Tomcat

Tomcat은 servlet을 호출, 관리할 수 있는 was 중 하나입니다.
- Servlet을 다룰 수 있는 다른 was의 예) netty
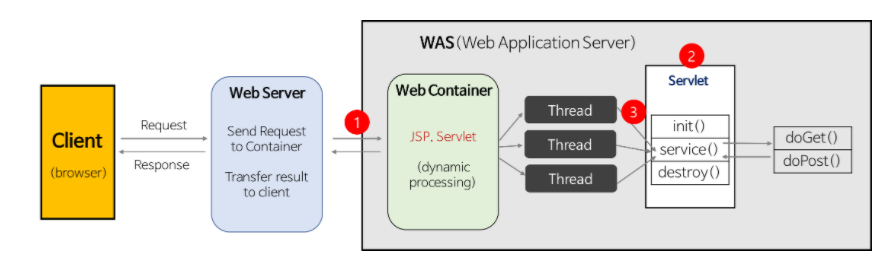
Tomcat은 Servlet container에서 servlet들을 관리하며 동적인 리소스를 처리합니다.
- Tomcat은 Servlet을 map으로 관리합니다.
Tomcat 5.5 버전 부터는 아파치의 httpd(웹서비스 데몬) native module을 가져와 정적 리소스를 처리하기 때문에 정적 리소스를 처리 역시 우수합니다.
하지만 Web server의 역할은 정적 리소스만 핸들링하는 것이 아닙니다.
Production 환경에서는 Nginx 또는 apache를 따로 web server로 둡니다.
하나의 Tomcat에는 여러개의 application server를 붙을 수 있습니다.
이 때 각 application server는 다른 jvm 위에서 동작합니다.
There is one context per "web application" per Java Virtual Machine.
from jakarta.ee 10 - servletConext docs
보통 하나의 tomcat에 하나의 web application을 구동하고 tomcat들을 web server에 연결하여 reverse proxy합니다.
Servlet
Servlet이란 동적 웹 페이지를 만들 때 사용되는 자바 기반의 웹 애플리케이션 프로그래밍 기술입니다.
Servlet은 웹 요청과 응답의 흐름을 간단한 메서드 호출만으로 체계적으로 다룰 수 있게 해줍니다.
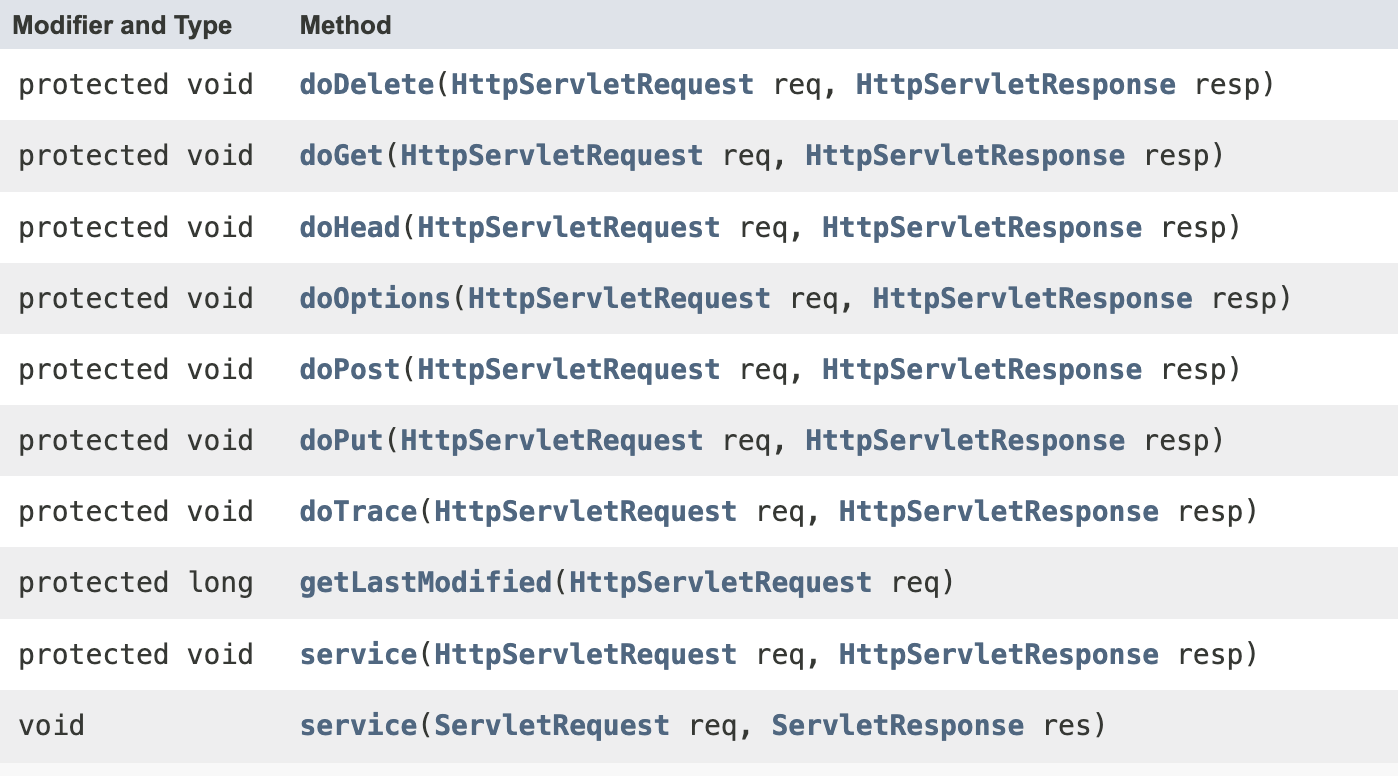
Servlet은 interface로 정의되어 있습니다.
