1️⃣ use strict모드를 사용할 경우 this는 어떻게 되나요?
this는 객체의 프로퍼티나 메서드를 참조하기 위한 자기 참조 변수이므로
일반적으로 객체의 메서드 내부 혹은 생성자 함수 내부에서만 의미가 있습니다.
strict mode가 적용된 일반 함수 내부의 this에는 undefined가 바인딩 된다.
2️⃣ 자바스크립트에서 this는 몇가지로 추론 될 수 있나요? 아는대로 말해주세요
(1) 일반 함수로 호출된 모든 함수 내부의 this는 전역 객체로 추론됩니다. 그리고 (2) 호출된 메서드나 프로토타입 메서드 내부에서는 메서드를 호출한 객체로, (3) 생성자 함수 내부에서는 생성자 함수가 생성할 인스턴스로 추론됩니다. (4) prototype의 call, apply, bind 함수를 사용하면 해당 함수의 인자로 전달된 객체를 this로 바인딩하게 되고, (5) strict 모드에서 일반 함수로 사용한 경우 undefined로 추론될 수 있습니다. (6) eventListener 안에서는 해당 eventListener가 부착된 html 요소 즉 e.currentTarget으로 추론됩니다.
3️⃣ 일반함수의 this와 화살표 함수의 this는 어떻게 다른가요?
일반 함수의 this는 window(전역 객체)을 가리키지만 화살표 함수의 this는 언제나 상위스코프의 this를 가리킨다.
4️⃣ 다음 코드를 보고 출력 결과를 말해보고 그 이유를 말해보자.
function Circle(radius){ this.radius = radius; this.getDiameter = function(){ return 2*this.radius; } } const circle3 = Circle(15); console.log(circle3); console.log(radius);Circle을 new 연산자 없이 일반 함수로 호출했으므로
첫번째 출력문에서는 Circle에는 반환문이 없으므로 undefined가 출력되고,
두번째 출력문에서는 일반 함수 내부의 this는 전역 객체를 가리키므로 15가 출력된다.
5️⃣ 다음 코드에서 foo 함수 내부의 this 바인딩을 말하고, 그렇게 생각한 이유를 밝혀보자.
const foo = function () { console.dir(this); }; // 1번 document.getElementById("btn").addEventListener("click", function(e){ let arr = [1,2,]; arr.forEach(foo()); }) const obj = {foo}; obj.foo(); // 2번 new foo(); // 3번 const bar = {name: 'bar'}; foo.call(bar); // 4번 foo.apply(bar); // 5번 foo.bind(bar); // 6번[1]
foo를 일반 함수로 호출하는 경우로foo함수 내부의this는 전역 객체window를 가리킨다. 그러므로 1번은 window가 2번 출력된다.
[2]foo를 프로퍼티 값으로 할당하여 호출하므로foo함수 내부의this는 메서드를 호출한 객체obj를 가리킨다. 그러므로 2번은 obj가 출력된다.
[3]foo함수를new연산자와 함께 생성자 함수로 호출하므로 this는 생성자 함수가 생성한 인스턴스를 가리킨다. 그러므로 3번은 foo {}가 출력된다.
[4][5][6]Function.prototype.apply/call/bind에 의해 간접 호출할 경우foo함수 내부의this는 인수에 의해 결정된다. 첫번째 인수로 bar를 전달했으므로 4,5,6번은 bar가 출력된다.
학습 내용
this
; 자신이 속한 객체 또는 자신이 생성할 인스턴스를 가리키는 자기 참조 변수*self-reference variable*
; this는 자바스크립트 런타임 시에 바인딩이 이루어지는 실행 컨텍스트 중 하나
- 코드 어디서든 참조 가능
- 키워드로 분류되지만 식별자 역할을 한다.
this가 필요한 이유
인스턴스가 생성되기 전에 property 또는 method를 추가하기 위해서, 자신이 속한 객체 또는 자신이 생성할 인스턴스를 미리 가리킬 수 있는 식별자가 필요하기 때문이다.
*생성자 함수 내부에서는 프로퍼티 또는 메서드를 추가하기 위해 자신이 생성할 인스턴스를 참조할 수 있어야 한다. 하지만 생성자 함수에 의한 객체 생성 방식은 먼저 생성자 함수를 정의한 이후 new 연산자와 함께 생성자 함수를 호출하는 단계가 추가로 필요하다. 다시 말해, 생성자 함수로 인스턴스를 생성하려면 먼저 생성자 함수가 존재해야 한다.
생성자 함수를 정의하는 시점에는 아직 인스턴스를 생성하기 이전이므로 생성자 함수가 생성할 인스턴스를 가리키는 식별자를 알 수 없다. 따라서 자신이 속한 객체 또는 자신이 생성할 인스턴스를 가리키는 특수한 식별자가 필요하다. 이를 위해 자바스크립트는 this 라는 특수한 식별자를 제공한다.*— 모던 자바스크립트 DeepDive p.343
this가 가리키는 값, 즉 this 바인딩은 함수 호출 방식에 의해 동적으로 결정된다.
