문제
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/8911
풀이
있는 그대로 구현했더니 코드량이 길어졌다.
F, B, L, R 중에 어떤 명령어인지, 그리고 E, W, S, N 중에 어느 방향을 바라보고 있는지에 따라 모두 케이스를 분류하여 방문한 좌표값들을 저장하였다.
현재 바라보는 방향에 따라 F, B 명령어는 x, y 좌표 값이 달라지고, L, R 명령어는 바라보는 방향이 달라진다.
그렇게 방문한 좌표들을 모두 저장한 뒤에, x 좌표의 최대, 최소의 차이로 직사각형의 너비를, y 좌표의 최대, 최소의 차이로 직사각형의 높이를 구하여, 최종적으로 직사각형의 넓이를 구했다.
// https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/8911
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
vector<pair<pair<int, int>, int>> coords;
enum Direction { E, W, S, N };
void handleFrontCase() {
auto lastElement = coords.back();
int x = lastElement.first.first;
int y = lastElement.first.second;
int nx = x, ny = y;
int curDirection = lastElement.second;
switch(curDirection){
case E: nx = x + 1; break;
case W: nx = x - 1; break;
case S: ny = y - 1; break;
case N: ny = y + 1; break;
}
coords.push_back({{nx, ny}, curDirection});
}
void handleBackCase(){
auto lastElement = coords.back();
int x = lastElement.first.first;
int y = lastElement.first.second;
int nx = x, ny = y;
int curDirection = lastElement.second;
switch(curDirection){
case E: nx = x - 1; break;
case W: nx = x + 1; break;
case S: ny = y + 1; break;
case N: ny = y - 1; break;
}
coords.push_back({{nx, ny}, curDirection});
}
void handleLeftCase(){
auto lastElement = coords.back();
int x = lastElement.first.first;
int y = lastElement.first.second;
int nx = x, ny = y;
int curDirection = lastElement.second;
switch(curDirection){
case E: curDirection = N; break;
case N: curDirection = W; break;
case W: curDirection = S; break;
case S: curDirection = E; break;
}
coords.push_back({{nx, ny}, curDirection});
}
void handleRightCase(){
auto lastElement = coords.back();
int x = lastElement.first.first;
int y = lastElement.first.second;
int nx = x, ny = y;
int curDirection = lastElement.second;
switch(curDirection){
case E: curDirection = S; break;
case S: curDirection = W; break;
case W: curDirection = N; break;
case N: curDirection = E; break;
}
coords.push_back({{nx, ny}, curDirection});
}
void saveAllVisitedCoords(string cmd) {
coords.push_back({{0,0}, N});
for(int i = 0; i < cmd.size(); i++){ // 최대 길이 500
switch(cmd[i]){
case 'F':
handleFrontCase(); break;
case 'B':
handleBackCase(); break;
case 'L':
handleLeftCase(); break;
case 'R':
handleRightCase(); break;
}
}
}
int getWidth(){
int min = 1e9, max = -1e9;
for(int i = 0; i < coords.size(); i++){
int x = coords[i].first.first;
if(x < min){
min = x;
}
if(x > max){
max = x;
}
}
return max - min;
}
int getHeight(){
int min = 1e9, max = -1e9;
for(int i = 0; i < coords.size(); i++){
int y = coords[i].first.second;
if(y < min){
min = y;
}
if(y > max){
max = y;
}
}
return max - min;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
string cmd;
cin >> cmd;
saveAllVisitedCoords(cmd);
int area = getWidth() * getHeight();
cout << area << "\n";
coords.clear();
}
return 0;
}개선된 풀이
상하좌우 방향을 나타내는 dx, dy 배열을 이용하면 더 쉽게 방향을 전환하고 좌표를 이동시킬 수 있다.