핵심 메소드는 init(), service(), destroy()입니다.
세 메소드의 호출 주체는 Servlet container입니다.
void init()
Called by the servlet container to indicate to a servlet that the servlet is being placed into service.
...
void service(...)
Called by the servlet container to allow the servlet to respond to a request.
...
Called by the servlet container to indicate to a servlet that the servlet is being taken out of service.
...
> Image Source: https://medium.com/@wminikuma/java-servlet-dc81ab09139cServlet의 생명주기
init()
- Servlet 객체가 있다면 재사용, 아니라면 생성합니다.
- init() 호출 시 파라미터로 넘어오는 ServletConfig를 통해 servlet 정보를 가져옵니다.
- 이 때 servletConfig.getServletConext()를 통해 servletContext를 가져올 수 있습니다.
- Servlet context는 아래서 다시 보겠습니다.
- 이 때 servletConfig.getServletConext()를 통해 servletContext를 가져올 수 있습니다.
Service()
- 실제 request를 처리하는 로직을 수행하고 responose를 반환합니다.
- Servlet을 구현한 클래스들은 해당 메소드를 override 해야합니다.
HttpServlet에서의 Service()
- Http Protocol인 경우 HttpServlet을 상속하여 Servlet을 구현하면 됩니다.
- HttpServlet의 service() 에서는 override한 service 메소드 내에서 http method에 doGet, doPost, doPut...을 호출하도록 작성해 놓았습니다.
- 이로 인해 개발자는 service()를 override하는 것이 아닌 doGet(), doPost(), doPut()..들만 override하면 됩니다.
- 템플릿 메서드 패턴
package jakarta.servlet.http;
abstract class HttpServlet extends GenericServlet {
...
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String method = req.getMethod();
if (method.equals("GET")) {
...
this.doGet(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("HEAD")) {
...
this.doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("POST")) {
this.doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("PUT")) {
this.doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("DELETE")) {
this.doDelete(req, resp);
} ...
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 개발자가 해당 method를 override하지 않으면 자동으로 에러 response를 줍니다.
String protocol = req.getProtocol();
String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_post_not_supported");
resp.sendError(this.getMethodNotSupportedCode(protocol), msg);
}
protected void doPut(HttpServletRequest req,
// 개발자가 해당 method를 override하지 않으면 자동으로 에러 response를 줍니다.HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String protocol = req.getProtocol();
String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_put_not_supported");
resp.sendError(this.getMethodNotSupportedCode(protocol), msg);
}
...
