🏗️ Overview
A distributed system is a computing model where multiple computers are connected through a network and work together as a single system. In a distributed system, managing data is crucial, so the choice of database plays a key role.
A database is essential for storing, retrieving, modifying, and managing the system's data. Specifically, distributed systems must consider factors such as data consistency, availability, and partition tolerance, which are commonly referred to as the CAP theorem.
Moreover, databases should ensure data consistency and reliability through the `ACID properties`.
The CAP theorem and ACID properties will be discussed in more detail in the following sections.
🦺 ACID
🦺 ACIDrefers to a set of core principles that ensuresdata consistencyandreliability. It consists of four key components:Atomicity,Consistency,Isolation, andDurability.
ACID specifically outlines how a database transaction, which is the smallest logical unit in database operations, should be conducted.
To better illustrate the idea of ACID, an example from the finance sector, where strict adherence to these principles appears essential may be considered.
⚛️ Atomicity
⚛️ Atomicity ensures that internal operations within a single transaction will not be partially reflected in a database, implying there will be either a complete success or a complete failure.
In other words, failing to achieve a single operation out of multiple operations would result in a failing over a whole transaction.
For instance, failing to conduct operation #2 from the financial operations below would result in operation #1 not reflected:
- withdraw $2 from an account A
- deposit $2 to an account B
🧱 Consistency
🧱
Consistencyensures that when atransactionis successfully completed, thedatabaseremains in a consistent state.
Specifically, if a transaction violates rules defined in the database, such as constraints, the transaction must be canceled to maintain consistency.
For instance, a financial transaction exceeding the remaining balance of a account may not be permitted.
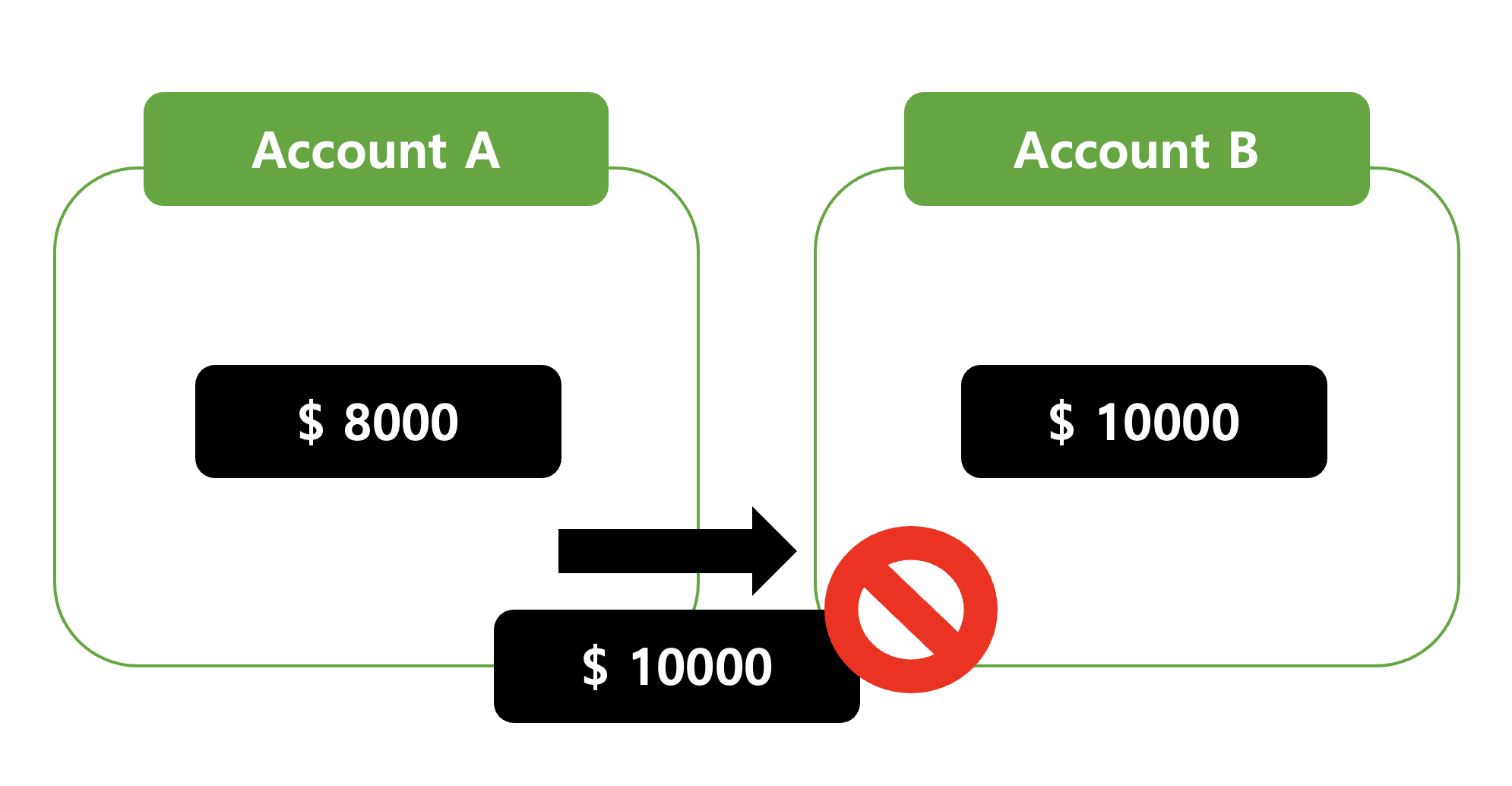
🏝️ Isolation
🏝️