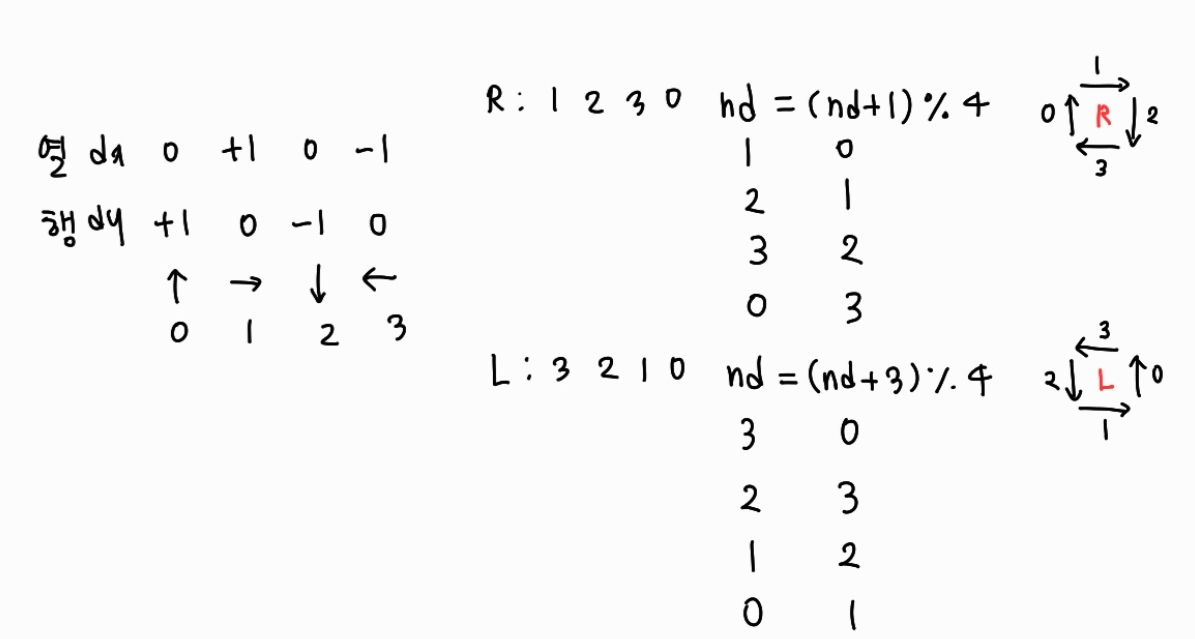
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
vector<pair<int, int>> coords;
int dx[] = { 0,1,0,-1 };
int dy[] = { 1,0,-1,0 };
void saveAllVisitedCoords(string cmd){
int nx = 0, ny = 0; // 초기 위치 원점
int nd = 0; // 초기 방향 북쪽
coords.push_back({nx, ny});
for(int i = 0; i < cmd.size(); i++){
char ch = cmd[i];
// 방향 전환
if(ch == 'L' || ch == 'R'){
if(ch == 'L'){
nd = (nd + 3) % 4;
}else{
nd = (nd + 1) % 4;
}
}else{
// 좌표 이동
if(ch == 'F'){
nx += dx[nd];
ny += dy[nd];
}else{
nx -= dx[nd];
ny -= dy[nd];
}
// 좌표에 변화가 있을 때만 저장
coords.push_back({nx, ny});
}
}
}
int getWidth(){
int min = 1e9, max = -1e9;
for(auto e: coords){
int x = e.first;
if(x < min) min = x;
if(x > max) max = x;
}
return max - min;
}
int getHeight(){
int min = 1e9, max = -1e9;
for(auto e: coords){
int y = e.second;
if(y < min) min = y;
if(y > max) max = y;
}
return max - min;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
string cmd;
cin >> cmd;
saveAllVisitedCoords(cmd);
int area = getWidth() * getHeight();
cout << area << "\n";
coords.clear();
}
return 0;
}명령어의 길이를 N (최대 500)이라고 했을 때, 위 풀이의 시간복잡도는 O(N)이라고 할 수 있다.
그리고 첫번째 풀이는 방향 전환만 하는 경우에도 모두 좌표값을 저장했지만, 두번째 풀이는 좌표 값에 변화가 있을 때만 coords 배열에 저장하기 때문에 x, y 좌표의 최대, 최소 값을 구할 때도 탐색 시간을 줄일 수 있다. (공간 복잡도도 줄어든다.)