalkingMateBackApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(WalkingMateBackApplication.class, args);
}
}- 실제 스케줄링 작업할 클래스를 만든다.
@Component(@Service 등) 즉, 스프링 빈에 등록된 클래스여야 한다. 이렇게 두 개의 어노테이션을 적기만 하면 설정은 끝이고 다음 규칙을 지키며 스케줄러 메소드를 만들자.@Service public class SchedulerService { @Scheduled(fixedDelay = 1000) // 1초마다 실행 public void run() { System.out.println("Hello CoCo World!); } }-
@Scheduled 규칙
- Method는 void 타입으로
- Method는 매개변수 사용 불가@Scheduled 속성
fixedDelay : milliseconds 단위로, 이전 Task의 종료 시점으로부터 정의된 시간만큼 지난 후 Task를 실행한다.
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 1000) public void run() { System.out.println("Hello CoCo World!"); }fixedDelayString : fixedDelay와 같은데 문자열로 값을 표현하겠다는 의미이다.
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = "1000") public void run() { System.out.println("Hello CoCo World!"); }fixedRate : milliseconds 단위로, 이전 Task의 시작 시점으로부터 정의된 시간만큼 지난 후 Task를 실행한다.
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 1000) public void run() { System.out.println("Hello CoCo World!"); }fixedRateString : fixedRate와 같은데 문자열로 값을 표현하겠다는 의미이다.
@Scheduled(fixedRateString = "1000") public void run() { System.out.println("Hello CoCo World!"); }
-
※ fixedDelay vs fixedRate
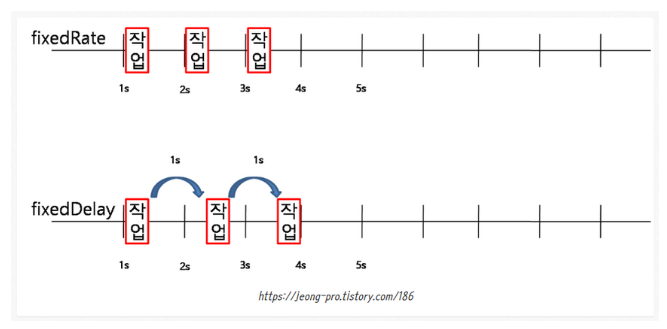
fixedRate는 작업 수행시간과 상관없이 일정 주기마다 메소드를 호출하는 것이고,
fixedDelay는 (작업 수행 시간을 포함하여) 작업을 마친 후부터 주기 타이머가 돌아 메소드를 호출하는 것이다.
initialDelay : 스케줄러에서 메소드가 등록되자마자 수행하는 것이 아닌 초기 지연시간을 설정하는 것이다.
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 5000, initialDelay = 3000)
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello CoCo World!");
}위와 같이 사용하면 3초의 대기시간(initialDelay) 후에 5초(fixedRate)마다 "Hello CoCo World!"를 출력하는 작업을 스케줄러가 수행해준다.
initialDelayString : 위와 마찬가지로 문자열로 값을 표현하겠다는 의미이다.
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 5000, initialDelayString = "3000")
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello CoCo World!");
}cron : Cron 표현식을 사용하여 작업을 예약할 수 있다.
@Scheduled(cron = "* * * * * *")
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello CoCo World!");
}첫 번째 * 부터 초(0-59), 분(0-59), 시간(0-23), 일(1-31), 월(1-12), 요일(0-6) (0: 일, 1: 월, 2:화, 3:수, 4:목, 5:금, 6:토), Spring @Scheduled cron은 6자리 설정만 허용하며 연도 설정을 할 수 없다.
- Cron 표현식
- : 모든 조건(매시, 매일, 매주처럼 사용)을 의미
- ? : 설정 값 없음 (날짜와 요일에서만 사용 가능)
- '-' : 범위를 지정할 때
- , : 여러 값을 지정할 때
- / : 증분값, 즉 초기값과 증가치 설정에 사용
- L : 마지막 - 지정할 수 있는 범위의 마지막 값 설정 시 사용 (날짜와 요일에서만 사용 가능)
- W : 가장 가까운 평일(weekday)을 설정할 때
- 예) 10W
- 10일이 평일 일 때 : 10일에 실행
- 10일이 토요일 일 때 : 가장 가까운 평일인 금요일(9일)에 실행
- 10일이 일요일 일 때 : 가장 가까운 평일인 월요일(11일)에 실행
- 예) 10W
- '#' : N번째 주 특정 요일을 설정할 때 (-요일에서만 사용 가능)
- 예) 4#2
- 목요일#2째주에 실행
zone : cron 표현식을 사용했을 때 사용할 time zone으로 따로 설정하지 않으면 기본적으로 Local의 time zone이다.
@Scheduled(cron = "* * * * * *", zone = "Asia/Seoul")
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello CoCo World!");
}cron 사용 예시
// 매일 오후 18시에 실행
@Scheduled(cron = "0 0 18 * * *")
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello CoCo World!");
}
// 매달 10일,20일 14시에 실행
@Scheduled(cron = "0 0 14 10,20 * ?")
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello CoCo World!");
}
// 매달 마지막날 22시에 실행
@Scheduled(cron = "0 0 22 L * ?")
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello CoCo World!");
}
// 1시간 마다 실행 ex) 01:00, 02:00, 03:00 ...
@Scheduled(cron = "0 0 0/1 * * *")
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello CoCo World!");
}
// 매일 9시00분-9시55분, 18시00분-18시55분 사이에 5분 간격으로 실행
@Scheduled(cron = "0 0/5 9,18 * * *")
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello CoCo World!");
}
// 매일 9시00분-18시55분 사이에 5분 간격으로 실행
@Scheduled(cron = "0 0/5 9-18 * * *")
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello CoCo World!");
}
// 매달 1일 10시30분에 실행
@Scheduled(cron = "0 30 10 1 * *")
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello CoCo World!");
}
// 매년 3월내 월-금 10시30분에 실행
@Scheduled(cron = "0 30 10 ? 3 1-5")
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello CoCo World!");
}
// 매달 마지막 토요일 10시30분에 실행
@Scheduled(cron = "0 30 10 ? * 6L")
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello CoCo World!");
}