Isolationensures thatmultiple transactionsexecutedconcurrentlyremainindependentof each other where thesetransactionsin the extreme settings could runsequentiallyat the cost ofperformances.
No operation outside a transaction can view or interfere intermediate data during the transaction's execution.
For instance, during a money transfer, if the total balance of Account A at $ 10,000, there may be moments when the total does not equal $ 10,000 during the transaction. However, other transactions must always see the total balance as $ 10,000.
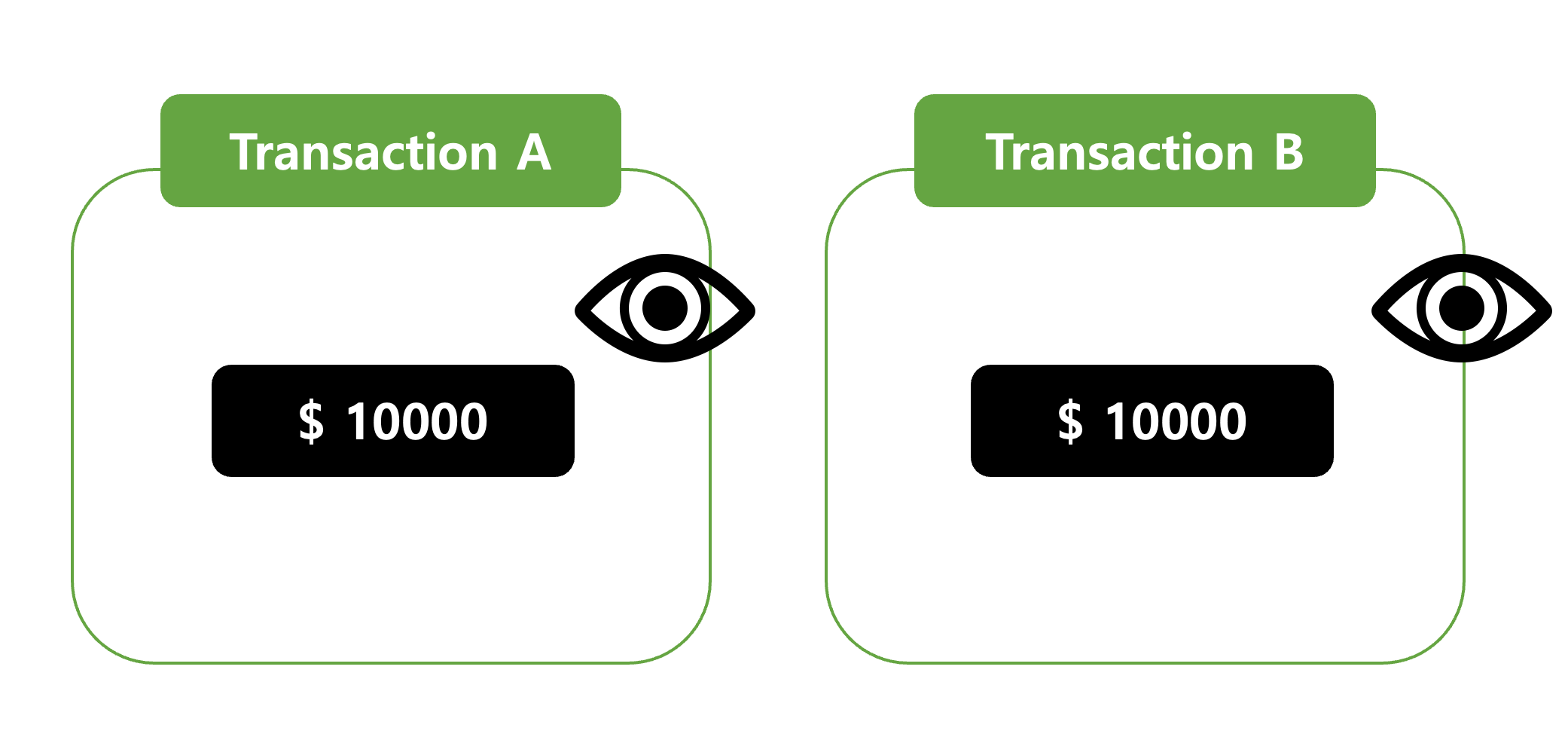
🔋 Durability
🔋
Durabilityensures that once atransactionis successfully completed, its effects are permanentlyrecorded.
Even if a system failure occurs, the results of a successful transaction must always be reflected in the database. Typically, transactions are logged, and only when the log is securely stored is a transaction considered successful. If a failure occurs later, the database can be recovered using these logs.
🦎 CAP
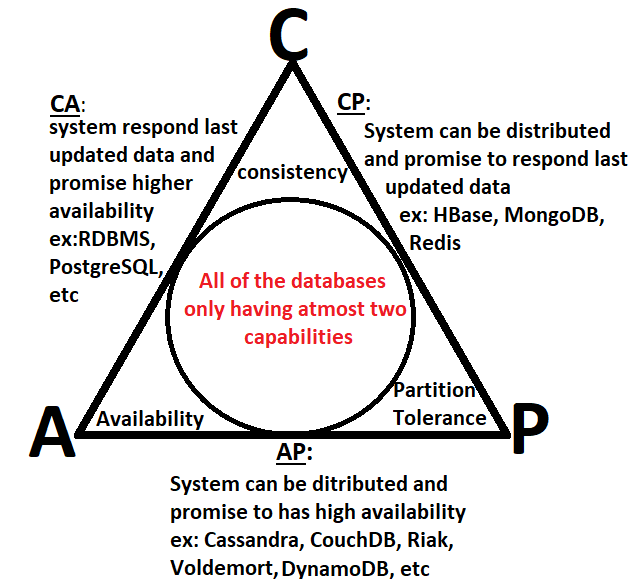
🦎 CAPrefers to atheoremwhere out ofConsistency,Availability, andPartition Toleranceat most twopropertiescan be logically attained.