*자바나 C++같은 클래스 기반 언어에서 this는 언제나 클래스가 생성하는 인스턴스를 가리킨다.
📌 렉시컬 스코프와 this 바인딩은 결정 시기가 다르다
함수의 상위 스코프를 결정하는 방식인 렉시컬 스코프Lexical scope는 함수 정의가 평가되어 함수 객체가 생성되는 시점에 상의 스코프를 결정한다.
하지만 this 바인딩은 함수 호출 시점에 결정된다.
- 생성자 함수에 메서드를 추가하는 방식
function Circle(radius){ this.radius = radius; } Circle.prototype.getDiameter = function (){ return 2*this.radius; } const circle = new Circle(5); console.log(circle.getDiameter()); // 10
// 1. 전역에서 this는 전역 객체 window를 가리킨다.
console.log(this); // 1 - window
// 2. 일반 함수 내부에서 this는 전역 객체 window를 가리킨다.
function square(number){
console.log(this); // 2 - window
return number * number;
}
square(2);
// 3. 메서드 내부에서 this는 메서드를 호출한 객체를 가리킨다.
const person = {
name: 'Lee',
getName(){
console.log(this); // 3 - {name: "Lee", getName: f}
return this.name;
}
};
console.log(person.getName()); // Lee
// 4. 생성자 함수 내부에서 this는 생성자 함수가 생성할 인스턴스를 가리킨다.
function Person(name){
this.name = name;
console.log(this); // 4 - Person {name: "Lee"}
}
const me = new Person("Lee");strict 모드에서의 this
strict mode가 적용된 일반 함수 내부의 this에는 undefined가 바인딩 된다.
📚 strict mode 적용에 의한 변화
‘use strict’;
- 함수를 일반 함수로 호출할 겨우
this에undefined가 바인딩 된다.
일반 함수 내부에서는 this를 사용할 필요가 없기 때문이다. 이때 에러는 발생하지 않는다.- 매개변수에 전달된 인수를 재할당 하여도
arguments객체에 반영되지 않는다.
1. 일반 함수 호출
- 기본적으로 this에는 전역 객체global object가 바인딩된다.
- 일반 함수로 호출된 모든 함수(중첩 함수, 콜백 함수 포함) 내부의 this에는 전역 객체가 바인딩된다.
- 전역 함수, 중첩 함수를 일반 함수로 호출하면 함수 내부의 this에는 전역 객체가 바인딩된다.
- 메서드 내에서 정의한 중첩 함수도 일반 함수로 호출되면 중첩 함수 내부의 this에는 전역 객체가 바인딩된다.
- 콜백 함수가 일반 함수로 호출된다면 콜백 함수 내부의 this에도 전역 객체가 바인딩된다.
⇒ 외부 함수인 메서드와 중첩 함수 또는 콜백 함수의 this가 일치하지 않아 중첩 함수/콜백 함수를 헬퍼 함수로 동작하기 어렵게 만든다.
⇒ (1)this를 별도 변수에 할당한 뒤 해당 변수를 참조하기 (2) Function.prototype.apply/call/bind 메서드 사용 (3) 화살표 함수 를 이용하여 this 바인딩을 일치시킨다.
2. 메서드 호출
- 메서드를 호출한 객체, 즉 메서드를 호출할 때 메서드 이름 앞의 마침표(.) 연산자 앞에 기술한 객체가 바인딩 된다. 왜냐하면, 메서드를 소유한 객체가 아닌 메서드를 호출한 객체에 바인딩 되기 때문이다.
const person = { name: 'Lee', getName() { return this.name; } }; const anotherPerson = { name: 'Kim' }; // getName 메서드를 anotherPerson 객체의 메서드로 할당 anotherPerson.getName = person.getName; const getName = person.getName; console.log(person.getName()); // Lee console.log(anotherPerson.getName()); // Kim console.log(getName()); // '' // 일반 함수로 호출 했으므로 this.name = window.name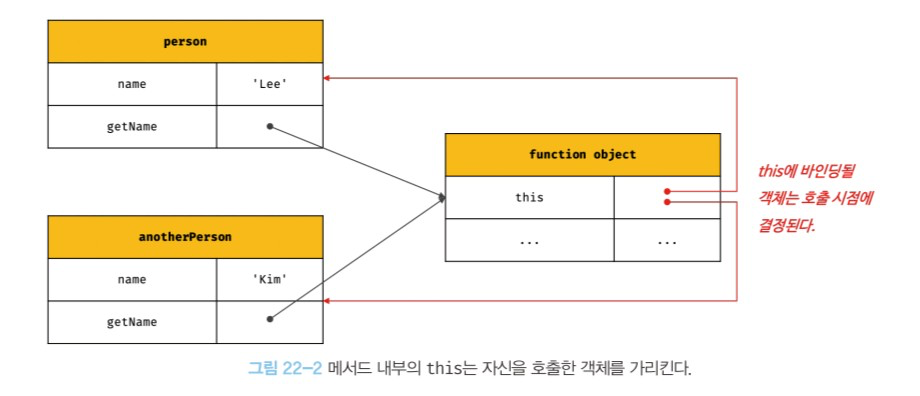
getName 프로퍼티가 가리키는 함수 객체, 즉 getName 메서드는 다른 객체의 프로퍼티에 할당하는 것으로 다른 객체의 메서드가 될 수도 있고 일반 변수에 할당하여 일반 함수로 호출될 수도 있다.
