변수란?
하나의 값을 저장할 수 있는 메모리 공간
변수의 선언
타입: 메모리 방의 크기와 데이터 (정수, 실수, 문자열 등) 지정
//int , double: 타입
//age , value : 변수 이름
int age;
double value;변수 이름, class 이름 작명(naming) 규칙 (rule)
- 변수 이름( variablenaming)
-영문, , $ 가 포함되는 것은 가능하다
=>$ , _로 변수명을 짖는 경우는 SW 제품안의 프로그램에서 사용
-변수명 첫번째에 숫자가 나오면 오류
변수명 중간이나 마지막에 넣는 것은 가능
-변수 이름은 소문자로 시작되는 것이 관행
-변수 이름은 여러개의 단어로 구성 가능한데 두번째 단어의 첫글자는 대문자로 표현하는 것이 관행
ex)interestRate : 이자율 => camel_notation (낙타 표기법)
-결론은 변수명 작명시 영어로만 작명하고 여러개의 단어를 사용할때는 camel_notation 사용
- class_name
-변수명과 동일 한데, 한 가지 차이점은 첫글자가 대문자로 시작
3.변수 사용 방법
3-1: 변수 선언 => 변수 타입(데이터의 크기와 성격) + 변수명
-변수 선언시 초기값을 줄 수도 있음
3-2: 변수 사용 => 선언된 변수에 할당된 메모리에 새로운 값으로 변경하거나 읽어오는 경우
리터럴(literal)
소스코드 내에서 직접 입력된 변수의 초기값
int junior = 15;
int adult = junior + 5;
double radius = 5.0; // 반지름
double interestRate = 0.1; //이자율
int age;
age = 30;escape 문자 : /가 포함된 문자 리터럴로 특수한 용도이다
escape_sequence: \n(enter 역할), \t(tab), \ ,\" , \'
=>특수문자(special character)로 문자열 안에서 사용됨
-\n = new_line
-\r = carrage_return
키보드에서 enter 를 누르면 2개의 escape sequence 문자가 발생 (\n\r)
문자열(String):"\n줄 바꿈\n연습"
문자 (character:'n','한','글'
System.out.println("줄 바꿈 연습");
System.out.println("\n줄 바꿈\n연습");
System.out.println("탭키 연습");
System.out.println("\t탭키\t연습");
System.out.println("\\ backslash 1개 출력");
System.out.println("큰 따옴표 \" 출력");
System.out.println("작은 따옴표 \' 출력");
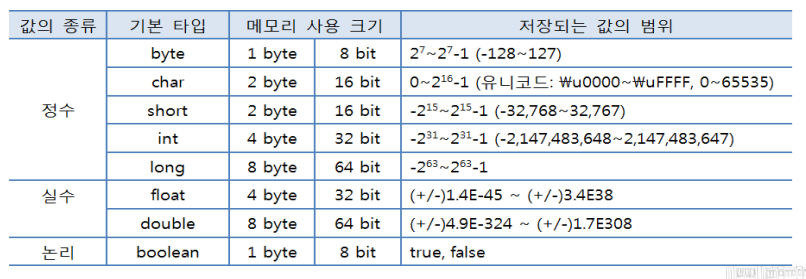
변수의 타입
정수 실수 문자 논리 리터럴을 직접 저장하는 타입
메모리의 최소 기억단위인 bit가 모여 byte가 형성(1byte = 8bit)
1.int literal
- 10진수 , 8진수 , 16진수 사용가능
- 16진수 (하드웨어와 연계된 프로그램, 통신프로그램)에서 사용
public class intEx {
public static void main(String[]args) {
int var1 = 10;
int var2 = 012; //8진수: 첫 자리에 0을 넣으면 된다
int var3 = 0xA; //16진수
System.out.println("var1 = "+var1);
System.out.println("var2 = "+var2);
System.out.println("var3 = "+var3);
}
}
2.실수값 literal
실수 literal 을 float타입에 넣을 경우 literal값 끝에 ~f를 붙여야 한다.
ex) 3.14f의 의미 : 3.14값을 float 타입인 4바이트로 생성해 달라는 명령어.
double var1 = 3.14;
float var3 = 3.14f;
double var4 = 0.1234567890123456789;
float var5 = 0.1234567890123456789f;
double var6 = 3e6; //3*10^6 E:Exponential
float var7 = 3e6f;
double var8 = 2e-3; //3*10^-3
3.char type
char type = 문자 한글자를 관리하기 위한 타입(2 bytes)
문자 예 : 'A' , '1' , '가'...