Geeks for Geeks Available at here
🍔 Consistency
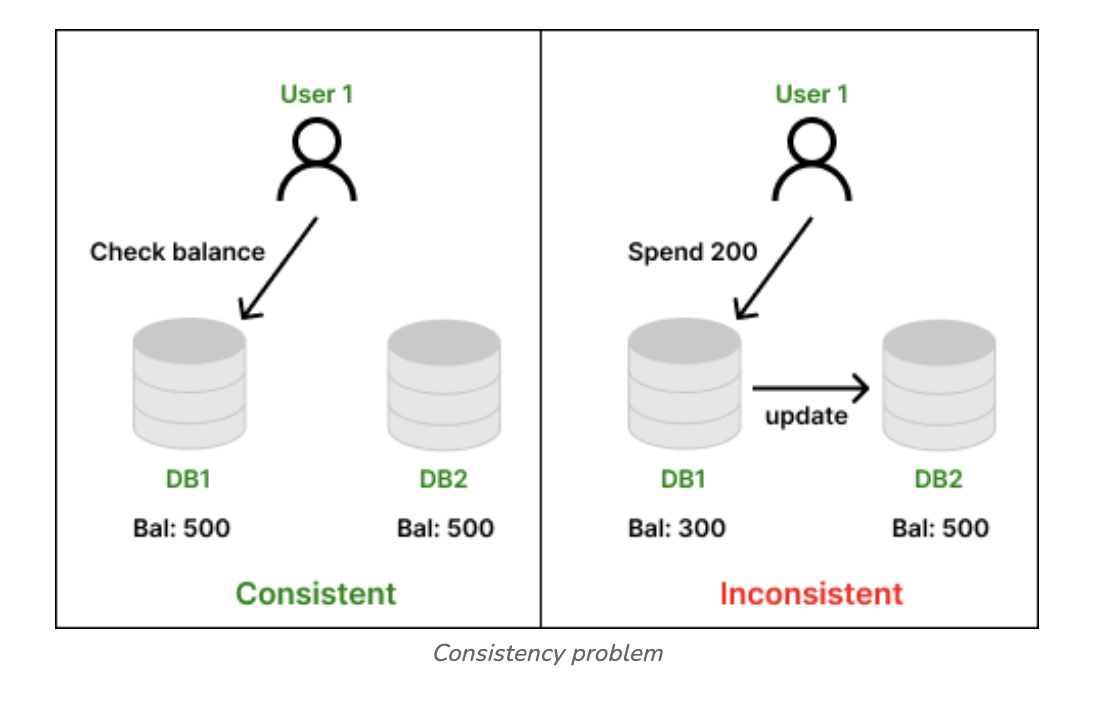
🍔
Consistencyensures that allnodes(databases) within anetworkhave identical and most up-to-date copies of areplicated data itemaccessible to varioustransactions.
Geeks for Geeks Available at here
🍙 Availability
🍙
Availabilityrefers that everyread or write requestfor adataitem will receive asuccessful responsewith it potentially being thenon-latest data.
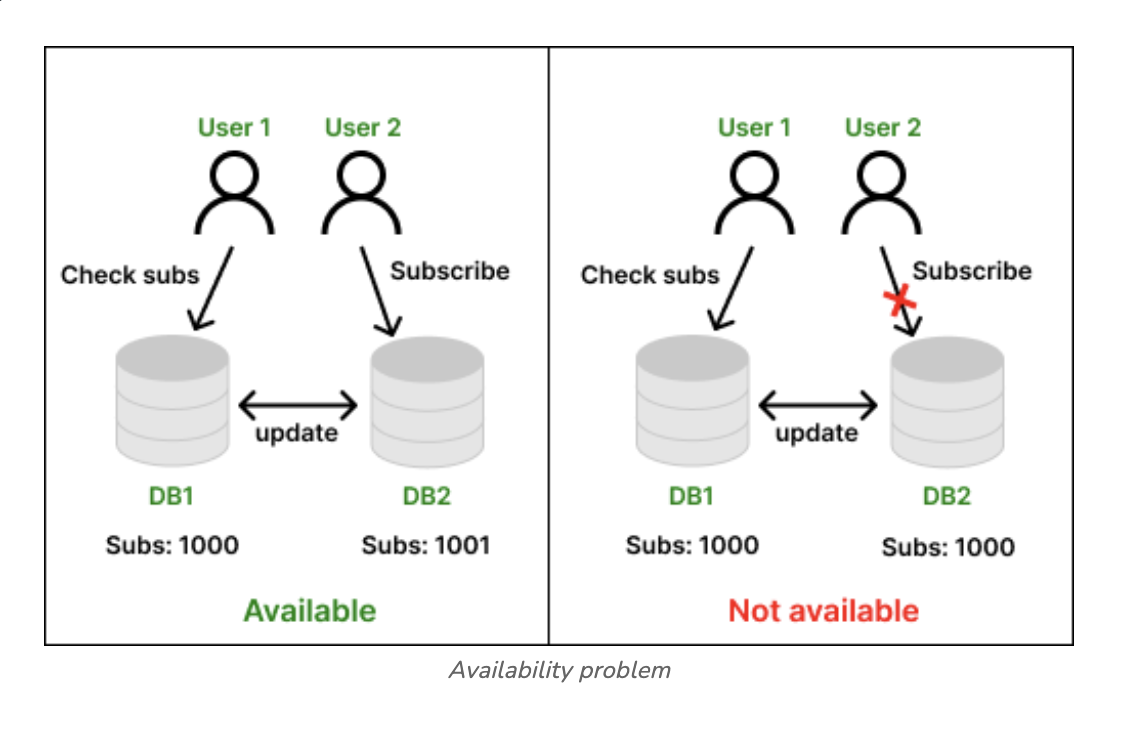
Geeks for Geeks Available at here
🎳 Partition Tolerance
🎳
Partition Tolerancemeans that thesystemremains operational even undernetwork failures.
