문제
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2108
풀이
주의할 점
산술평균
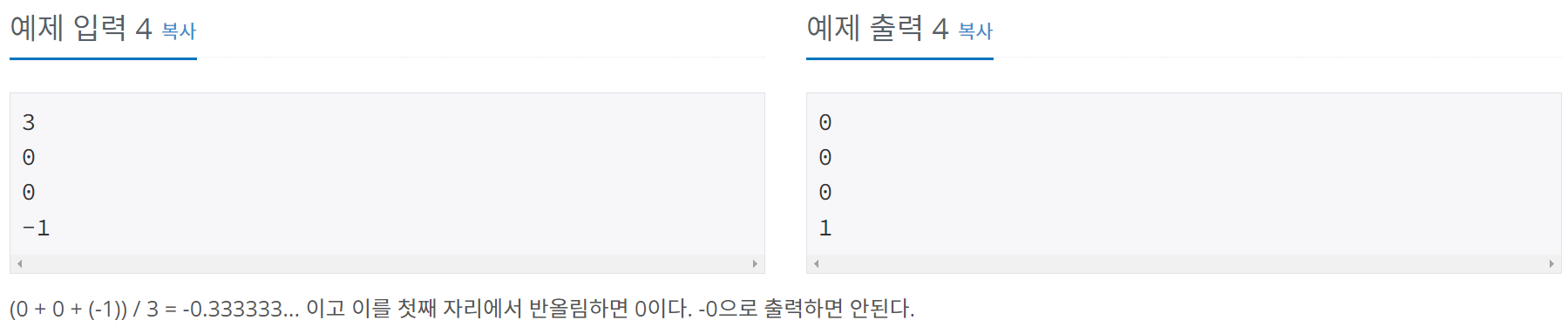
산술평균이 -0.5보다 크고 0.0보다 작은 경우에는 첫째 자리에서 반올림한 결과가 -0이 아니라 0으로 출력되어야 한다.
최빈값
최빈값 (N개의 수들 중 가장 많이 나타나는 값)이 여러 개 있을 때에는 두 번째로 작은 값을 출력한다.
답안
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
// -4000 ~ 4000 까지의 숫자가 각각 몇개인지 세기 위한 배열
// 인덱스는 음수가 될 수 없으므로 임시로 인덱스에 4000을 더한다.
int counting[8001]; // 0으로 초기화
int calcMode(){
// 일단 counting 배열에서 최댓값을 구하자.
int maxCount = *max_element(counting, counting + 8001);
// 해당 개수만큼 등장하는 숫자들을 따로 저장한다.
vector<int> modeCandidate;
for(int i = 0; i < 8001; i++){
if(counting[i] == maxCount){
// 크기가 작은 순서대로 삽입된다.
modeCandidate.push_back(i - 4000);
}
}
if(modeCandidate.size() == 1){
return modeCandidate[0];
}
// 두번째로 작은 값 리턴
return modeCandidate[1];
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n; // 최대 50만 (홀수)
vector<int> arr;
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int val;
cin >> val;
arr.push_back(val);
sum += val;
counting[val + 4000] += 1;
}
// 소수점 첫째 자리에서 반올림 한 산술평균
float mean = sum / (float)n;
if(mean > -0.5 && mean < 0.0){
mean = 0;
}else{
mean = round(mean);
}
cout << mean << "\n";
// 중앙값
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end());
cout << arr[n / 2] << "\n";
// 최빈값
cout << calcMode() << "\n";
// 범위
cout << arr.back() - arr.front() << "\n";
return 0;
}


