1. Application for Polymorphism
이번 글에서는 [인프런] Do it! 자바 프로그래밍 입문 with 은종쌤 의 '다형성 활용과 다운캐스팅' 강의에서
다형성 활용하기 편을 다룹니다.
다형성 활용하기
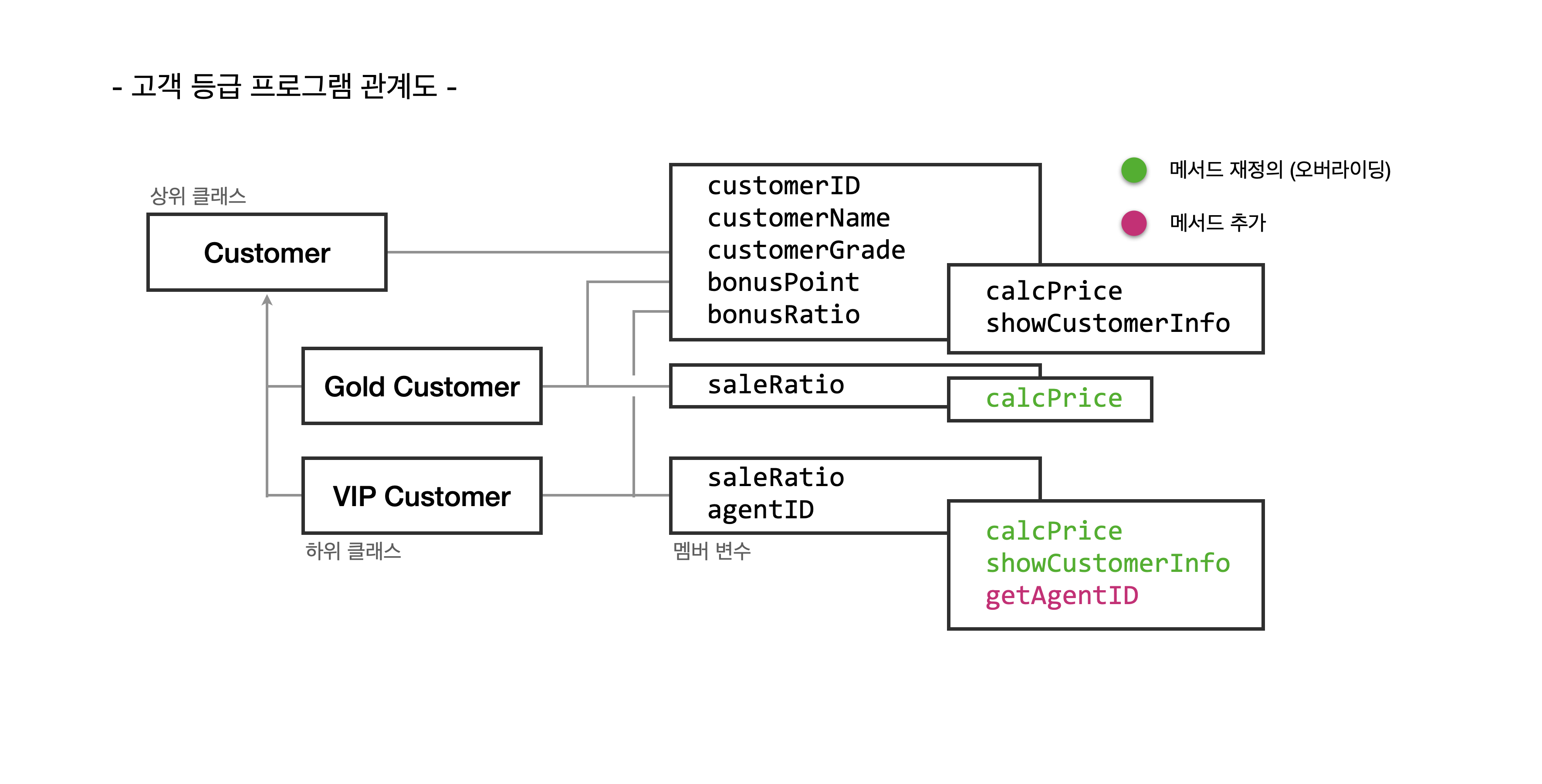
지난 강의에서 'Customer' 클래스의 하위 클래스를 만들어 고객 등급을 나눠
등급 간 혜택의 차이를 두는 프로그램을 만들었는데요, 이번에는 객체를 생성해 배열의 요소로 저장하고
각 고객이 물건을 구매할 때의 가격과 보너스 포인트를 계산합니다.