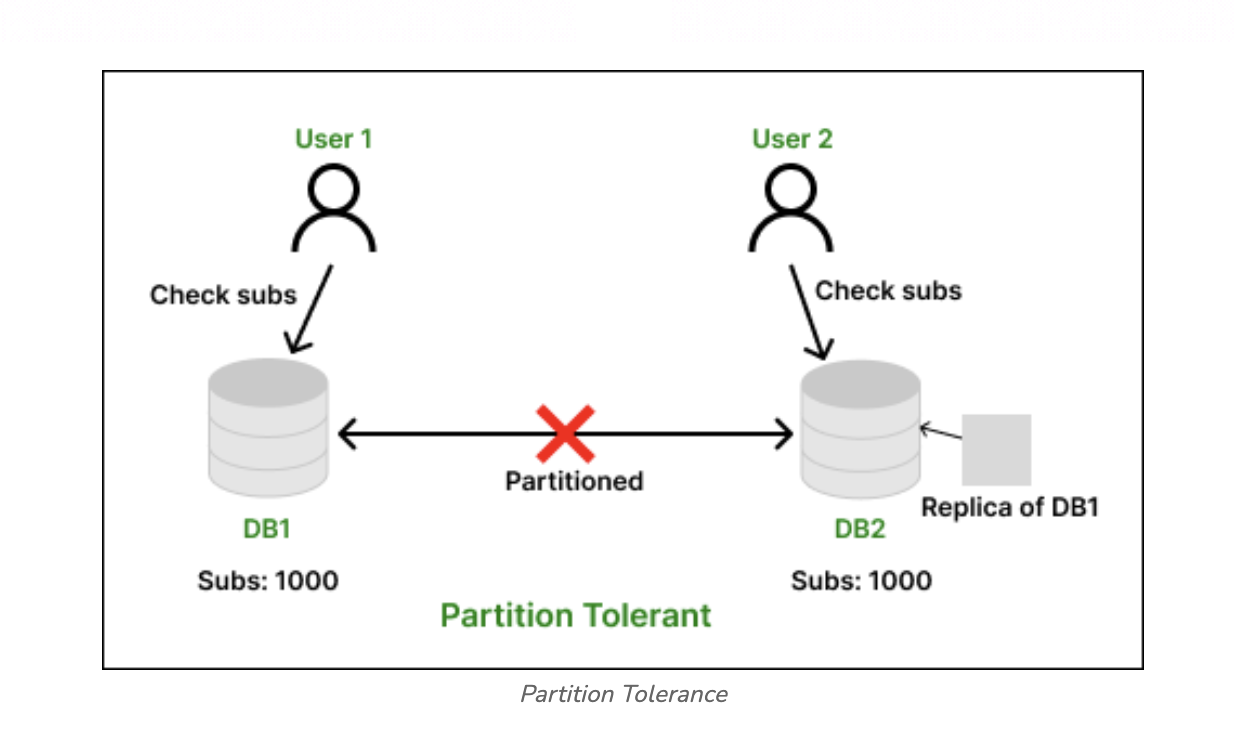
Geeks for Geeks Available at here
🎥 Scenarios
🎆 CA (Consistency + Availability)
-
e.g. centralised database
- only way to avoid
databasesrunning in differentnetworks. - cannot
scaleoverhigh traffic.
- only way to avoid
🎇 CP (Consistency + Partition Tolerance)
-
e.g. inventory databases
- for tasks like
inventoriesthat require highreliability,consistencycan be chosen over aavailbility.
- for tasks like
🌅 AP (Availability + Partition Tolerance)
-
e.g. social media databases
👍 likesmay not have to be as consistent asinventories, hence,availabilitycan be chosen over aconsitency.
