뒤에 코드리뷰를 할 것이기 때문에 요약은 최대한 간결하게 하겠다.
요약
Graph Anomaly Detection에서 대부분의 접근 방식은 graph에 low pass filter를 적용하는 방식으로 해석될 수 있기 때문에, anomaly를 탐색하는 데에는 적합하지 않다. 주변의 node와 비슷한 representation을 가지게 되는 graph의 특성에 대비하여 anomaly는 그와 정반대되는 특징을 가지고 있기 때문이다.
Adaptive Multi-frequency Graph Neural Network(AMNet)는 graph filter를 attention mechanism을 이용해 선택하여 low pass filter와 high pass filter를 그래프에 이용할 수 있도록 하는 방법이다.
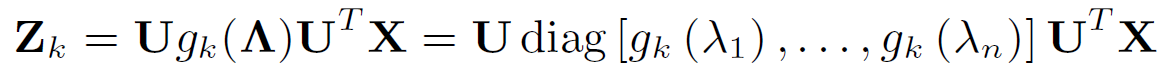
K개의 frequency의 graph filter group을 로 지칭했을 때, graph signal 는 위와 같이 정의될 수 있다.
이를 attention을 이용해 각 node와 graph filter의 연관성을 계산할 수 있는데,
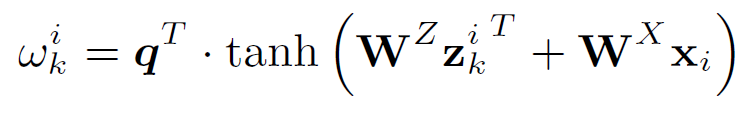
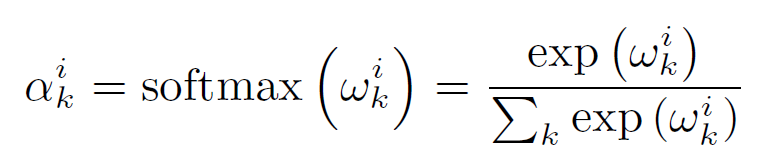
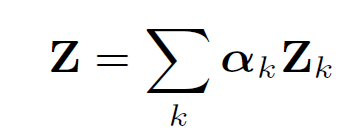
위와 같이 계산 가능한데, 기존의 attention과 비슷하면서도 graph에 맞게 변형한 모습으로 보인다.
전체 구조는 아래와 같다.
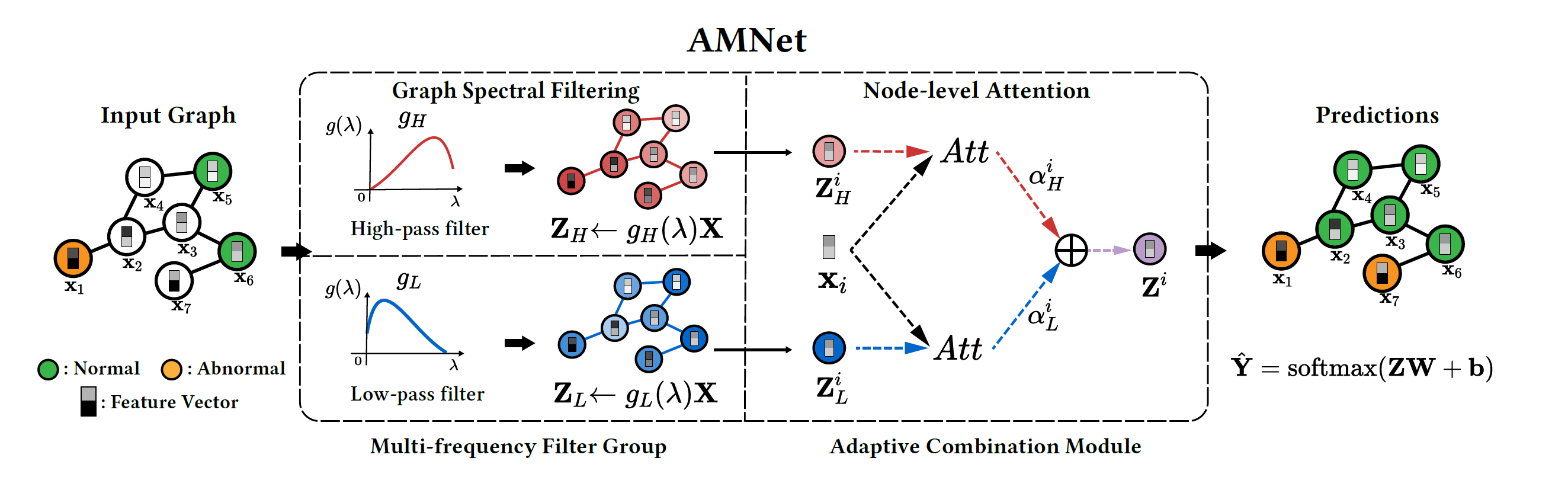
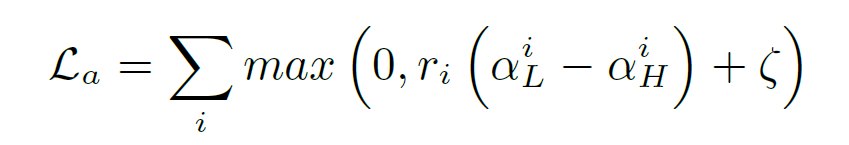
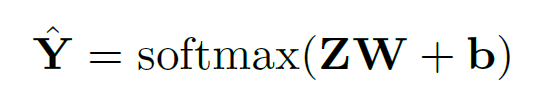
loss로는 anomaly node와 normal node에서의 filter와의 attention의 차이를 margin만큼 둘 수 있는 margin-based attention loss와 Z embedding으로 classification을 한 후 이를 label과 cross entropy로 계산한 classification loss를 더한 값을 최종 loss로 한다.
