자료 구조 HW12
HW12-1
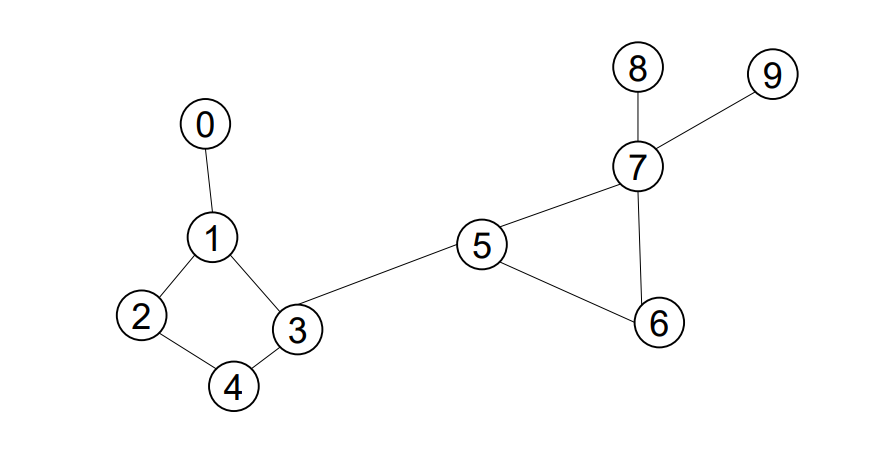
(1) 교재에 있는 그래프에 대하여 정점 3에서 출발하여 너비 우선 탐색을 한 경우의
방문 순서를 쓰세요.
풀이과정)
위 문제는
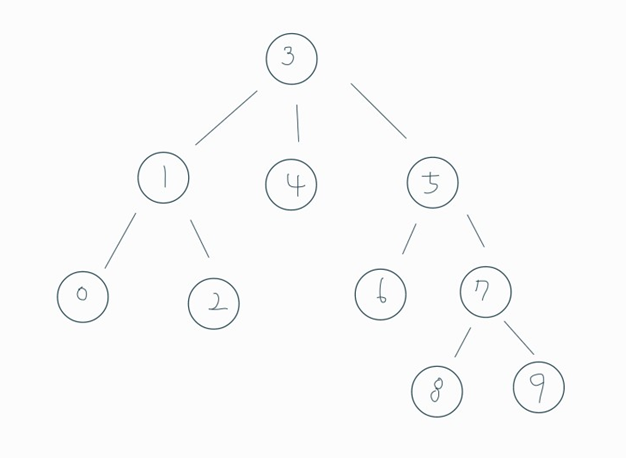
으로 볼 수 있다.
BSF는 단계별로 방문하므로 답은
3 -> 1 -> 4 -> 5 -> 0 -> 2 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> 9
이다.
답)
3 -> 1 -> 4 -> 5 -> 0 -> 2 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> 9
(3) 정점 3에서 출발하여 깊이 우선 탐색을 한 경우의 방문순서를 쓰세요.
풀이과정)
DSF는 제일 깊이 들어간 다음에 막다른 길이 나오면 되돌아 나오므로

위를 참고하였을때 방문순서는
3-> 1 -> 0 -> 2 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> 9
이다.
답)
3-> 1 -> 0 -> 2 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> 9
HW12-2
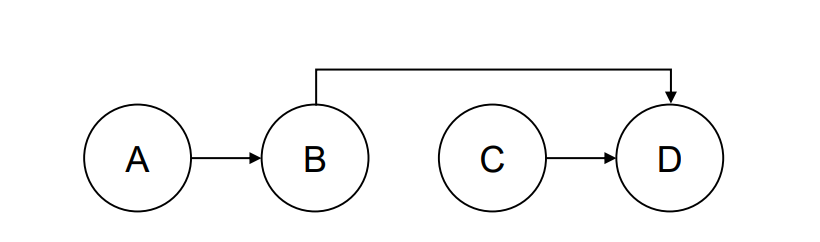
• 위와 같이 그래프가 주어졌을 때, V(정점 집합), E(간선 집합)을 쓰세요.
답)
V = {A, B, C, D}
E = {(A, B), (B,D), (C,D)}
• Adjacent list(인접 리스트)를 쓰세요.
답)
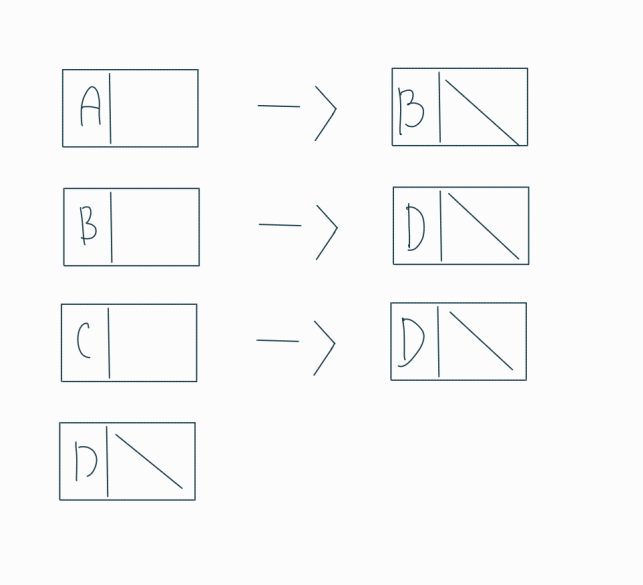
• Topological sort(위상 정렬)하여 정점을 나열하세요.