}
참고
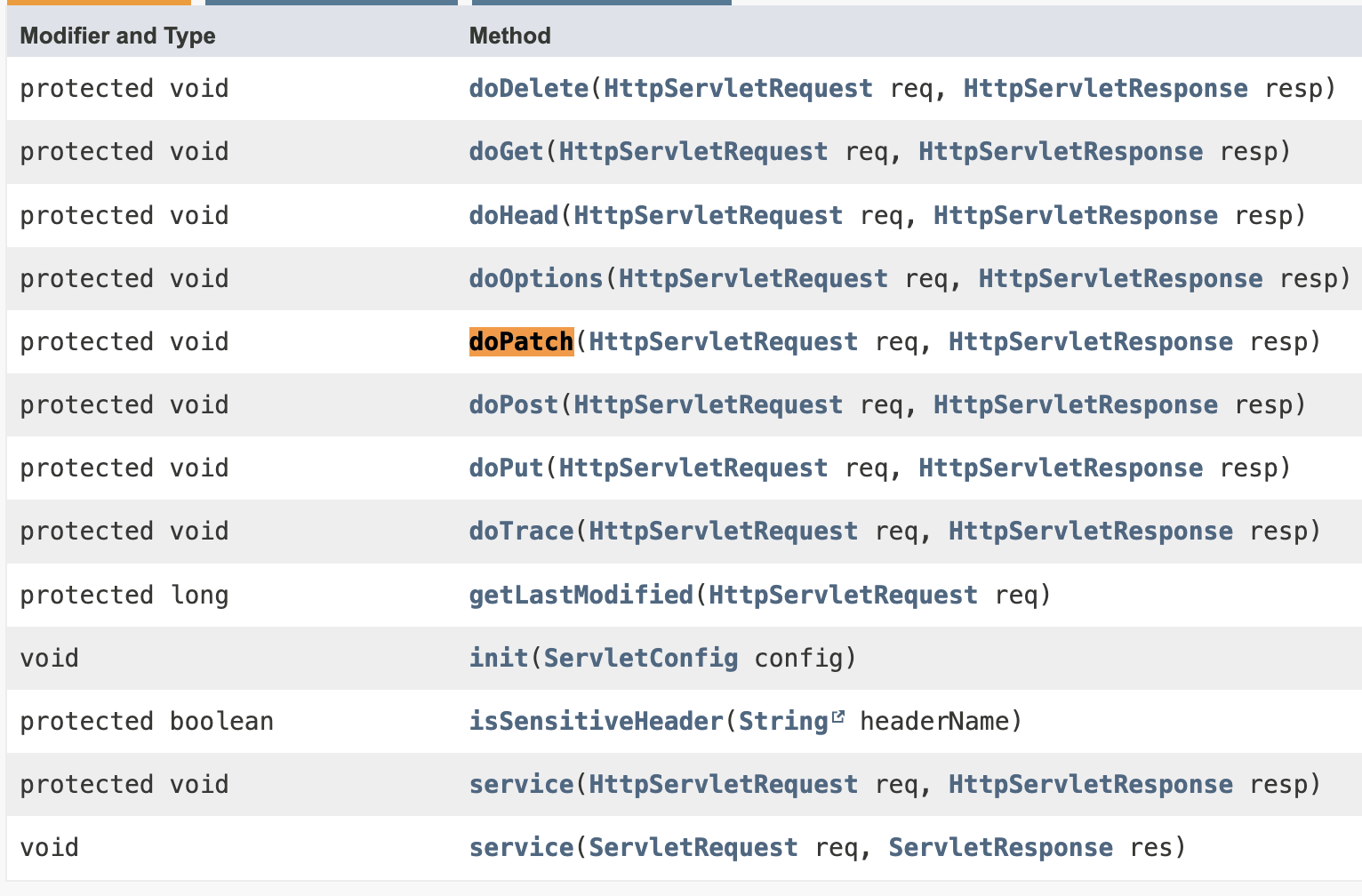
doPatch의 경우 과거 HTTP 표준이 아니었기 때문에 존재하지 않았지만, Servlet 6.0 이 후 HttpServlet에 추가되었습니다.하지만 jarkarta ee 9, jarkarta ee 10의 HttpServlet는 doPatch()가 존재하지 않습니다.
tomcat- 10.0 api docs(Servlet 5.0), jarkarta ee 9, jarkarta ee 10
destroy()
destroy()가 호출되는 조건은 아래와 같습니다.
- timeout이 발생한 경우
- application이 종료되는 경우
- 수동으로 호출하는 경우
destroy()에는 해당 Servlet이 종료되기 전 clean up code를 구현하면 됩니다.
- database 연결 해제
Object.finalize()와 같은 이유로 사용하지 않은 것을 권장합니다.
- 리소스가 부족한 상황에서 메소드 호출 시 리소스를 추가적으로 사용하게 되어 성능 감소, 프로그램이 종료될 수 있습니다.
Servlet context
Servlet context는 servlet container가 servlet 사이의 연동을 위한 메소드를 지원하는 interface 입니다.
- 서블릿 컨테이너가 종료되면 소멸합니다.
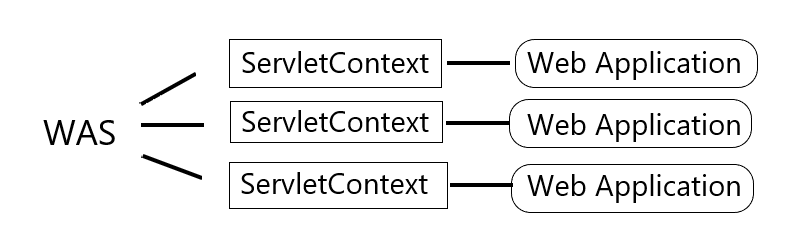
> Image source: https://velog.io/@suhongkim98/DispatcherServlet%EA%B3%BC-%EC%8A%A4%ED%94%84%EB%A7%81-%EC%BB%A8%ED%85%8C%EC%9D%B4%EB%84%88-%EC%83%9D%EC%84%B1-%EA%B3%BC%EC%A0%95Tomcat은 여러개의 Web application을 구동할 수 있습니다.