public class CustomerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Customer> customerList = new ArrayList<Customer>();
Customer customerLee = new Customer(10010, "이순신");
Customer customerShin = new Customer(10011, "신사임당");
GoldCustomer customerHong = new GoldCustomer(10012, "홍길동");
GoldCustomer customerYul = new GoldCustomer(10013, "이율곡");
VIPCustomer customerKim = new VIPCustomer(10014, "김유신", 12345);
customerList.add(customerLee);
customerList.add(customerShin);
customerList.add(customerHong);
customerList.add(customerYul);
customerList.add(customerKim);
System.out.println("====== 고객정보 출력 ======");
for (Customer customer : customerList) {
System.out.println(customer.showCustomerInfo());
}
System.out.println("\n====== 할인율과 보너스 포인트 결과 출력 ======");
int price = 10000;
for (Customer customer : customerList) {
int cost = customer.calcPrice(price);
System.out.println(customer.getCustomerName() + "님이 " + cost + "원을 지불하였습니다.");
System.out.println(customer.showCustomerInfo() + "\n");
}
}
}
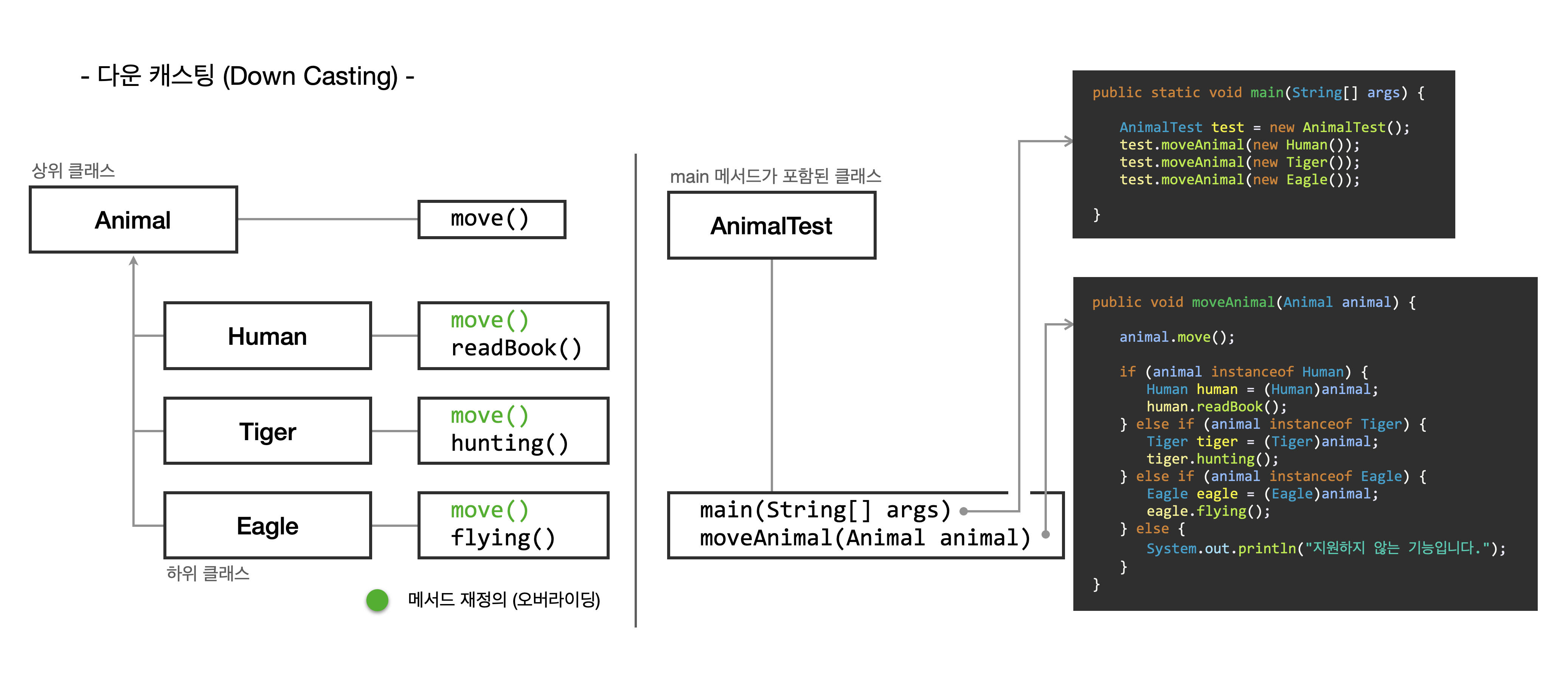
2. Down Casting - 'instanceof'
하위 클래스가 상위 클래스로 형 변환 되는 것은 묵시적으로 이루어집니다.