풀이과정)
위의 그래프에서는 사이클이 없으므로 위상 정렬이 가능하다.
indegree가 0인 정점은 A와 C이다.
A를 먼저 본다면 순서는 A -> C -> B -> D 혹은 A -> B -> C -> D 이다.
C를 먼저 본다면 순서는 C -> A -> B -> D이다.
답)
A -> C -> B -> D
or
A -> B -> C -> D
or
C -> A -> B -> D
• 위상 정렬 알고리즘 pseudo code로 작성하세요.
답)

HW12-3
교재 p.448-450
• 교재 프로그램 11.11, 11.12 프로그램을 본인 코드로 옮겨 봅니다.
답)
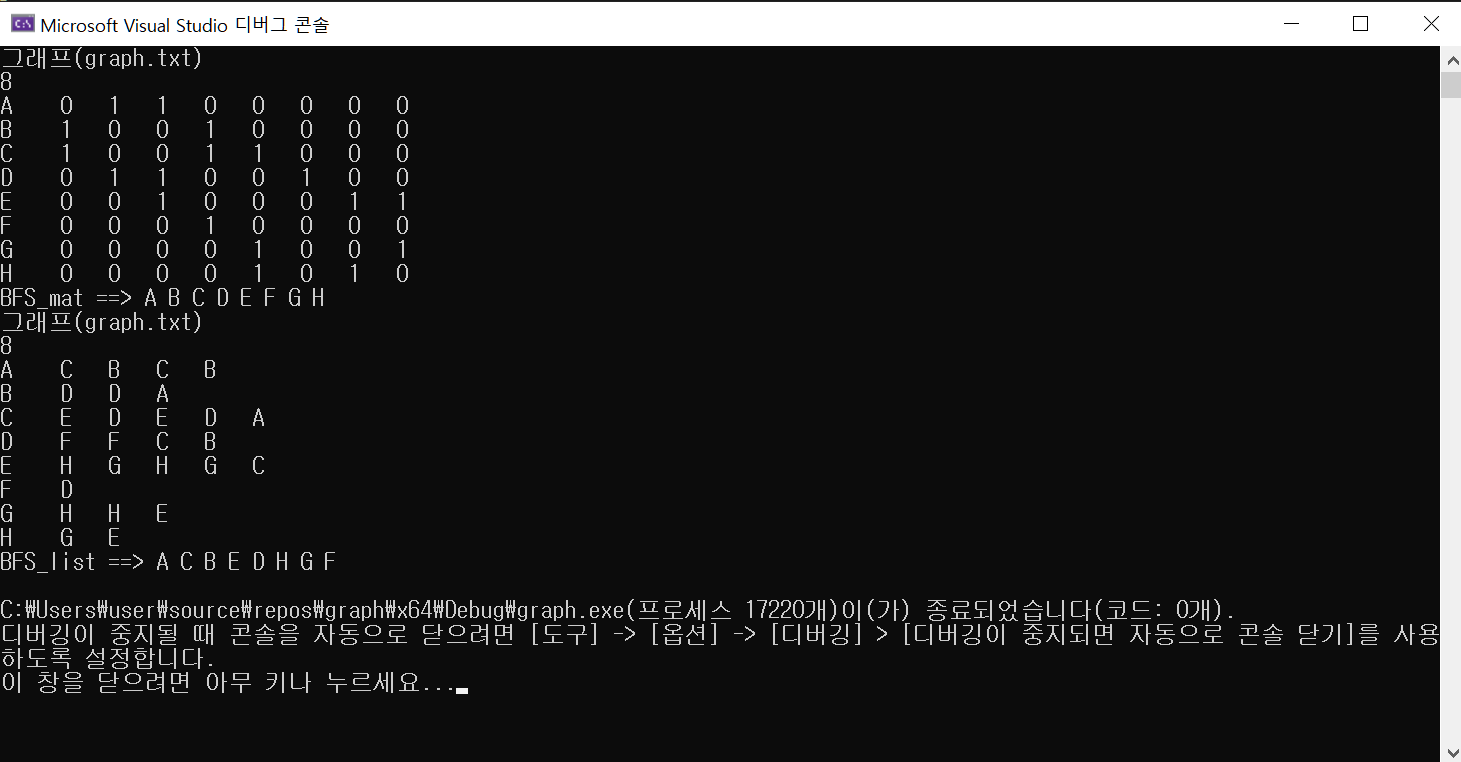
인접행렬을 이용한 BSF
void BFS_mat(int v) {
visited[v] = true;
std::cout << getVertex(v) << " ";
CircularQueue que;
que.enqueue(v);
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
int v = que.dequeue();
for (int w = 0; w < size; w++)
if (isLinked(v, w) && visited[w] == false) {
visited[w] = true;
std::cout << getVertex(w) << " ";
que.enqueue(w);
}
}
}인접 리스트를 이용한 BSF
void BFS_list(int v) {
visited[v] = true;
std::cout << getVertex(v) << " ";
CircularQueue que;
que.enqueue(v);
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
int v = que.dequeue();
for (Node* w = adj[v]; w != NULL; w = w->getLink()) {
int id = w->getId();
if (!visited[id]) {
visited[id] = true;
std::cout << getVertex(id) << " ";
que.enqueue(id);
}
}
}
}• 주어진 ‘graph.txt’ 파일을 일고, 이를 너비 우선 탐색하여 교재와 같은 결과를 확인합니다.
답)