모든 문자를 unicode로 저장
1.ASCII (American Standard Code Information Interchange) code table
키보드의 숫자 ,영문자 대문자/소문자, 특수기호 등에 대하여 2진수 코드로 매핑한 것
2.Unicode 코드 테이블: 2bytes
-ASCII도 포함
-한국어, 중국어 , 일어 , 독일어 등의 전세계 언어의 문자를 코드화 한것
public class CharEx {
public static void main(String []args) {
char c1 = 'A';
char c2 = 65; // 10진수
char c3 = '\u0041'; // \\u = unicode를 의미
//실제 출력시 똑같이 A를 출력
char c4 = '가';
char c5 = 44032;
char c6 = '\uac00';
//위와 마찬가지로 똑같이 가 를 출력한다
}
}4.boolean type
1.literal 값이 true , false 만 사용 가능
2.if while for 등의 제어문 혹은 반복문 에서 사용
3.현실에서는 필요하지 않는 데이터 타입이지만 ,프로그래밍 시에는 핵심적인 타입이다.
public class booleanEx {
public static void main(String[]args) {
boolean stop = true;
boolean start = false;
}
}
5. byte type
1byte의 데이터 값만 저장 가능(-128 ~ 127)
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte var1 = -128;
byte var2 = -30;
byte var3 = 0;
byte var4 = 30;
byte var5 = 127;
}
}
타입 변환(형변환)
데이터 타입을 다른 타입으로 변환하는 것
promotion : 작은 데이터 타입(작은 데이터 값)에서 큰 데이터 타입으로 자동 변환시켜 줄 때
ex) int-> long , long -> float
casting : 큰 데이터 타입에서 작은 데이터 타입으로 강제 형변환
(코딩할 때 강제 형변환을 하겠다는 의사표현을 해야함)
casting의 단점 : 큰 data type의 값이 작은 data type으로 변환되면서 데이터가 유실 될수 있다.
promotion
public class PromotionEx {
public static void main(String[]args) {
byte byteValue = 10;
int intValue = byteValue;
System.out.println("intValue = "+intValue);
char charValue = '가';
intValue = charValue;
System.out.println("intValue = "+intValue);
intValue = 500;
long longValue = intValue;
System.out.println("longValue = "+longValue);
float floatValue = longValue;
System.out.println("floatValue = "+floatValue);
double doubleValue = longValue;
System.out.println("doubleValue = "+doubleValue);
}
}위의 코드를 실행하면 다음과 같이 출력된다
intValue = 10
intValue = 44032
longValue = 500
floatValue = 500.0
doubleValue = 500.0
각각의 변수를 새롭게 초기화 할때마다 promotion이 발생된다
casting
public class CastingEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char ch = 'A';
int num = 88;
double d = 100.04;
long l = (long)d;
// double 에서 long 등 int type으로 강제형변환(casting) 하면 소숫점 이하 숫자를 삭제
int i = (int)l;
System.out.println("ch = " + ch);
ch = (char)num;
//(char) : int type 인 num을 char type으로 강제 형변환(casting)
System.out.println("ch = " + ch);
System.out.println("l = " + l);
System.out.println("i = " + i);
}
}위의 코드를 실행하면 다음과 같이 출력된다
ch = A
ch = X
l = 100
i = 100
정수형 산술 연산에서의 데이터 타입 자동형변환
int 보다 작은 byte short char 을 사용하여 산술 연산을 수행하면 무조건 int 타입으로 자동형변환
long type 이나, float double 등의 타입과 다른 타입이 산술 연산을 수행하면 큰 데이터 타입으로 자동형변환 시킴
public class TypeConversionInExpressionEx {
public static void main(String[]args) {
byte b1 =42;
byte b2 = 10;
byte sum ;
char c1 = 20;
char c2 = 30;
char csum;
int isum;
long l1 = 15;
long result;
double dresult;
/*
* b1 + b2 를 기계어로 수행시
* 1. byte 타입인 b1을 int 타입으로 promotion 시킴(즉 ,1 byte => 4byte 크기로 확장)
* 2. byte type 인 b2을 int 타입으로 promotion 시킴
* 3. b1+b2 수행
* 4. int 인 결과값을 byte 타입인 sum에 넣으려고 하니까 에러가 발생한다.
*/
// sum = b1 + b2;
sum = (byte) (b1 + b2); //(byte): casting(강제형변환)
isum = b1 + b2;
// csum = c1 + c2;
/*
* 기계어로 변환시
* 1. b1 + c1 연산하여 int type으로 변환하여 메모리에 4byte로 저장
* 2. b1 + c1 의 결과값과 l1을 덧셈 연산하기 위해서는
* -2.1:b1 + b2의 결과값을 8byte 인 long type으로 변환(promotion 발생)
* -2.2: l1과 덧셈 연산 수행
* 3. 최값을 long type 인 result에 넣음
*/
result = b1 + c1 + l1;
/*
*long 타입인 l1과 double 타입인 0.5 를 더할경우 기계어로는
*1. l1을 double 타입으로 변환
*2. 0.5를 더하여 연산 결과가 double 타입으로 만듬
*/
// result = l1 + 0.5;
dresult = l1 + 0.5;
}
}강의를 들은후 느낀점
당시에 대학교에서 자바를 배운 후 였기에 가볍게 다시 상기시킨다는 의미로 들었는데 생각보다
강사님이 굉장히 디테일하게 강의를 해주셨던 기억이 있다.
강의를 들을때 기계어로의 표현까지 할 필요가 있을까 라는 생각을 했지만 추후 다른 강의를 들으면서 이래서 기계어로의 표현을 간략하게 나마 설명해주신거구나 라고 생각을 한다