// 묵시적 형변환 ex)
Customer customerKil = new VIPCustomer();다시 원래 자료형인 하위 클래스로 형 변환 하려면 명시적으로 다운캐스팅을 해야 합니다.
이때 원래 인스턴스의 타입을 체크하는 예약어는 instanceof 입니다.
// 상위 클래스
class Animal {
public void move() {
System.out.println("동물이 움직입니다.");
}
}// 하위 클래스
class Human extends Animal { // 'Animal' 상속
public void move() { // 오버라이딩
System.out.println("사람이 두 발로 걷습니다.");
}
public void readBook() { // 'Humal' 클래스의 메서드
System.out.println("사람이 책을 읽습니다.");
}
}
class Tiger extends Animal { // 'Animal' 상속
public void move() { // 오버라이딩
System.out.println("호랑이가 네 발로 뜁니다.");
}
public void hunting() { // 'Tiger' 클래스의 메서드
System.out.println("호랑이가 사냥합니다.");
}
}
class Eagle extends Animal { // 'Animal' 상속
public void move() { // 오버라이딩
System.out.println("독수리가 하늘을 납니다.");
}
public void flying() { // 'Eagle' 클래스의 메서드
System.out.println("독수리가 하늘을 납니다.");
}
}public class AnimalTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnimalTest test = new AnimalTest(); // 'Animal' 클래스의 인스턴스 'test' 생성
test.moveAnimal(new Human()); // 매개변수로 하위 클래스 인스턴스를 받아
test.moveAnimal(new Tiger()); // 'moveAnimal()' 메서드를 실행합니다.
test.moveAnimal(new Eagle());
}
// 'AnimalTest' 클래스의 메서드, 매개 변수로
public void moveAnimal(Animal animal) {
animal.move();
// 컴파일은 되지만(다운캐스팅) 다른 클래스의 객체가 포함되어 이를 호출하면 오류가 납니다.
//Human human = (Human)animal;
//human.readBook();
// 다운캐스팅을 할 때 다른 클래스의 객체가 포함되는 경우
// 아래와 같이 조건문에 instanceof 예약어를 사용해 비교해 메서드를 호출해야 합니다.
if (animal instanceof Human) {
Human human = (Human)animal;
human.readBook();
} else if (animal instanceof Tiger) {
Tiger tiger = (Tiger)animal;
tiger.hunting();
} else if (animal instanceof Eagle) {
Eagle eagle = (Eagle)animal;
eagle.flying();
} else {
System.out.println("지원하지 않는 기능입니다.");
}
}
}[결과]
사람이 두 발로 걷습니다.
사람이 책을 읽습니다.
호랑이가 네 발로 뜁니다.
호랑이가 사냥합니다.
독수리가 하늘을 납니다.
독수리가 하늘을 납니다.'moveAnimal()'를 호출하면 먼저 인스턴스의 'move()' 메서드를 호출하고
이후 조건문을 통해 인스턴스의 타입을 비교해 그에 맞는 인스턴스별 메서드를 호출합니다.