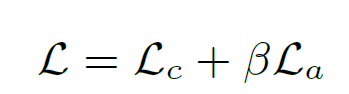
이후엔 구현에 관한 디테일이 설명되어 있으나, 이 부분은 생략한다. 궁금하면 직접 논문을 읽어보면 좋을 것 같다. Bernstein polynomial
코드를 보면

config는 이런 식으로 작성하면 되고,
데이터셋을 열어보면 이런 식으로 되어있다.
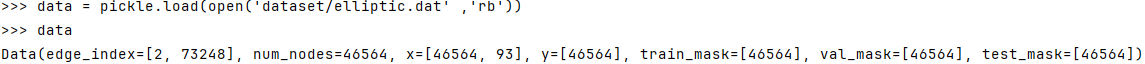
class AMNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, hid_channels, num_class, K, filter_num, dropout=0.3):
super(AMNet, self).__init__()
self.act_fn = nn.ReLU()
self.attn_fn = nn.Tanh()
self.linear_transform_in = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(in_channels, hid_channels),
self.act_fn,
nn.Linear(hid_channels, hid_channels),
)
self.K = K
self.filters = nn.ModuleList([BernConv(hid_channels, K, normalization=True, bias=True) for _ in range(filter_num)])
self.filter_num = filter_num
self.W_f = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(hid_channels, hid_channels),
self.attn_fn,
)
self.W_x = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(hid_channels, hid_channels),
self.attn_fn,
)
self.linear_cls_out = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(dropout),
nn.Linear(hid_channels, num_class))
self.attn = list(self.W_x.parameters())
self.attn.extend(list(self.W_f.parameters()))
self.lin = list(self.linear_transform_in.parameters())
self.lin.extend(list(self.linear_cls_out.parameters()))
self.reset_parameters()여기서 BernConv 클래스를 보면
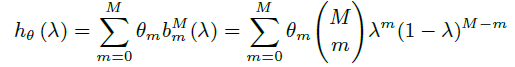
이 부분을 계산해준다. 이를 통해 x와 edge를 통해 여러 h를 만든 후에, 이를 W_f로 projection하고 x를 W_x로 projection 하여 이를 둘을 matmul하고 softmax를 거쳐 score를 만든다.
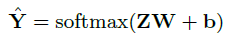
이후 결과는 attention score에 h를 곱해서 Z를 만든 후 이를 linear 변환해 만든다.
def forward(self, x, edge_index, label=None):
"""
:param label:
:param x:
:param edge_index:
:return:
"""
x = self.linear_transform_in(x)
h_list = []
for i, filter_ in enumerate(self.filters):
h = filter_(x, edge_index)
h_list.append(h)
h_filters = torch.stack(h_list, dim=1)
h_filters_proj = self.W_f(h_filters)
x_proj = self.W_x(x).unsqueeze(-1)
score_logit = torch.bmm(h_filters_proj, x_proj)
soft_score = F.softmax(score_logit, dim=1)
score = soft_score
res = h_filters[:, 0, :] * score[:, 0]
for i in range(1, self.filter_num):
res += h_filters[:, i, :] * score[:, i]
y_hat = self.linear_cls_out(res)
marginal_loss = 0.
if self.training:
anomaly_train, normal_train = label
normal_bias = score[normal_train][:, 1] - score[normal_train][:, 0]
anomaly_bias = score[anomaly_train][:, 0] - score[anomaly_train][:, 1]
normal_bias = torch.clamp(normal_bias, -0.)
anomaly_bias = torch.clamp(anomaly_bias, -0.)
normal_bias = torch.mean(normal_bias)
anomaly_bias = torch.mean(anomaly_bias)
bias = anomaly_bias + normal_bias
marginal_loss = bias
if self.training:
return y_hat, marginal_loss
else:
return y_hat
