스트림의 연산
스트림이 제공하는 기능 - 중간 연산과 최종 연산
- 중간 연산 - 연산 결과가 스트림인 연산, 반복적으로 적용 가능
- 최종 연산 - 연산 결과가 스트림이 아닌 연산, 단 한 번만 적용 가능(스트림의 요소를 소모)
stream.distinct().limit(5).sorted().forEach(System.out::println)
-> distinct(), limit(), sorted() : 중간 연산
forEach(System~) : 최종 연산String[] strArr = {"dd", "aaa", "CC", "cc", "b"};
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of(strArr); // 문자열 배열이 소스인 스트림
Stream<String> filteredStream = stream.filter(); // 걸러내기(중간 연산)
Stream<String> distinctedStream = stream.distinct(); // 중복 제거(중간 연산)
Stream<String> sortedStream = stream.sort(); // 정렬 (중간 연산)
Stream<String> limitedStream = stream.limit(5); // 스트림 자르기 (중간 연산)
int total = stream.count(); // 요소 개수 세기 (최종 연산) - 스트림 닫힘 closed스트림의 중간 연산
Stream<T> distinct() : 중복 제거
Stream<T> filter(Predicate<T> predicate조건식) : 조건에 안 맞는 요소 제외
Stream<T> limit(long maxSize) : 스트림의 일부를 잘라낸다
Stream<T> skip(long n) : 스트림의 일부를 건너뛴다(n개를 건너뛴다)
Stream<T> peek(Consumer<T> action) : 스트림의 요소에 작업 수행, 작업이 잘 처리됐는지 중간에 확인할 때 많이 사용됨
Stream<T> sorted() : 스트림 요소가 갖고 있는 기본 정렬의 기준에 맞게 정렬한다
Stream<T> sorted(Comparator<T> comparator) : 스트림의 요소를 정렬 기준에 맞게 정렬한다.
중간 연산의 핵심은 map, flatMap
스트림의 요소를 변환하는 것, 어떻게 변환하는지를 람다식으로 주어짐
Stream<R> DoubleStream, IntStream, LongStream
- map(Function<T, R> mapper)
- mapToDouble(ToDoubleFunction<T> mapper)
- mapToInt(ToIntFunction<T> mapper)
- mapToLong(ToLongFunction<T> mapper)
- flatMap(Function<T, Stream<R>> mapper)
- flatMapToDouble(Function<T, DoubleStream> m)
- flatMapToInt(Function<T, IntStream> m)
- flatMapToLong(Function<T, LongStream> m)
최종 연산
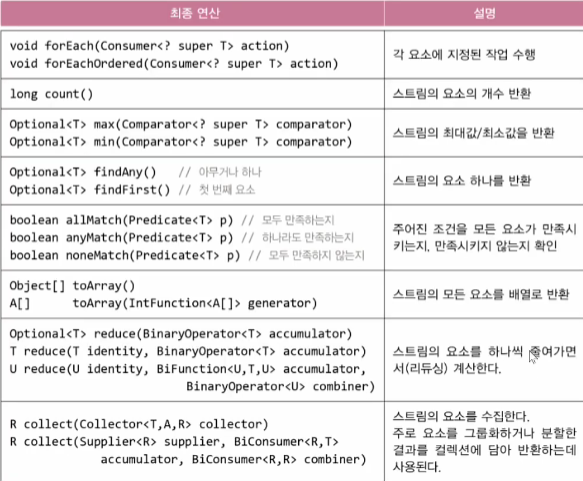
- forEachOrdered : 순서 유지, 병렬 스트림일 때 사용하면 스트림의 요소들의 순서를 유지하여 작업함, 상관이 없으면 forEach 사용
- max(Comparator~), min(Comparator~) 최소, 최대값은 Comparator 기준을 줘서 판단
- findAny : 병렬 스트림 처리할 때, filter()와 함께 사용됨. 즉 조건에 맞는 것을 반환
findFirst : 직렬 스트림 처리할 때, 요소의 첫 번째를 반환할 때
Optional
Wrapper Class
작업 결과를 Optional 객체에 담아서 줌
작업 결과가 null일 수도 있는데, null이어도 객체로 담아서 주면 좋으니까
-
allMatch(조건식) : 스트림 요소 중 해당 조건식을 모두 만족한다면 TRUE
-
anyMatch(조건식) : 스트림 요소 중에 해당 조건식을 만족하는 게 하나라도 있으면 TRUE
-
noneMatch(조건식) : 스트릶 요소 중에 해당 조건식을 모두 만족하지 않을 때 TRUE
-
toArray() : 스트림의 모든 요소를 배열로 반환
-
A[] toArray(IntFunction<A[]> generator) : 특정 타입으로 반환 받을 수 있음
reduce,collect가 최종 연산의 핵심
reduce를 이해하면collect도 쉽게 이해할 수 있다.- reduce(BinaryOperator<T> accumulator) : 스트림의 요소를 하나씩 줄여가면서(리듀싱) 계산(작업, count, sum 등..)
- collect : reduce를 이용해서 group 작업하는 것