- 같은 톰켓에 배포된 어플리케이션끼리는 다른 세션을 가집니다. (distributed)
- 어플리케이션마다 servlet context를 초기화고 생성합니다.
There is one context per "web application" per Java Virtual Machine.
In the case of a web application marked "distributed" in its deployment descriptor, there will be one context instance for each virtual machine.
In this situation, the context cannot be used as a location to share global information (because the information won't be truly global). Use an external resource like a database instead.
Servlet Container
Servlet을 관리하는 container입니다.
- Servlet container는 엔진이라고도 불립니다.
Servlet container는 servlet들을 기본적으로 singletone으로 관리합니다.
- 멀티스레드 환경에서 동작하도록 설계
- 메모리 성능을 위해
아래는 Servlet이 Singletone이 아닌 경우입니다.
- 사용자가
new연산자를 통해 Servlet을 생성한 경우 deprecated된 방법을 사용하는 경우
> Image Source: https://siliconvalleygazette.com/posts/different-containers-available-in-servlet.png
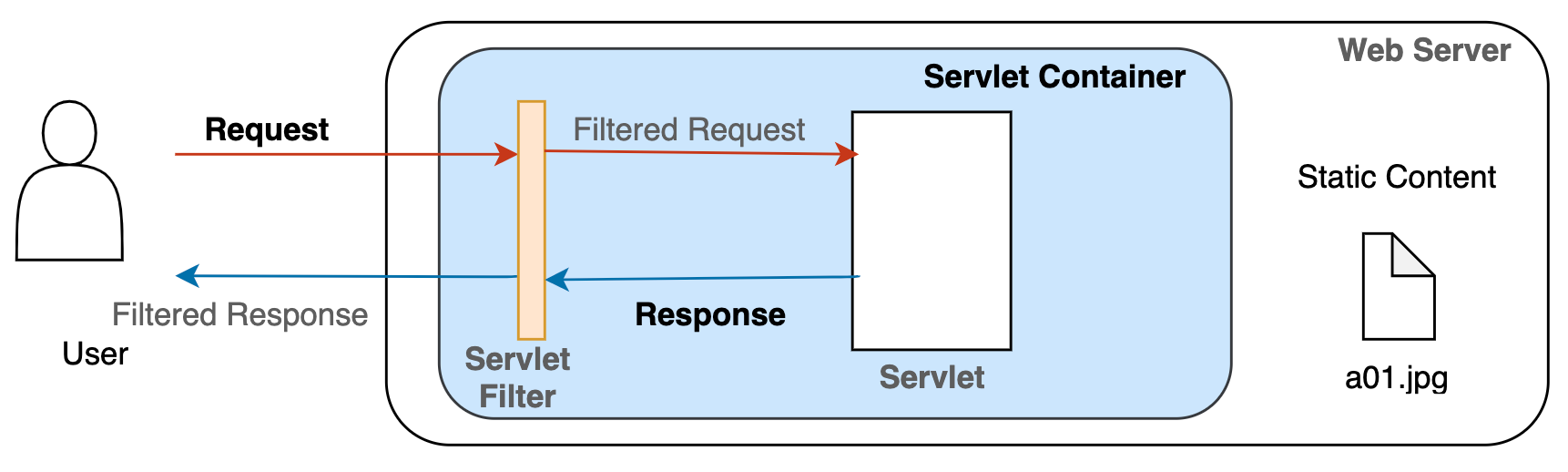
요청이 들어오면 아래 과정이 순서대로 진행됩니다.
- ServletRequest, ServletResponse 객체 생성
- Protocol에 따라 ServletRequest / Response를 상속하여 구체적인 데이터를 제공하는 객체를 생성할 수 있습니다.
- ex) Http protocol인 경우
HttpServletRequest,HttpServletResponse를 생성합니다.
- Servlet filter를 통해 request filtering
- Filter는 체인 형태로 구성되며 중간에 필터를 자유롭게 추가할 수 있습니다.
- 어느 servlet에 대해 요청한 것인지 탐색 (url과 target servlet을 mapping)
- 개발자는 Web.xml, servlet config 등에 url과 target servlet을 설정해 놓습니다.
- 해당 servlet의 service()를 호출
- servlet이 존재하지 않으면 init() 후 호출합니다.
- 이 때 같은 servlet이더라도 다른 thread를 통해 service()를 호출합니다.
현재는 레거시 이외에는 web.xml을 거의 사용하지 않습니다.
web.xml의 단점과 대체 역사가 궁금하시다면 아래 글을 읽는 것이 도움이 될 것 같습니다.
참조
jarkarta.ee 10
jarkarta.ee 9
oracle.java.ee 7
tomcat - 11.0 api docs(Servlet 6.0)
tomcat - 10.0 api docs(Servlet 5.0)