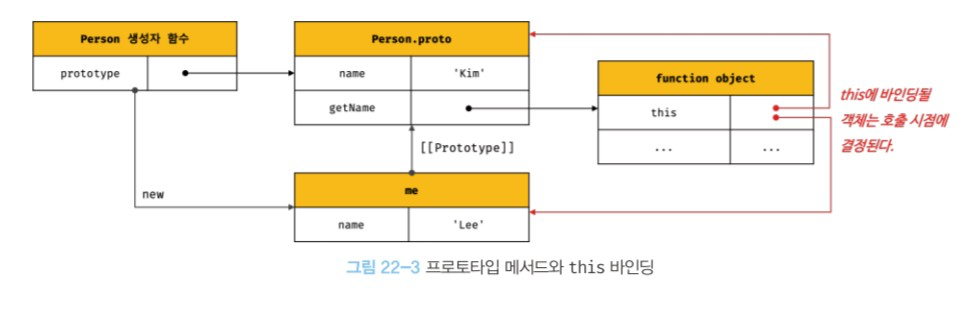
- 프로토타입 메서드 내부에서 사용된 this도 일반 메서드와 마찬가지로 해당 메서드를 호출한 객체에 바인딩 된다.
function Person(name){ this.name = name; } Person.prototype.getName = function(){ return this.name; }; const me = new Person('Lee'); console.log(me.getName()); // Lee Person.prototype.name = 'Kim'; console.log(Person.prototype.getName()); // Kim
3. 생성자 함수 호출
📌
생성자 함수란?
; 객체(인스턴스)를 생성하는 함수
- 일반 함수와 동일한 방법으로 정의
- new 연산자와 함께 호출한다.
new 연산자와 함께 호출하지 않으면 일반 함수로 동작한다.
생성자 함수 내부의 this에는 생성자 함수가 (미래에) 생성할 인스턴스가 바인딩된다.
4. Function.prototype.apply/call/bind 메서드에 의한 간접 호출
; Function.prototype의 메서드 → 모든 함수가 상속 받아서 사용 가능
- apply와 call 메서드는 함수를 호출한다.
- 함수를 호출하면서 첫 번째 인수로 전달한 특정 객체를 호출한 함수의 this에 바인딩한다.
- 유사 배열 객체에 배열 메서드를 사용하는 경우에 주로 사용
arguments객체는 배열 ❌Array.prototype.slice사용 ❌ butapply나call메서드를 사용하면 가능하다.function convertArgsToArray(){ // arguments 객체를 배열로 변환 // Array.prototype.slice를 인수 없이 호출하면 배열의 복사본을 생성한다. const arr = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments); return arr; } convertArgsToArray(1,2,3); // [1,2,3]
- bind 메서드는 함수를 호출하지 않는다. 다만 첫 번째 인수로 전달한 값으로 this 바인딩이 교체된 함수를 새롭게 생성해 반환한다.
const person = { name: 'Lee', foo(callback){ setTimeout(callback.bind(this),100); } }; person.foo(function(){ console.log('Hi! my name is ${this.name}.'); // Hi! my name is Lee. });
function getThisBinding(){
console.log(arguments);
return this;
}
const thisArgs = {a:1}; // this로 사용할 객체
console.log(getThisBinding.apply(thisArgs, [1,2,3]));
console.log(getThisBinding.call(thisArgs, 1,2,3));
console.log(getThisBinding.bind(thisArgs)); // getThisBinding
console.log(getThisBinding.bind(thisArgs)()); // {a:1}5. eventListener
- addEventListener가 부착된 html 요소, 즉
e.currentTarget과 같은 의미이다.
<button id = "btn">click</button>
<script>
document.getElementById("btn").addEventListener("click",
function(e){
console.log(this); // <button id="btn">click</button>
});
</script>참고 자료
모던 자바스크립트 DeepDive
https://devowen.com/276#this는 JavaScript에서 어떻게 작동하는지 설명해주세요.-1
https://manon-kim.tistory.com/entry/JS-this?category=1037367

아주 유용한 정보네요!